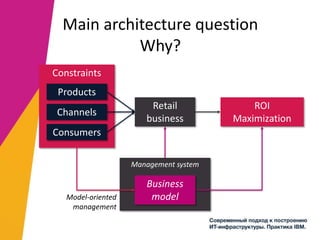
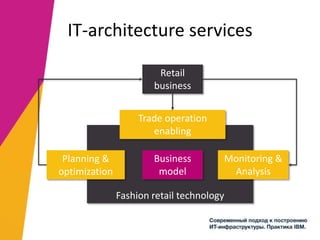
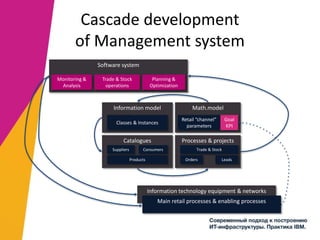
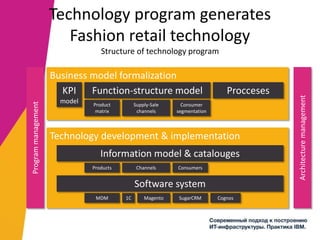
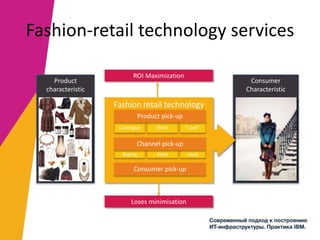
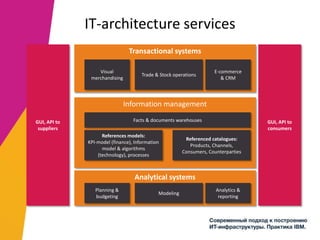
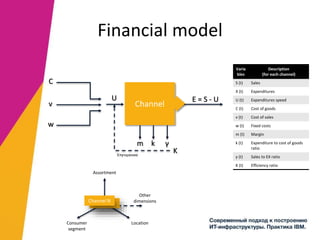
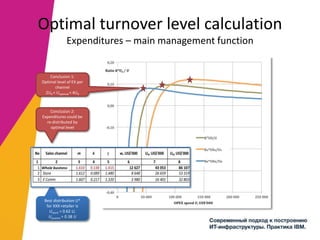
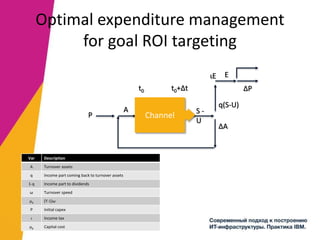
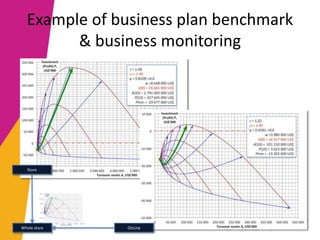
The document discusses the alignment of IT architecture with business goals in a retail context, specifically focusing on a fashion department store's revenue generation through online channels and the implementation of digital technologies. It highlights the importance of a formalized business model that connects KPIs with operational parameters and emphasizes the need for an integrated information system to monitor and optimize performance. Key conclusions suggest that effective management of expenditures and technology can enhance ROI and competitiveness in the retail sector.