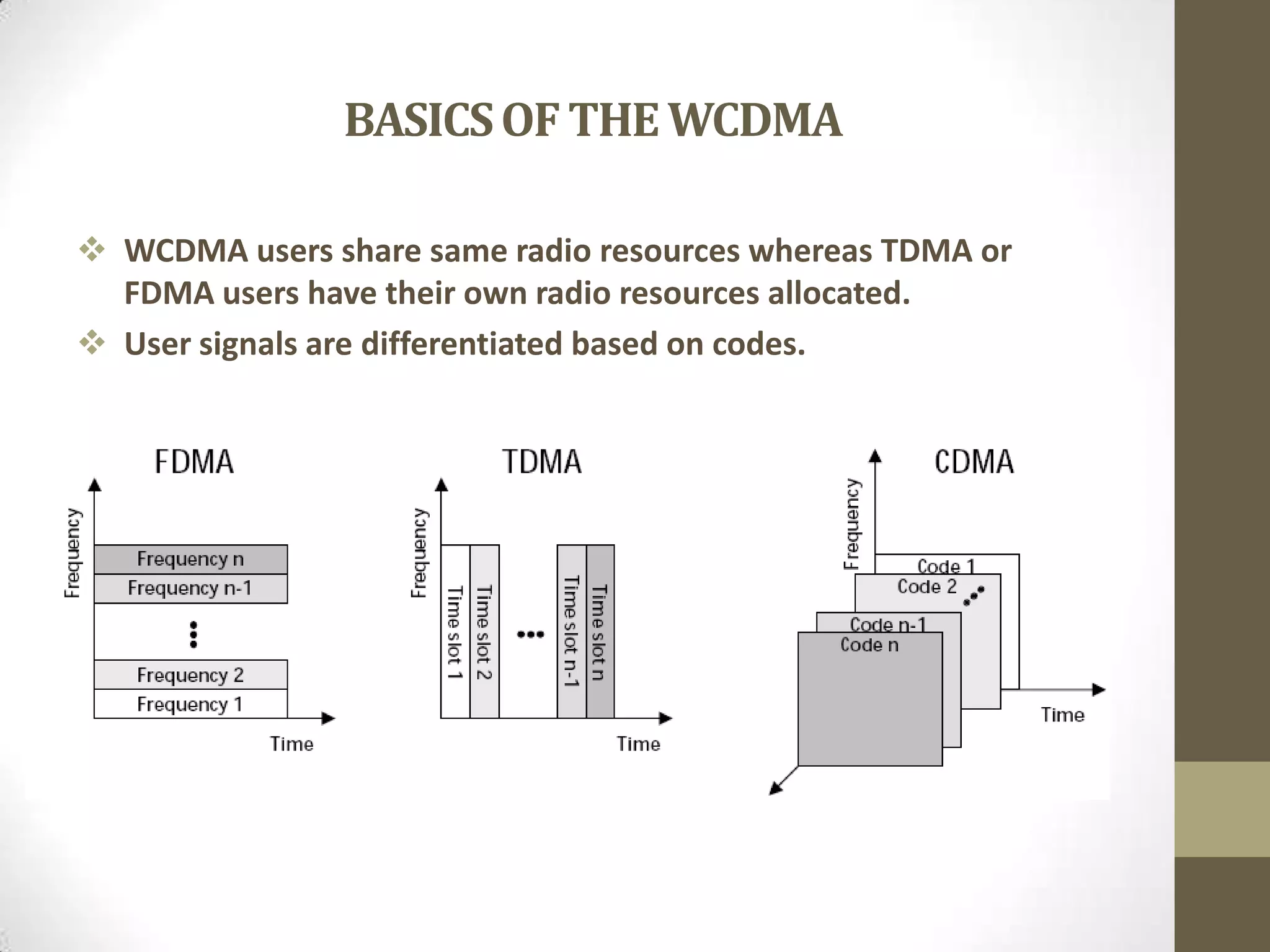
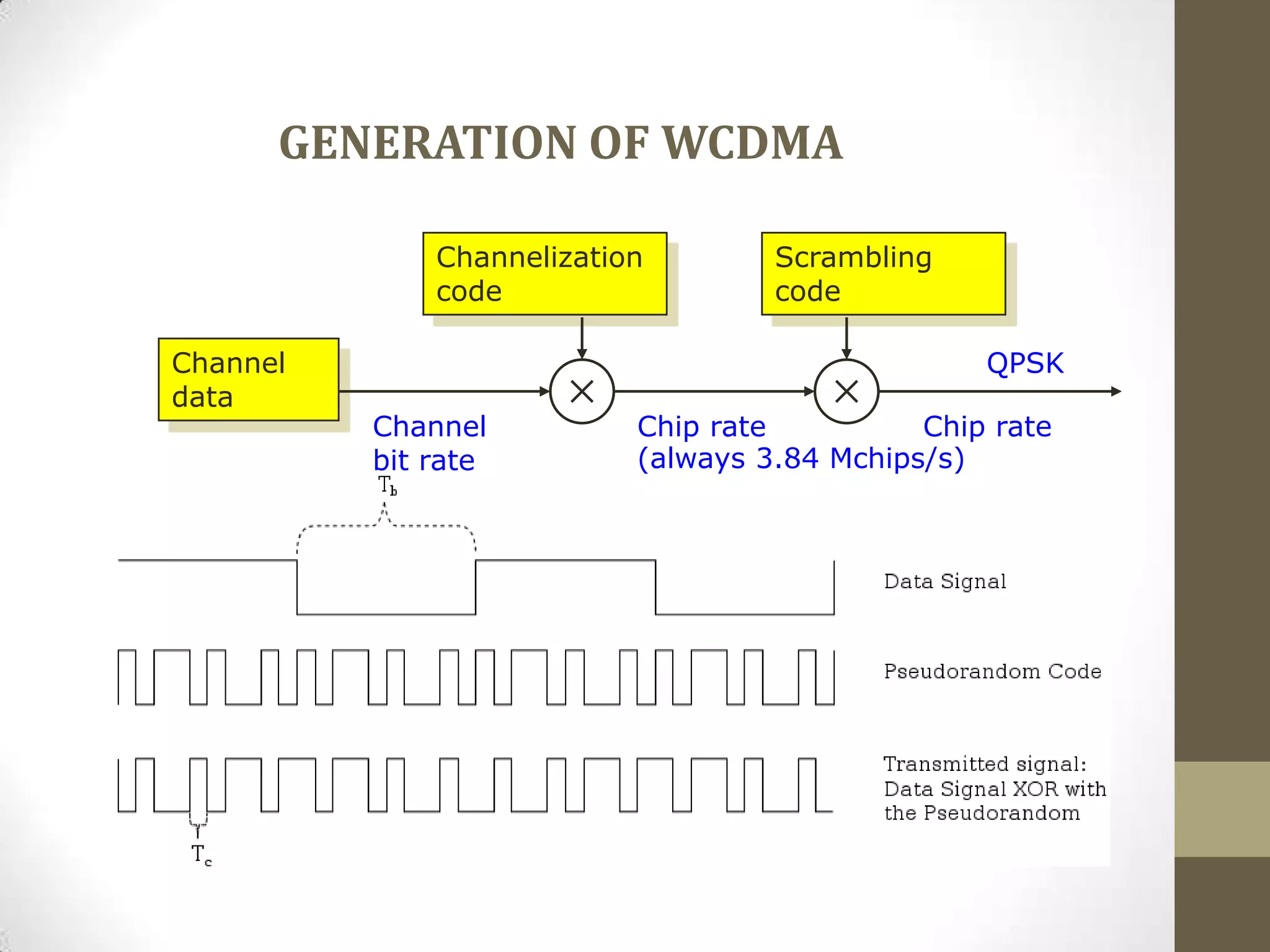
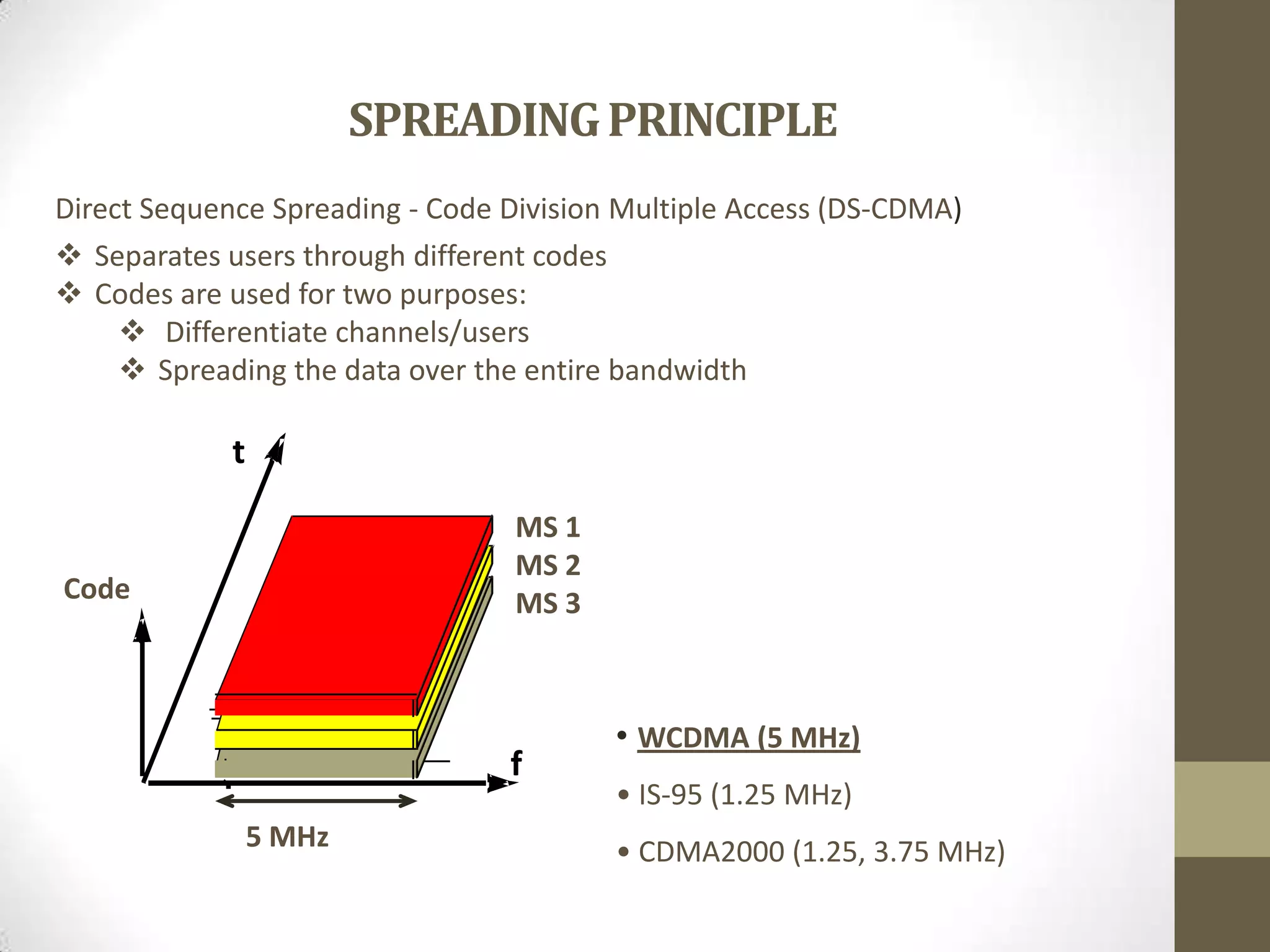
