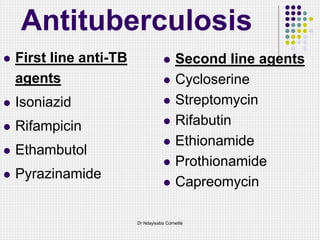
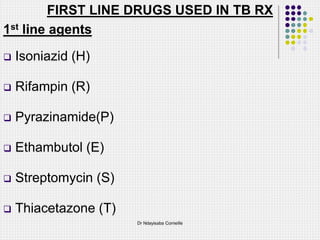
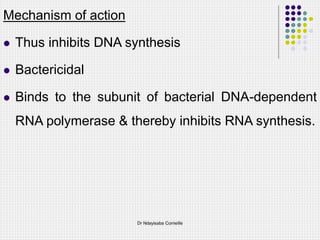
This document discusses first-line drugs used to treat tuberculosis (TB), including isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. It provides details on the mechanisms of action, mechanisms of resistance, pharmacokinetics, clinical uses, and adverse reactions of each drug. It emphasizes that combinations of two or more drugs are required to prevent the emergence of drug resistance during TB treatment, which typically lasts for months to years depending on the drug regimen used.








![ 5 mg/kg/d, or 900 mg, may be used in some
situations
Given IV or PO & is readily absorbed frm
GIT.
It diffuses readily into all body fluids &
tissues.
The [CNS & CSF]s ranges btn 20% & 100%
of simultaneous [serum]s.
Metabolism is esp by acetylation by liver N-
acetyltransferase & this is genetically
determined.
Dr Ndayisaba Corneille](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/firstlinetbdrugs-221007191316-f999675b/85/First-Line-TB-Drugs-pptx-12-320.jpg)
![ Rapid clearance of drug occurs in rapid
acetylators but its usually of no
therapeutic consequence whn appropriate
doses are administered daily.
[subtherapeutic]s may occur if drug is
administered as a once-weekly dose or if
there is malabsorption.
Drug metabolites & a small amount of
unchanged drug are excreted mainly in
Dr Ndayisaba Corneille](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/firstlinetbdrugs-221007191316-f999675b/85/First-Line-TB-Drugs-pptx-13-320.jpg)











![Pharmacokinetics
Dosage is usually 600 mg/d (10 mg/kg/d)
Given PO & well absorbed frm GIT with wide
distribution in body fluids & tissues.
Relatively highly protein-bound & adequate [CSF]s
are achieved only in presence of meningeal
inflammation.
Dr Ndayisaba Corneille](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/firstlinetbdrugs-221007191316-f999675b/85/First-Line-TB-Drugs-pptx-26-320.jpg)







![ It crosses BBB only if meninges are
inflamed with highly variable [CSF]s of drug,
(4% to 64%) of serum levels in the setting of
meningeal inflammation.
About 20% of drug is excreted in feces &
50% in urine in unchanged form.
It accumulates in renal failure.
Dose shld be reduced by half if creatinine
clearance is < 10 mL/min.
Dr Ndayisaba Corneille](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/firstlinetbdrugs-221007191316-f999675b/85/First-Line-TB-Drugs-pptx-37-320.jpg)












![Pharmacokinetics
Given IM or IV
Typical adult dosage is 1g/day (15 mg/kg/d )daily
for adults & 7.5–15 mg/kg/d for children
It penetrates into cells poorly & is active mainly
against extracellular tubercle bacilli.
It crosses BBB & achieves [therapeutic]s with
inflamed meninges.
Dr Ndayisaba Corneille](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/firstlinetbdrugs-221007191316-f999675b/85/First-Line-TB-Drugs-pptx-50-320.jpg)







