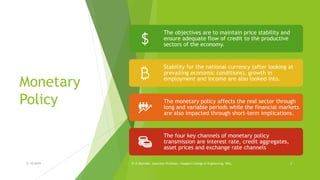
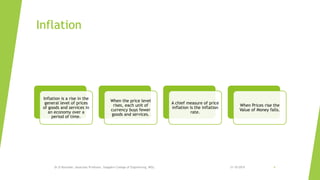
This document is a presentation by Dr. D. Ravinder about monetary and fiscal policy in India. It discusses the objectives and instruments of monetary policy, including maintaining price stability and ensuring credit flows to productive sectors. It also discusses inflation and how monetary policy transmission occurs through interest rates, credit, asset prices, and exchange rates. The document then explains fiscal policy and its instruments, which include reducing government expenditure, increasing taxation, issuing public debt, and maintaining budget surpluses. It aims to use fiscal policy to influence aggregate demand and maintain economic stability.