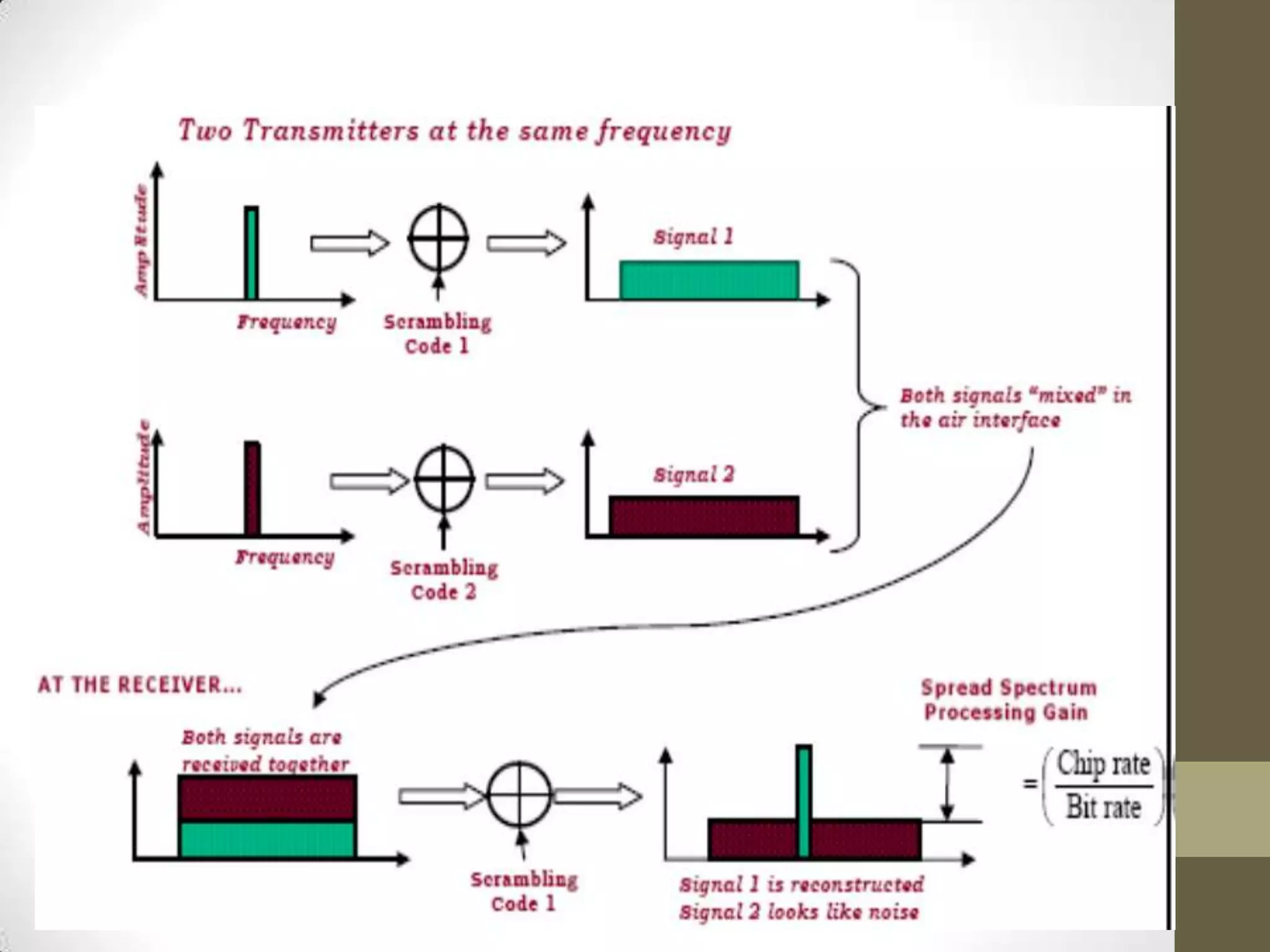
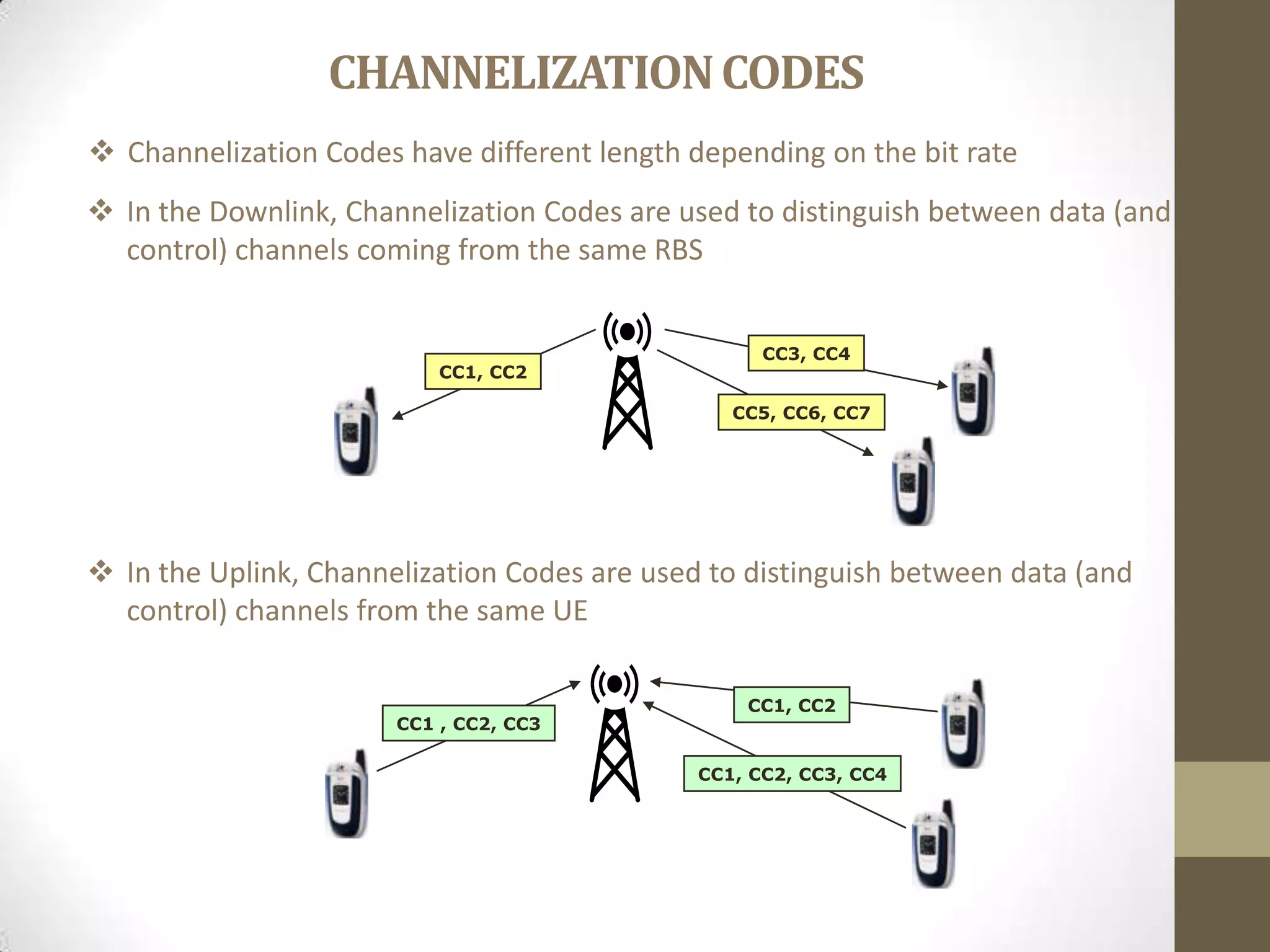
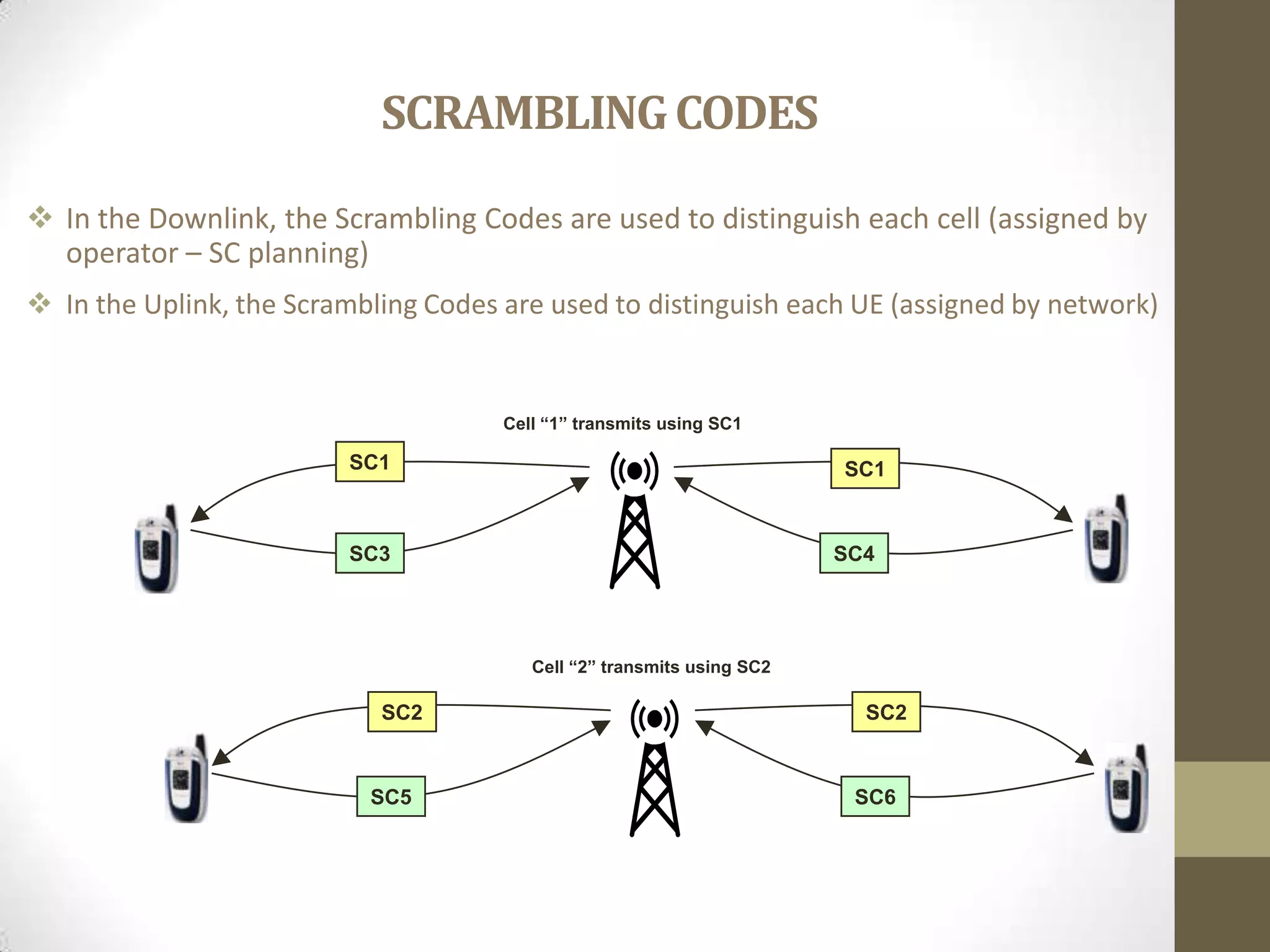
