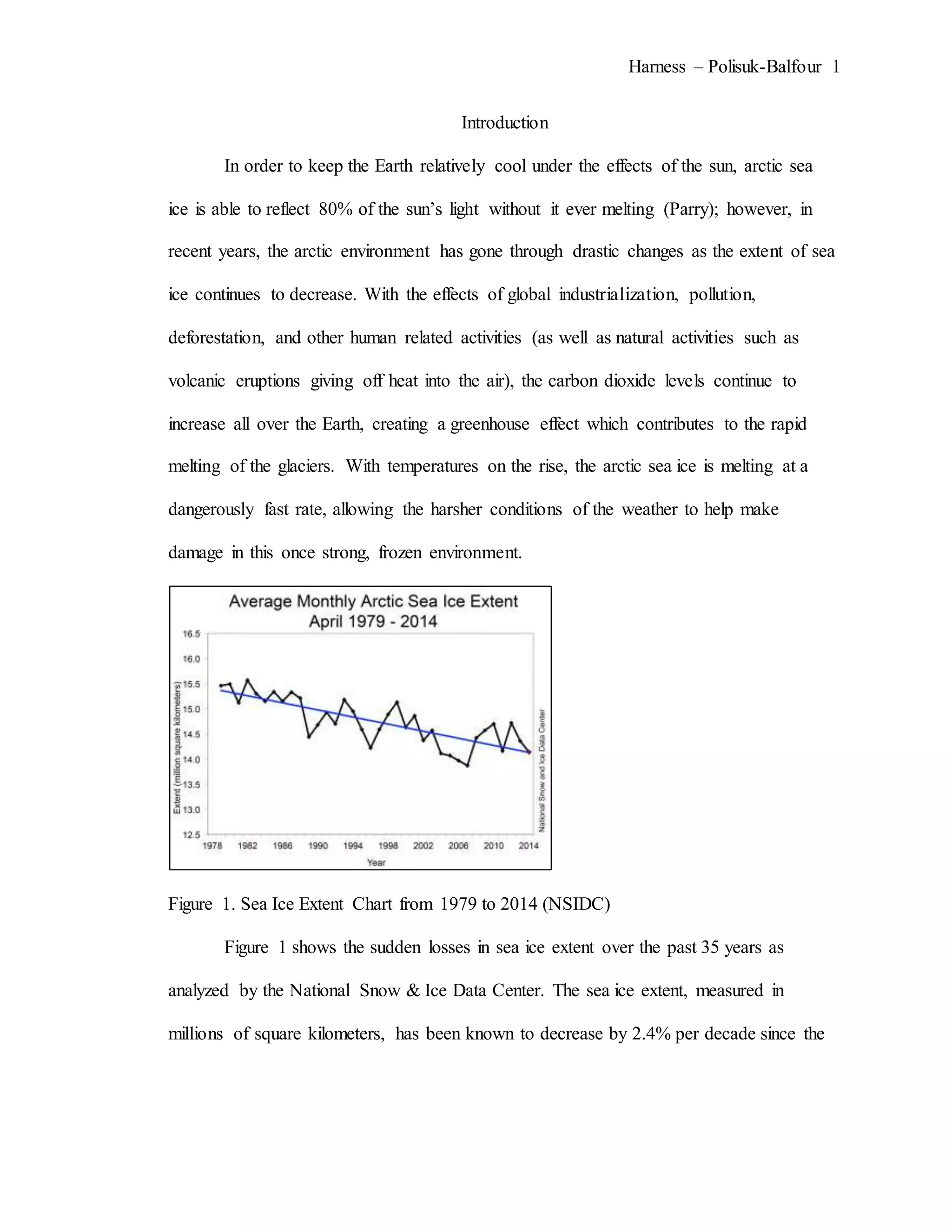
