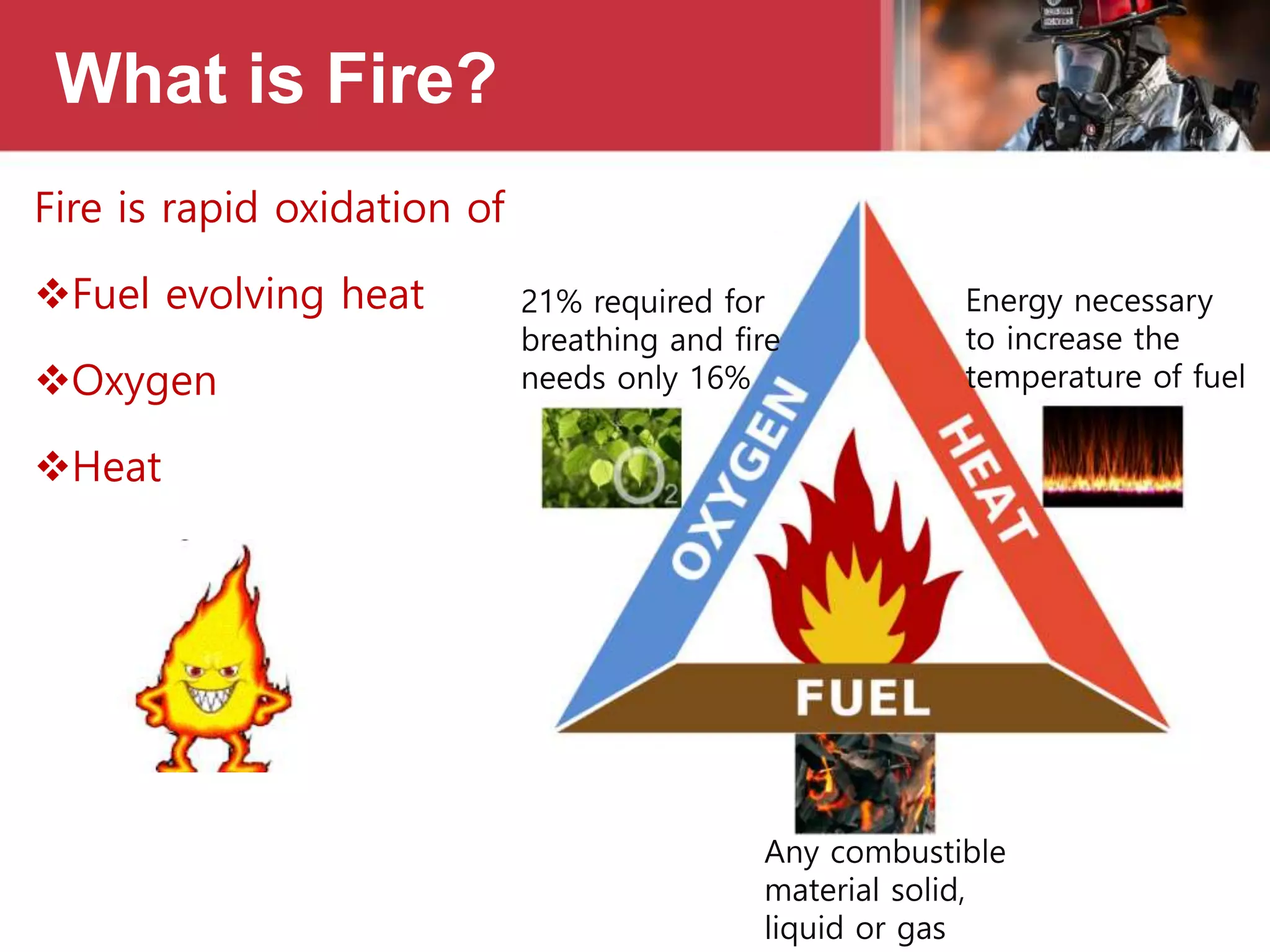
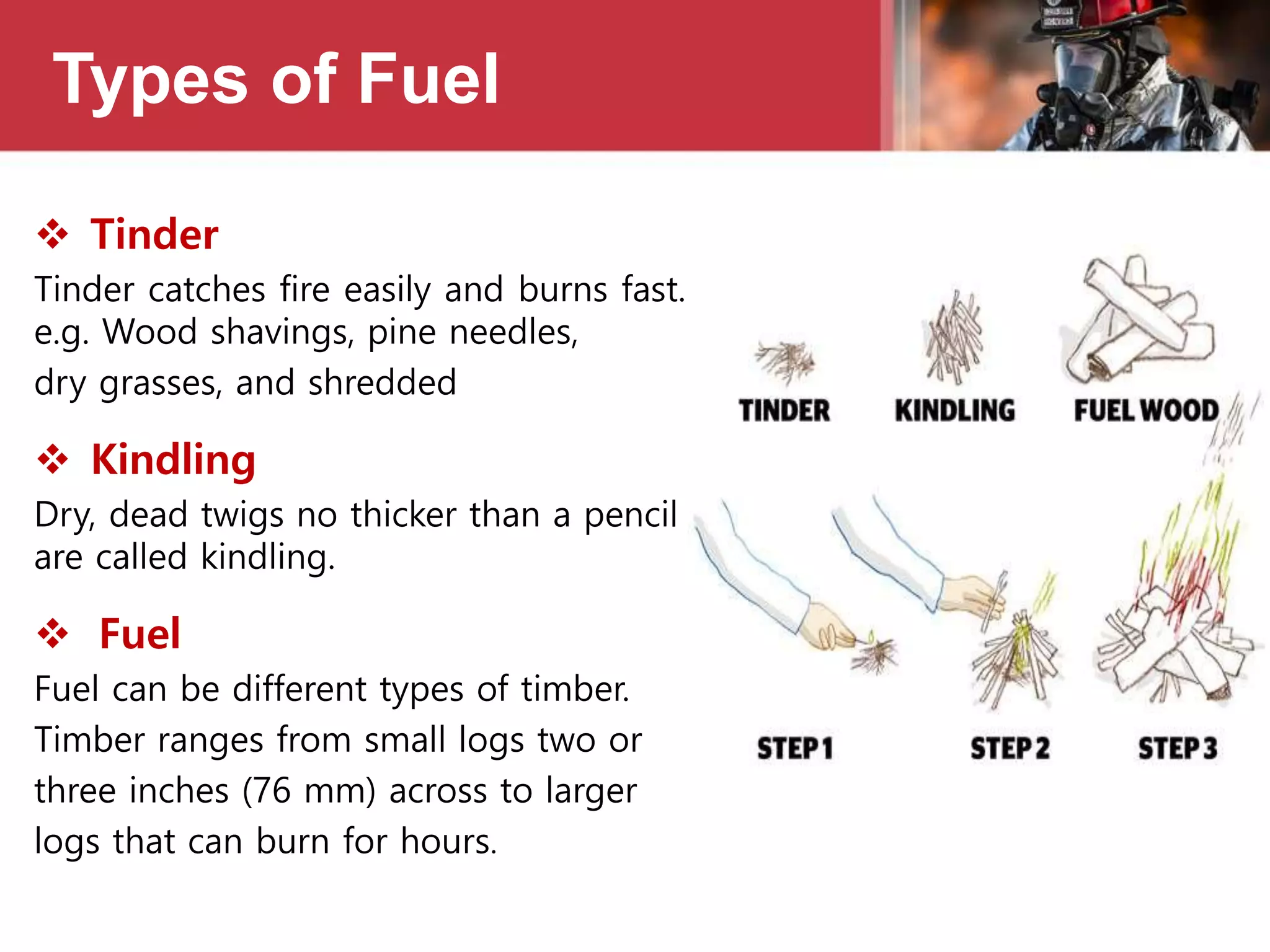
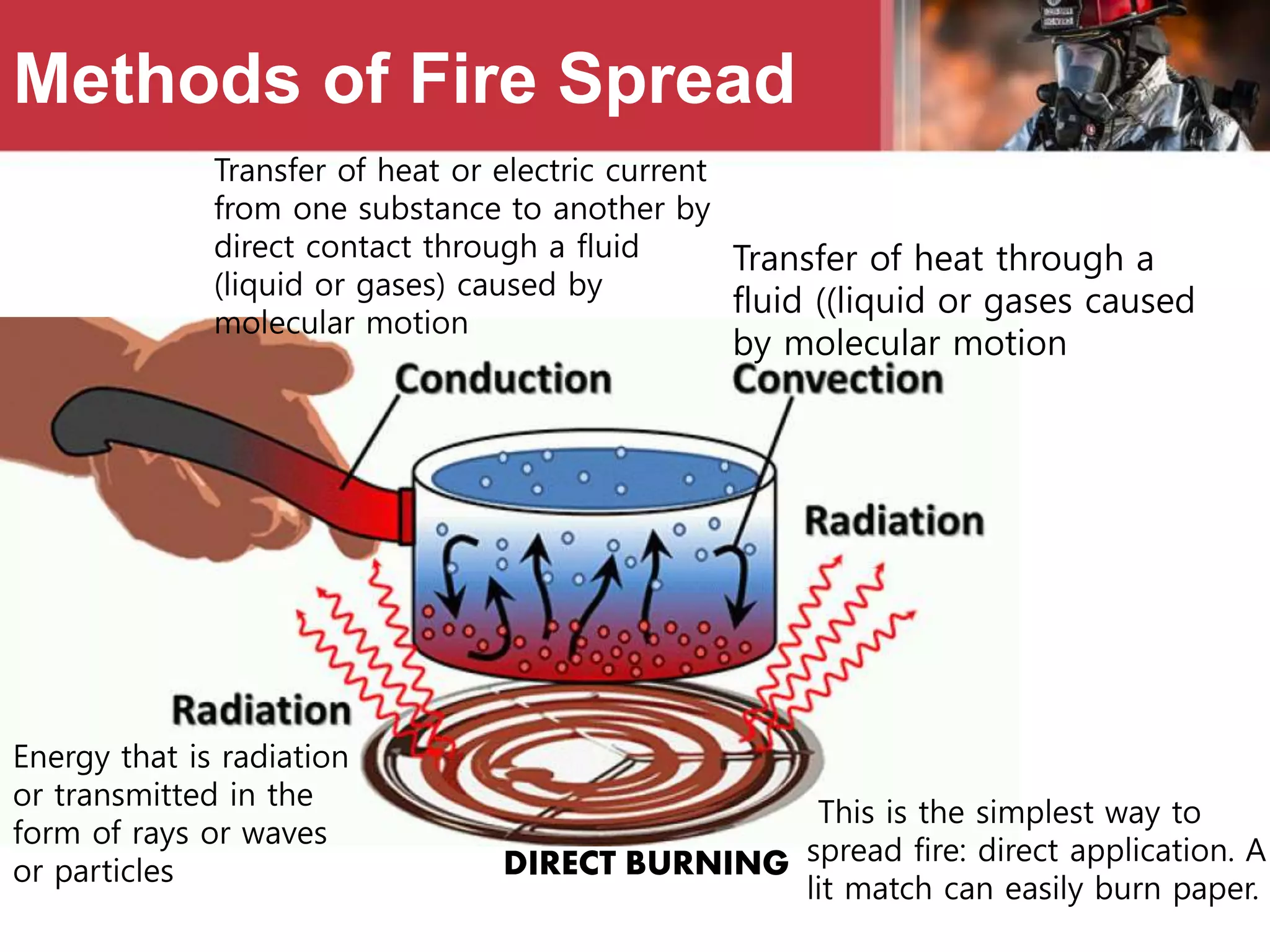
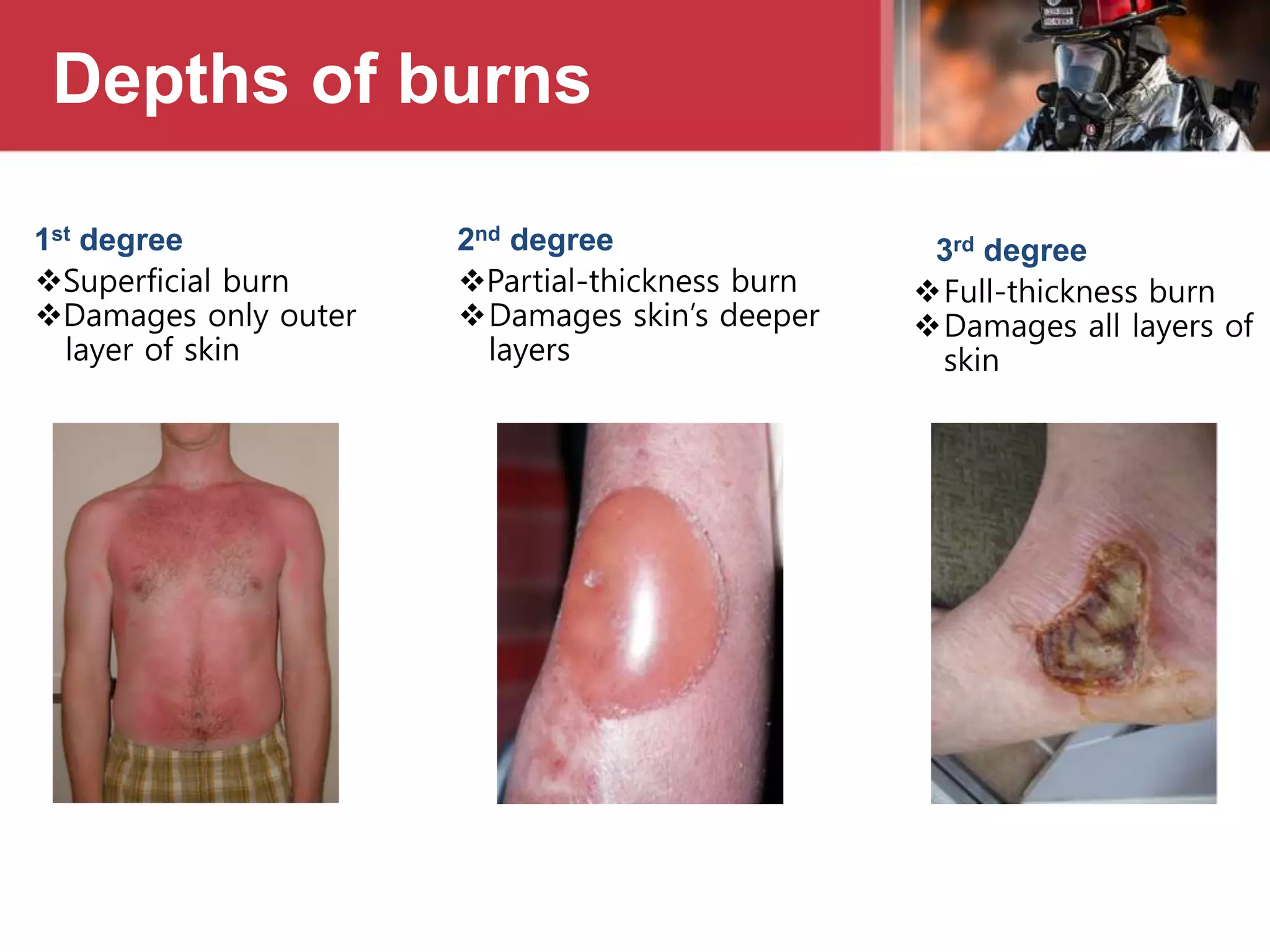
This document provides information on fire safety and firefighting. It defines civil defence and describes what constitutes a fire. It outlines different fire classes and methods of fire extinguishment. Various types of fire extinguishers are described, including water, carbon dioxide, dry chemical powder, wet chemical, AFFF foam, and buckets. Causes of fire ignition and spread are listed. Basic first aid for burns is also covered.