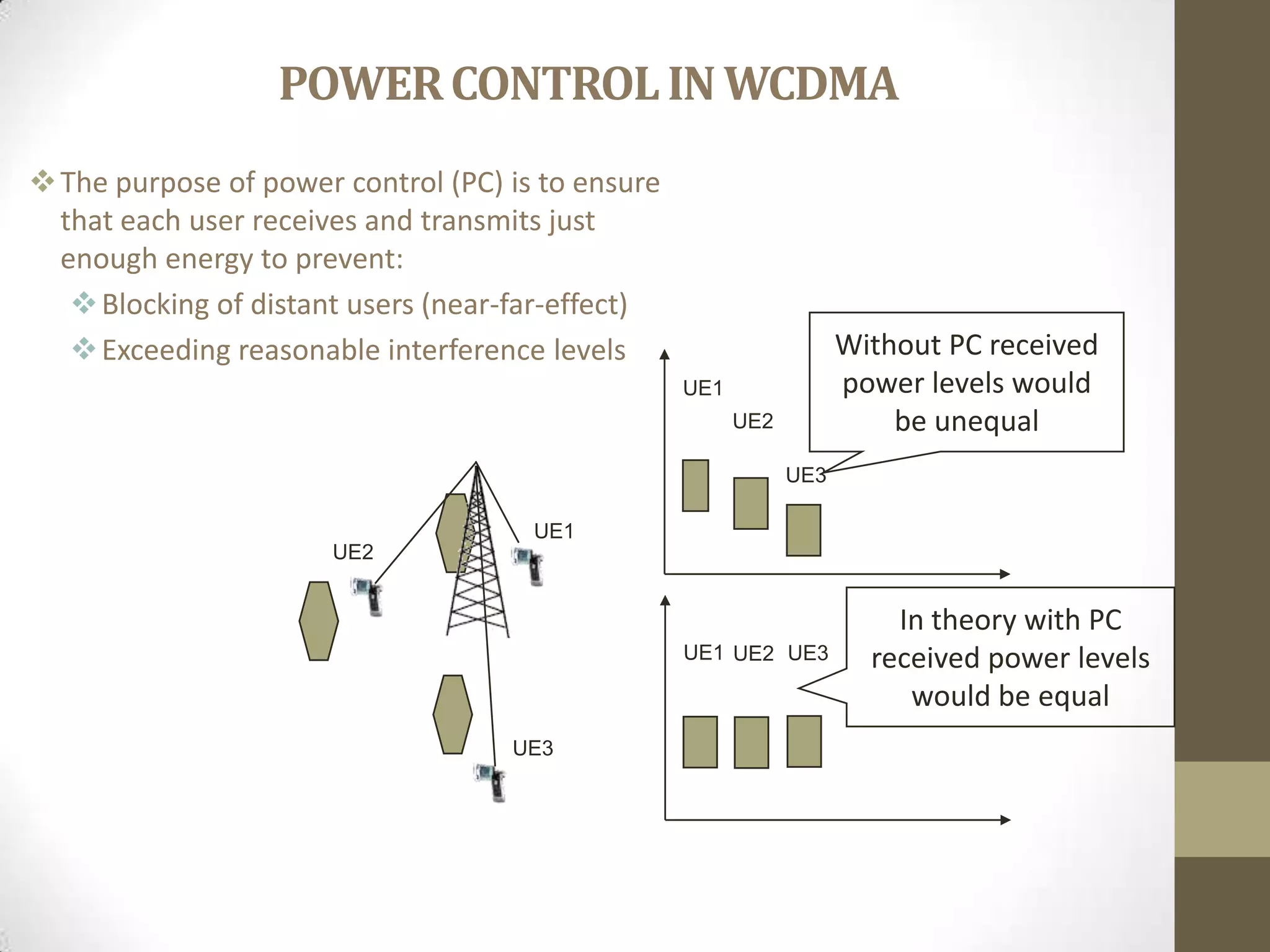
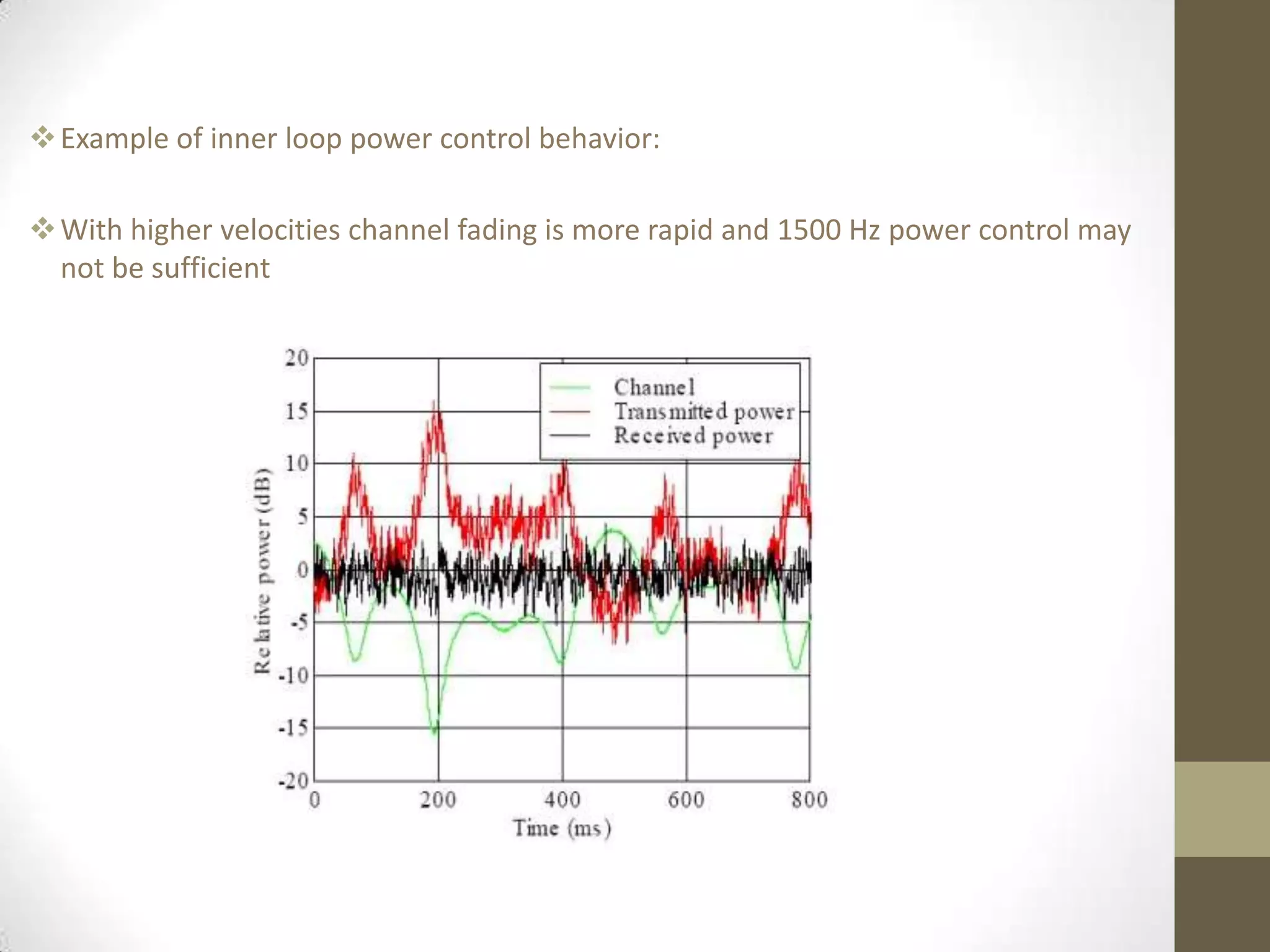
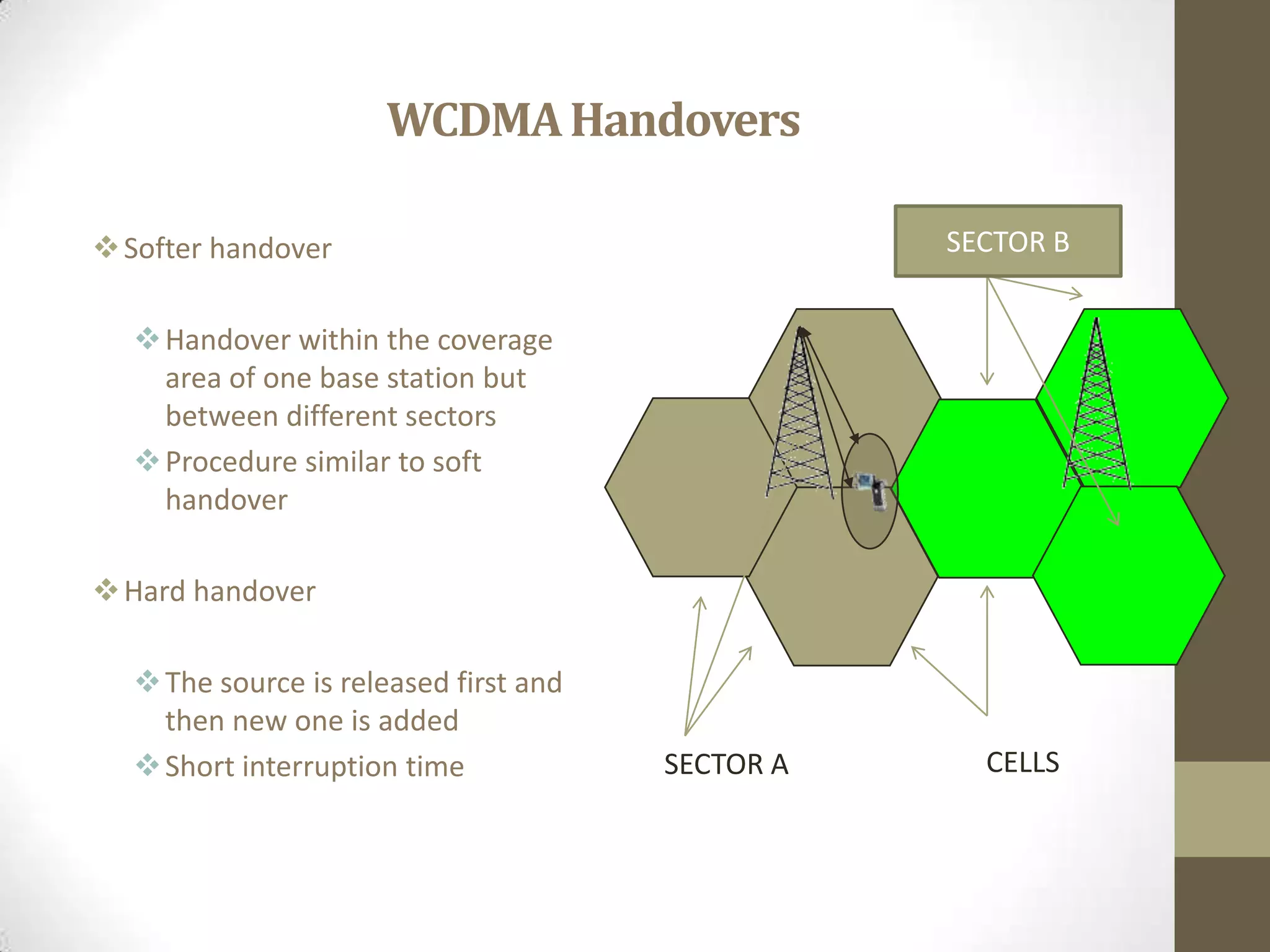