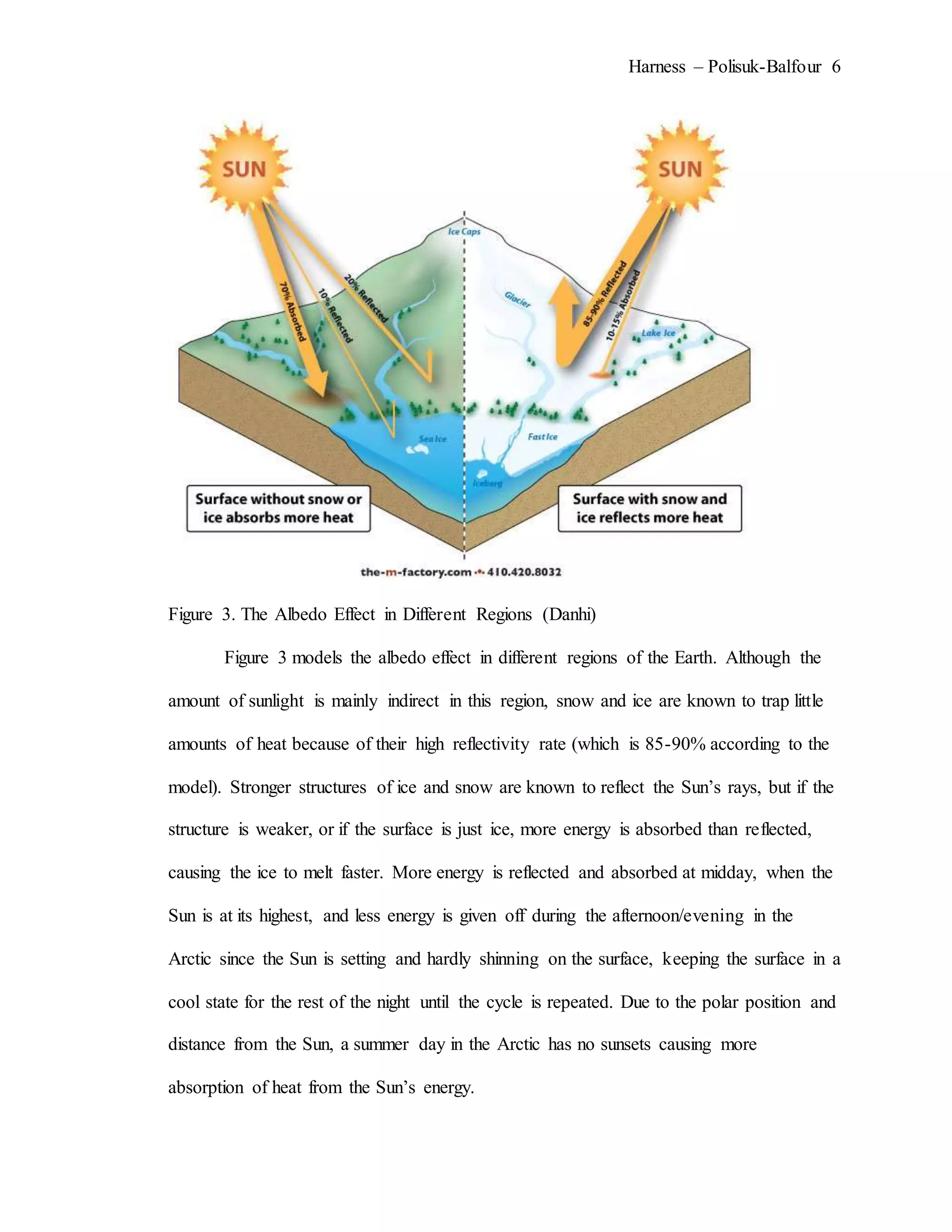
