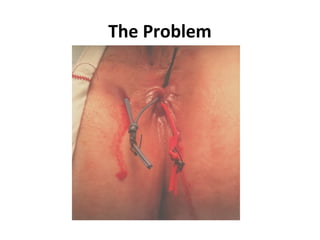
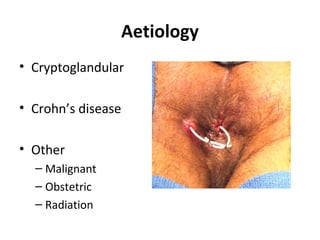
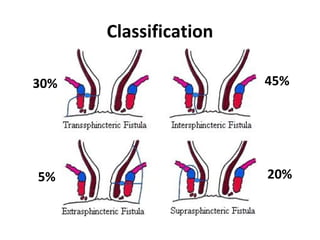
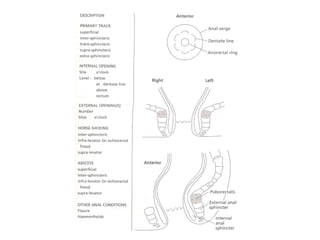
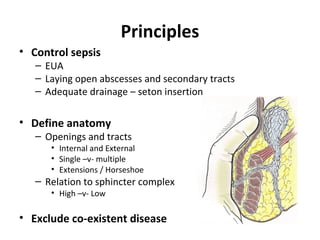
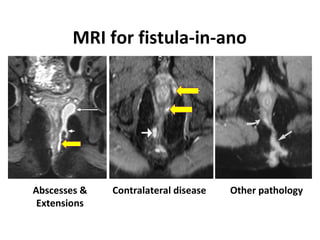
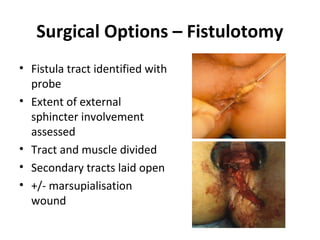
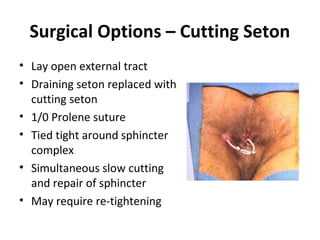
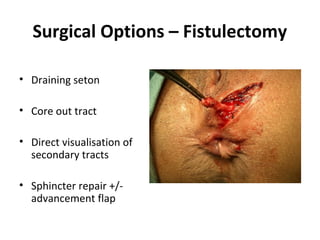
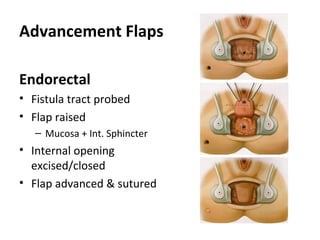
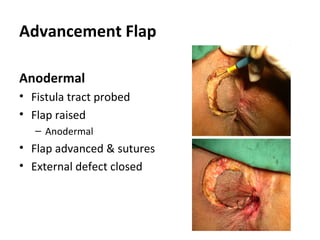
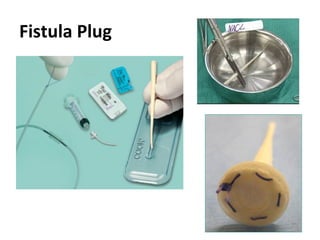
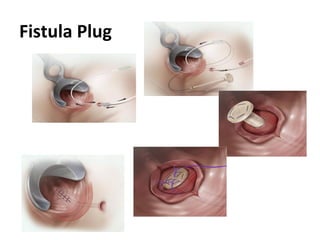
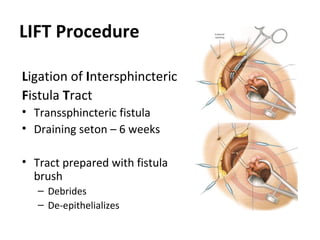
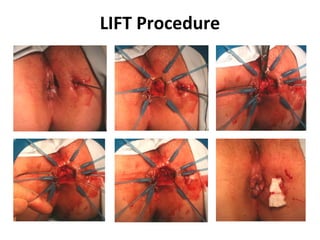
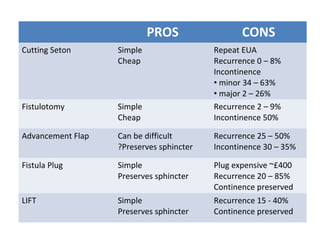
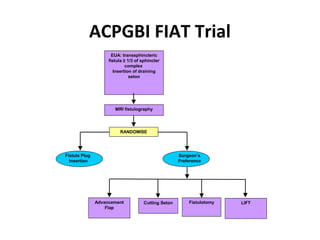
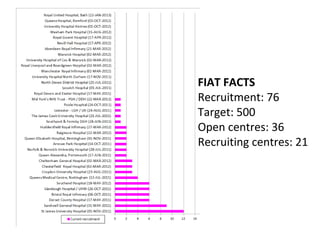
This document summarizes the treatment options for fistula-in-ano including fistulotomy, cutting seton, fistulectomy, advancement flaps, fistula plugs, and the LIFT procedure. It discusses the pros and cons of each approach and highlights an ongoing randomized controlled trial called FIAT that is comparing fistula plug insertion to the surgeon's preferred treatment to determine the best approach for preserving continence and healing the fistula.