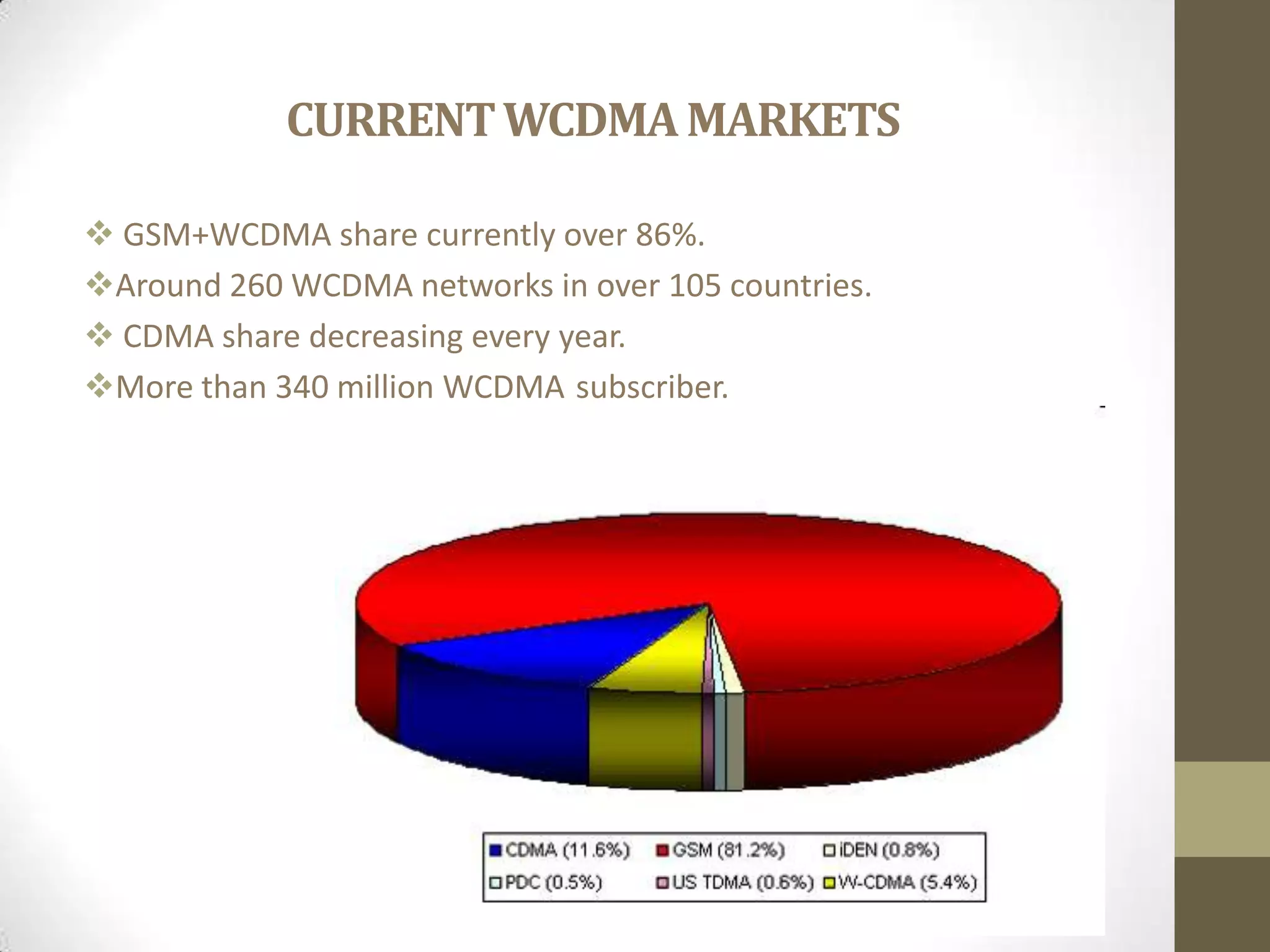
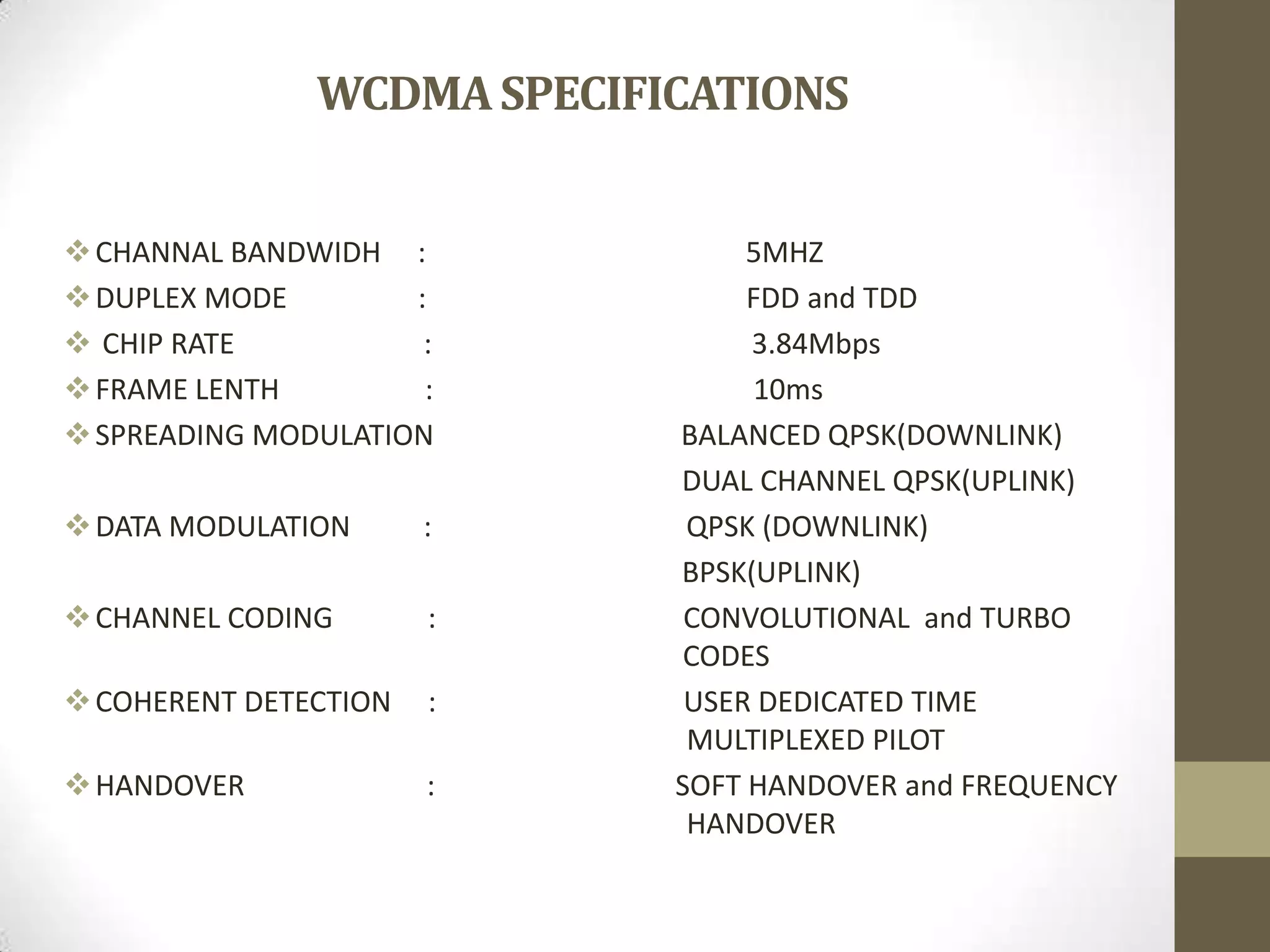
This document provides an overview of Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) technology. It discusses the basics of WCDMA including that it uses direct sequence spread spectrum technology and differentiates users through the use of spreading codes. It also describes key aspects of WCDMA such as power control, handovers between cells, and current market adoption of WCDMA networks. The document aims to inform readers about the specifications and advantages of the 3G wireless standard known as WCDMA.