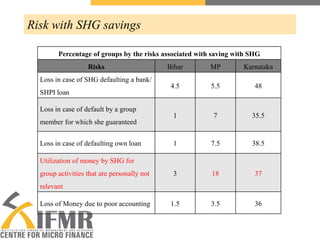
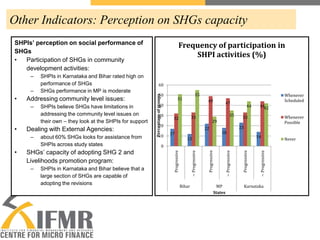
The document provides an overview of a study on self-help group (SHG) bank linkage practices in the states of Madhya Pradesh, Bihar and Karnataka in India. It examines the financial and operational performance of SHGs, including their savings, lending, borrowing, bookkeeping and interactions with banks. Some key findings are that compulsory savings contributions and discipline varies significantly across states, internal lending rates are generally higher than bank rates but penalties for defaults are often too low, and most SHGs require further training and support to improve their record keeping. The document concludes with recommendations around savings products, credit policies, default management and bank responsibilities.