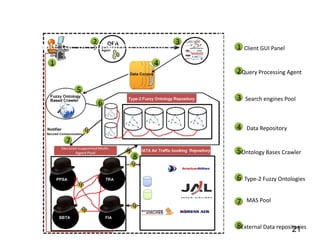
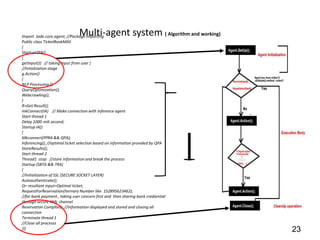
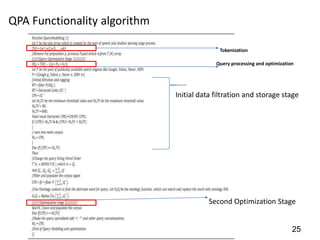
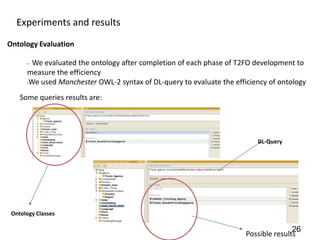
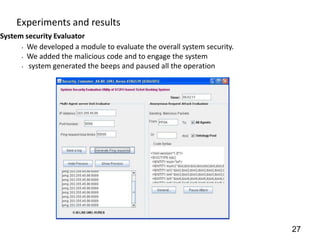
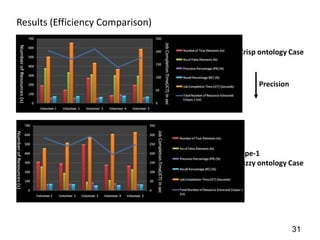
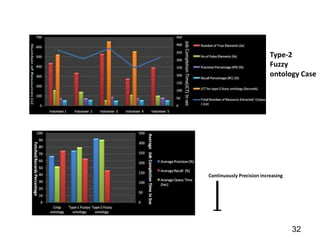
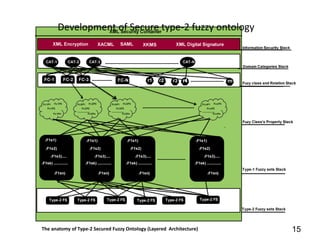
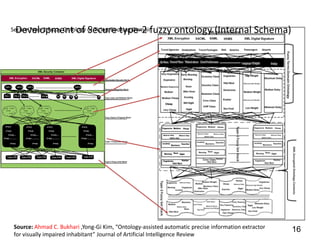
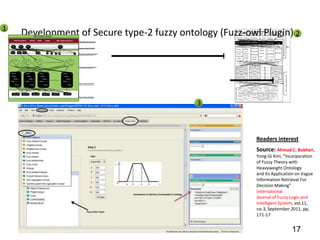
This document discusses developing a secure type-2 fuzzy ontology to automate personalized itinerary planning. It proposes using a type-2 fuzzy ontology, multi-agent system, natural language processing and information security to optimally extract information and make timely decisions. It reviews type-1 and type-2 fuzzy systems and ontologies. It also outlines the development process for a type-2 fuzzy ontology, including defining fuzzy classes, properties and relationships between classes.









![Secure Type-2 Fuzzy Ontology
Common definitions and(A quick review of terminologies) set and type-2
concepts about type-1 Fuzzy
Type-1 Fuzzy system
• The fuzzy set theory was introduced by Lotfi Zadeh in 1965 to deal with vague
and imprecise concepts.
• In classical set theory, elements either belong to a particular set or they don’t
belong.
• However, in fuzzy set theory the association of an element with a particular set
lies between ‘0’ and ‘1’ which is called degree of association or membership
degree. A fuzzy set can be defined as:
Definition 1: A fuzzy set ‘s’ over universe of discourse ‘X’ can be defined by its
membership function µ_s which maps element ‘x’ to values between [0,1].
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalthesispresentaation-130406104523-phpapp02/85/Type-2-Fuzzy-Ontology-10-320.jpg)




![Secure Type-2 Fuzzy Ontology
(Information security: Application scheme)
<? XML version="1.0"?>
<! DOCTYPE Ontology [
<! ENTITY xsd "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#" > ]>
<owlx:Ontology owlx:name="http://www.ailab.gnu.ac.kr/t2fo"
xmlns:owlx="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/owl-xml">
<CustomerInfo xmlns='http://www.ailab.gnu.ac.kr/st2fo-mas/person_ontology'>
<Name>ahmad chan</Name>
Public Key encryption algorithm
<EncryptedData Type='http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#Element'
xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#'>
<EncryptionMethod Algorithm='http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#tripledes-cbc'/>
<KeyInfo xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#'>
<EncryptedKey xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#'>
<EncryptionMethod Algorithm='http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#rsa-1_5'/>
<KeyInfo xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#'>
<KeyName>white tiger</KeyName>
</KeyInfo>
<CipherData> XML Data level encryption
<CipherValue>vHE@#$&&JUIOFdefghj...</CipherValue>
</CipherData>
</EncryptedKey>
</KeyInfo>
<CipherData>
<CipherValue>yyFE%!JJNIcflijnvcthsdrtg...</CipherValue>
</CipherData>
</EncryptedData>
</CustomerInfo>
</owlx:Ontology>
Code view of W3C XML security recommendations 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalthesispresentaation-130406104523-phpapp02/85/Type-2-Fuzzy-Ontology-19-320.jpg)