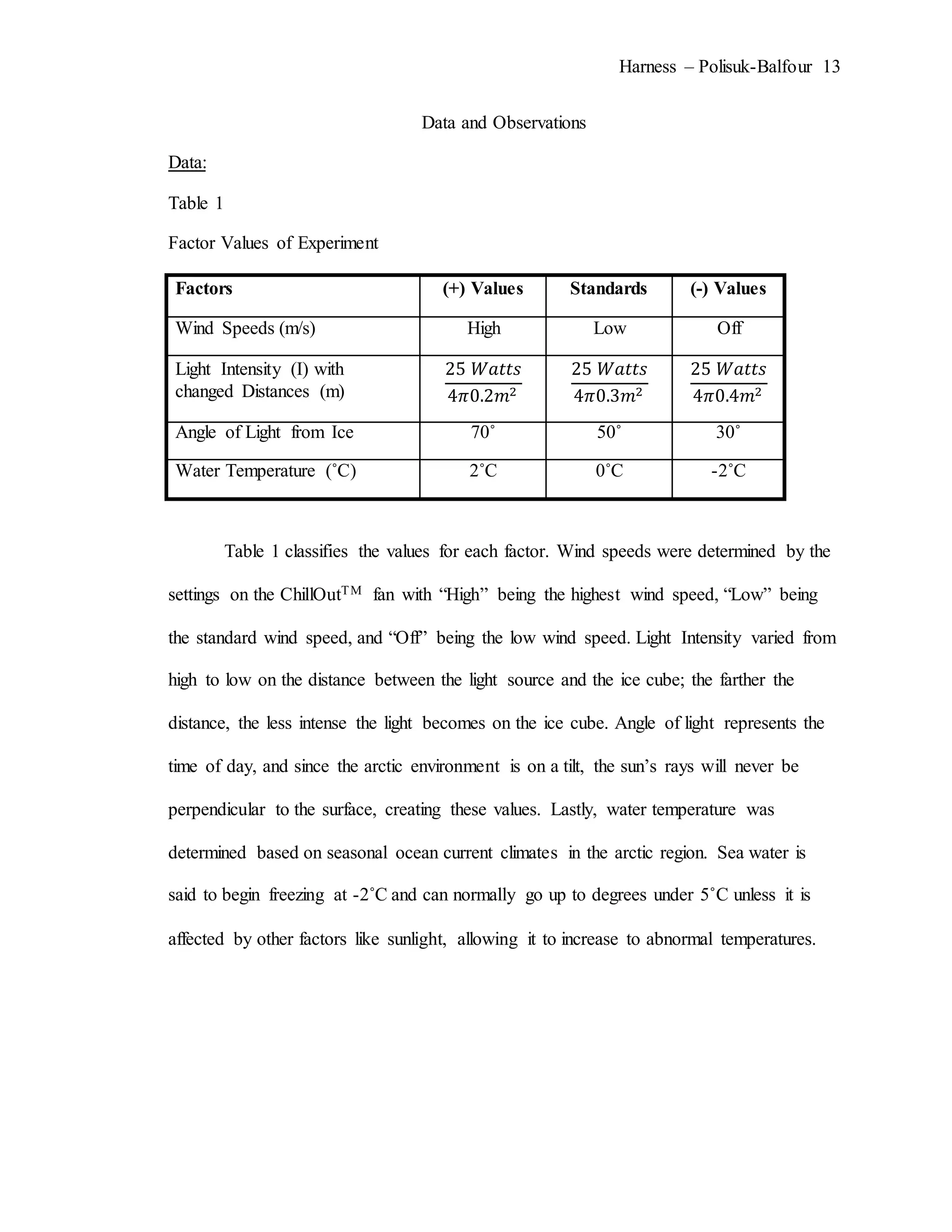
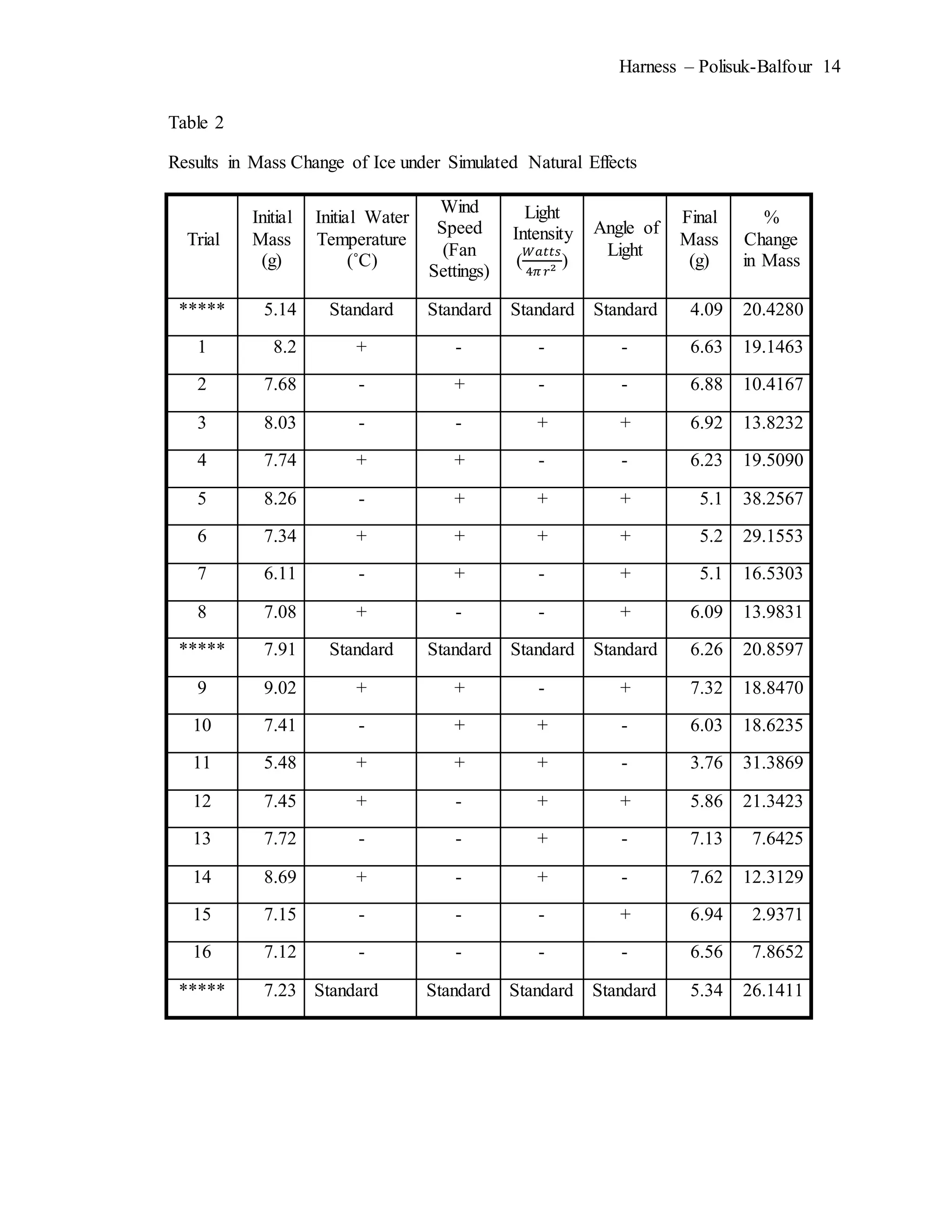
