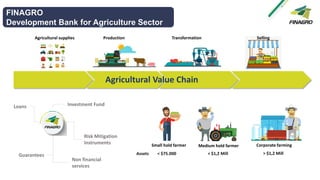
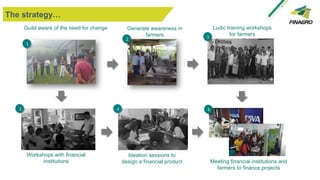
The document discusses Colombia's agricultural sector and the role of Finagro in financing adaptation to climate change, highlighting barriers faced by smallholder farmers and the strategies implemented to improve their productivity. It emphasizes the need for awareness and education, as well as the collaboration between financial institutions, government, and private entities to promote sustainable banking practices. Additionally, it addresses the challenges in the agricultural industry, including climate risks and a lack of technical assistance, while outlining the supportive role of the government in enhancing financial access and resources for farmers.