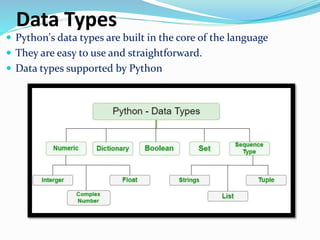
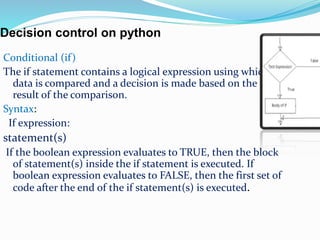
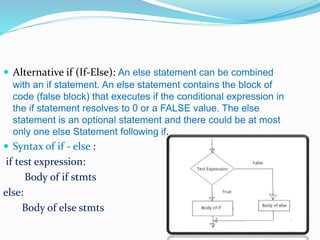
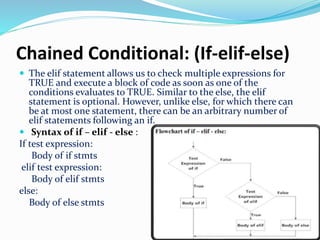
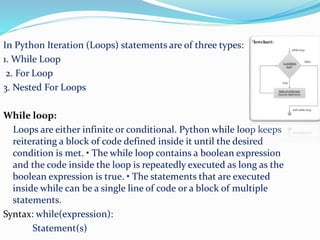
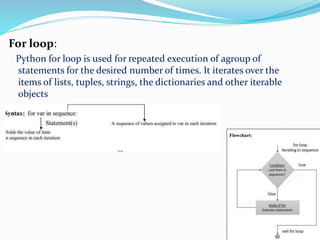
The document discusses the need for programming languages to communicate with computers to solve problems. It then provides an overview of the Python programming language, including that it was created by Guido van Rossum in 1991. The summary highlights Python's advantages as being portable, extendable, object-oriented, dynamically typed, free and open source. It also discusses Python variables, strings, keywords, data types, decision control statements like if/else, loops, and some applications of Python like web applications, game development, and machine learning.