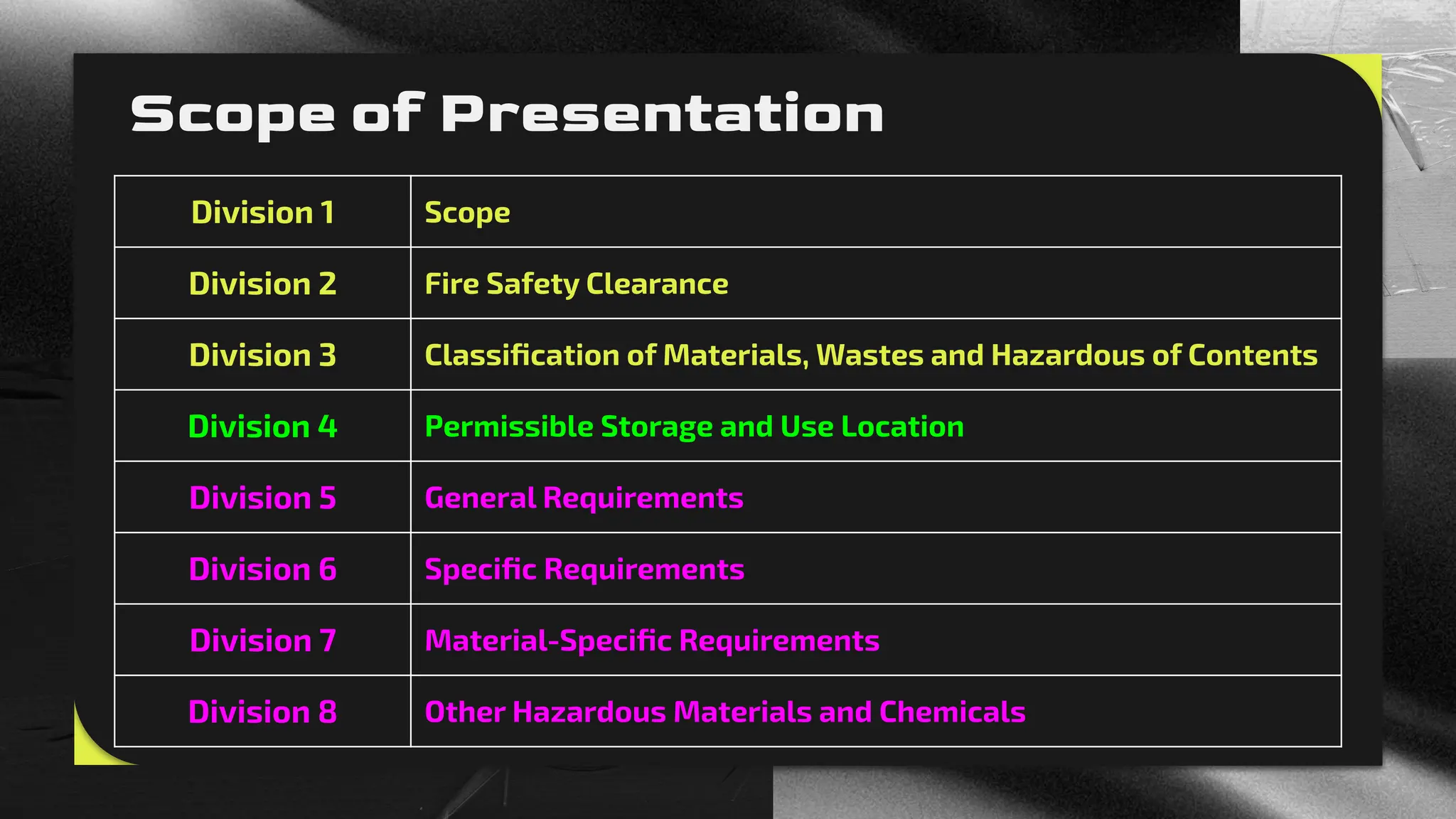
Chapter 3 discusses fire safety protocols for hazardous materials, including classifications, storage, and handling requirements. It outlines the process for obtaining a fire safety clearance (FSC) from the Bureau of Fire Protection (BFP) necessary for installations and conveyances of hazardous materials. The chapter categorizes hazardous materials based on their physical and health hazards, detailing various categories and conditions that pose risks during storage and use.