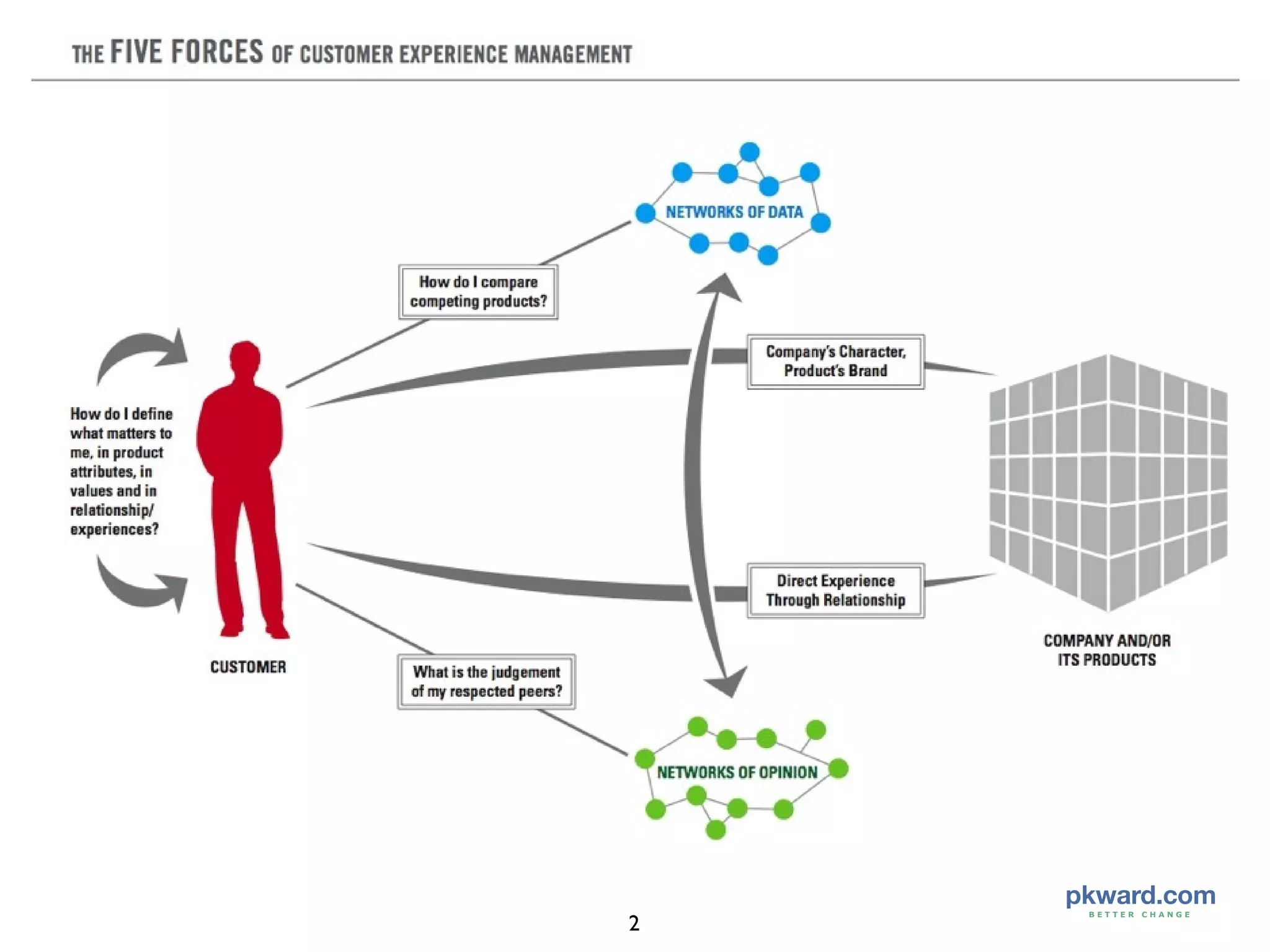
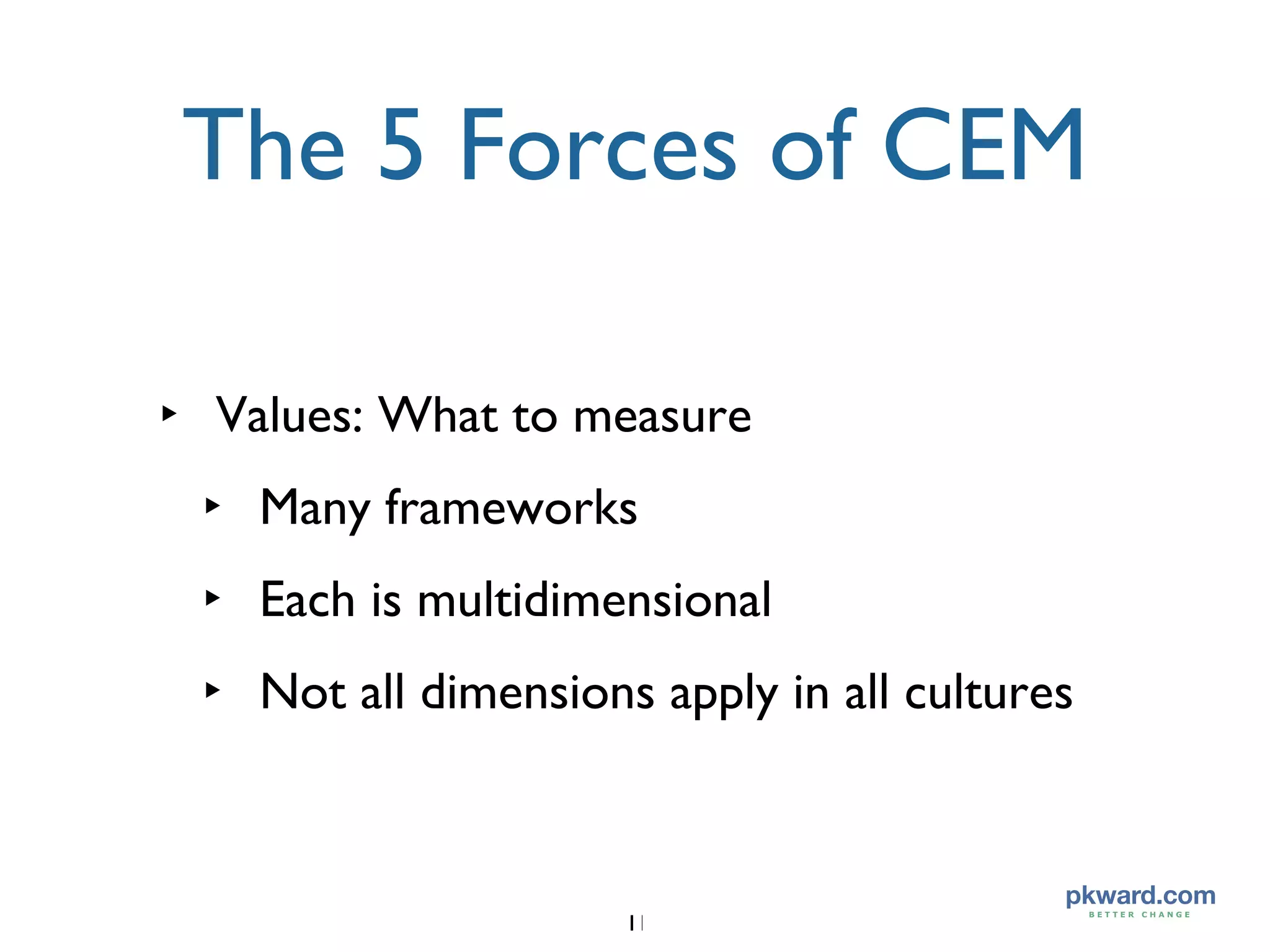
The document discusses the five forces that shape customer experience management (CEM), focusing on understanding customer emotions, data networks, word-of-mouth influence, company character, and direct customer experience. It highlights the importance of aligning brand values with customer expectations and creating memorable experiences to drive growth. The analysis also contrasts consumer decision-making styles across different cultures, particularly the implications for companies like Wal-Mart entering foreign markets such as Germany.







