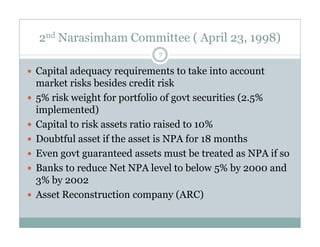
The document discusses financial sector reforms in India. It outlines deficiencies in the existing system including declining productivity and profitability. The objectives of reform are to establish prudent regulatory norms, upgrade managerial competence, and reform the financial structure. The first phase of reforms in the early 1990s focused on reducing reserve requirements, interest rate deregulation, and establishing capital adequacy norms. The second phase emphasized specialization among banks, risk management, and consolidation in the banking sector.