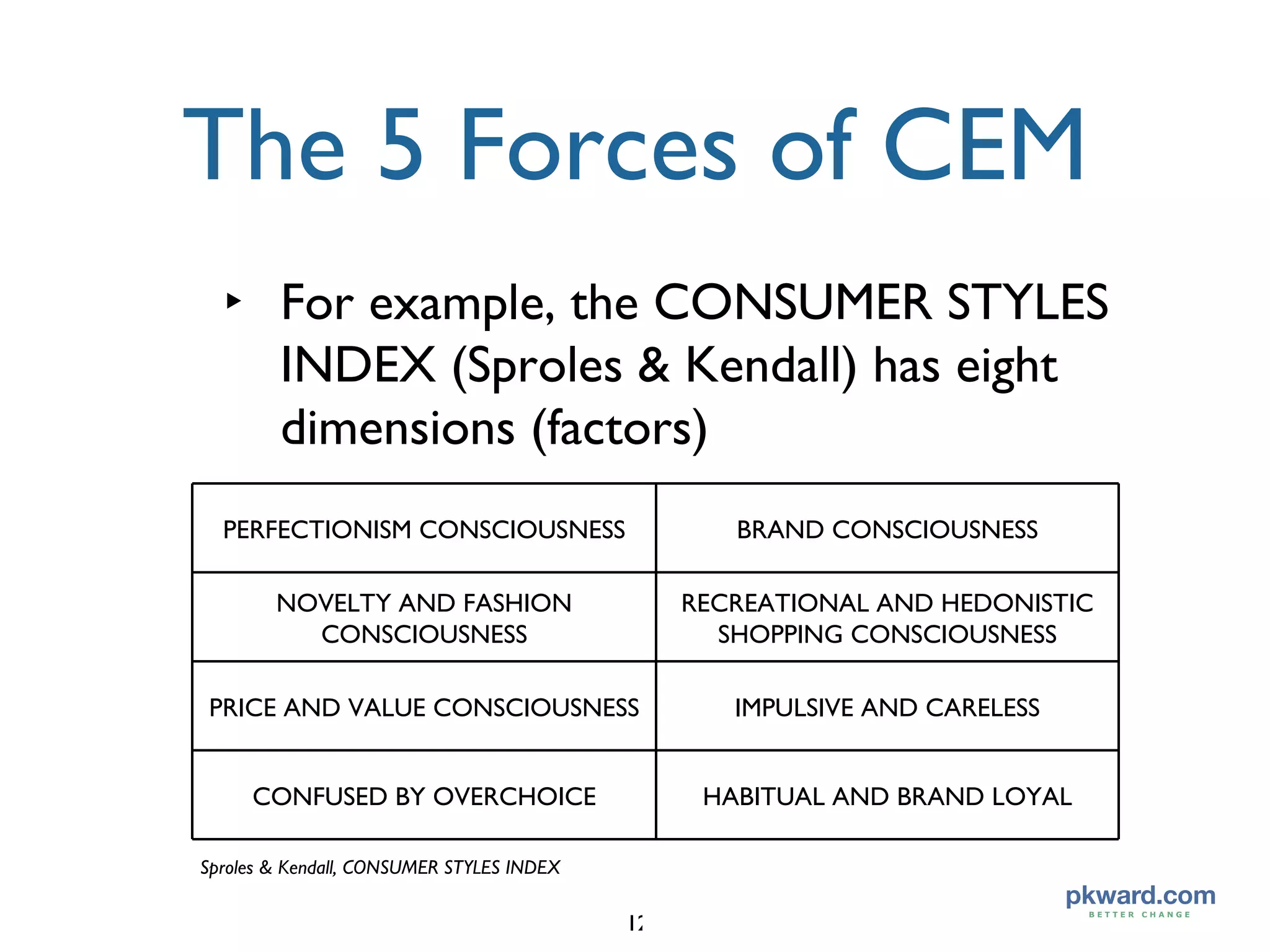
![The 5 Forces of CEM “ The original U.S. eight-factor model could not be confirmed completely, but support [in German culture] was found for six factors: Brand Consciousness, Perfectionism, Recreational/Hedonism, Confused by Overchoice, Impulsiveness, and Novelty-Fashion Consciousness. Variety Seeking was novel to Germany and replaced brand loyalty and price-value consciousness factors found in previous countries.” German Consumer Decision-Making Styles Authors: Gianfranco Walsh, Vincent-Wayne Mitchell, and Thorsten Hennig-Thurau](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/five-forcescourse-1233085128904268-2/75/Five-Forces-of-Customer-Experience-Management-13-2048.jpg)