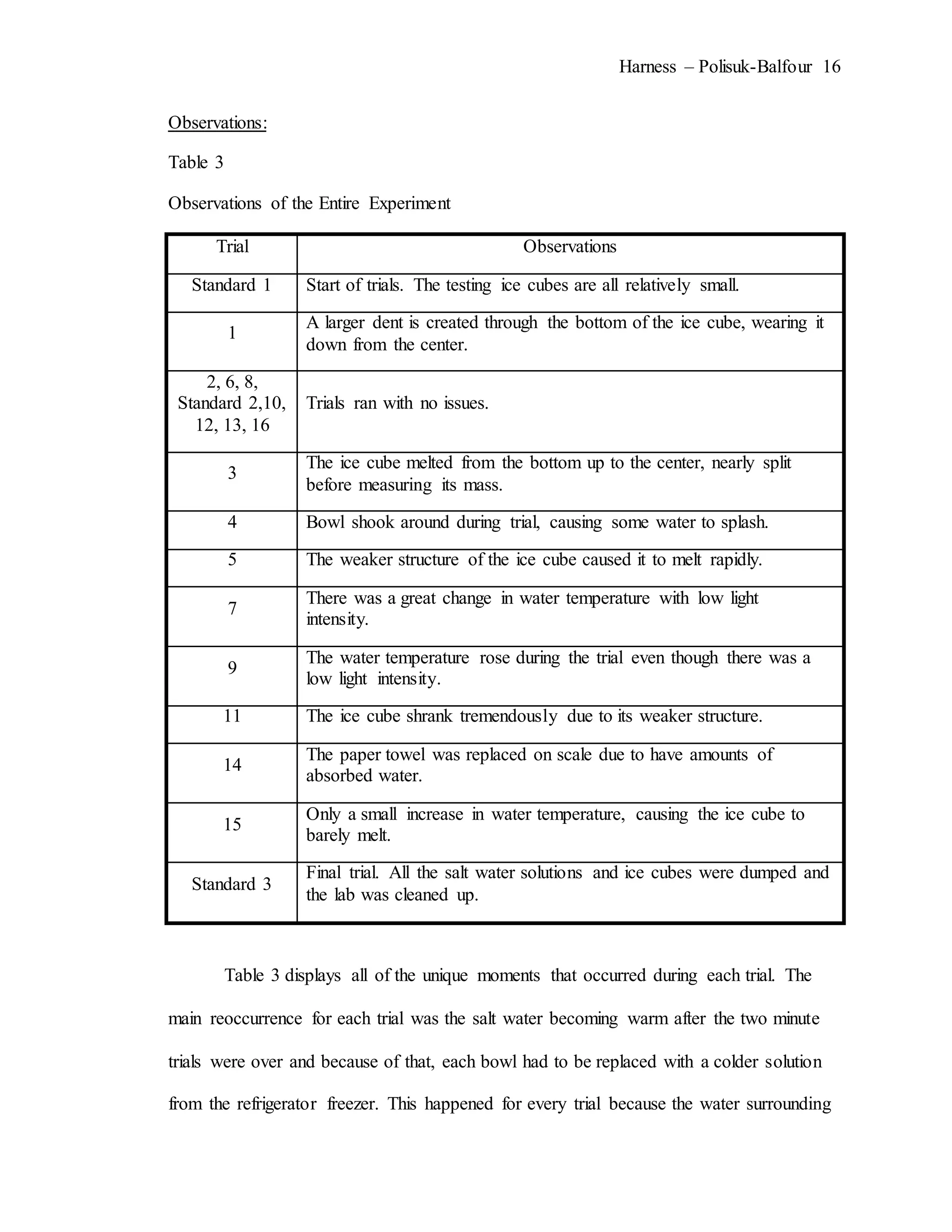
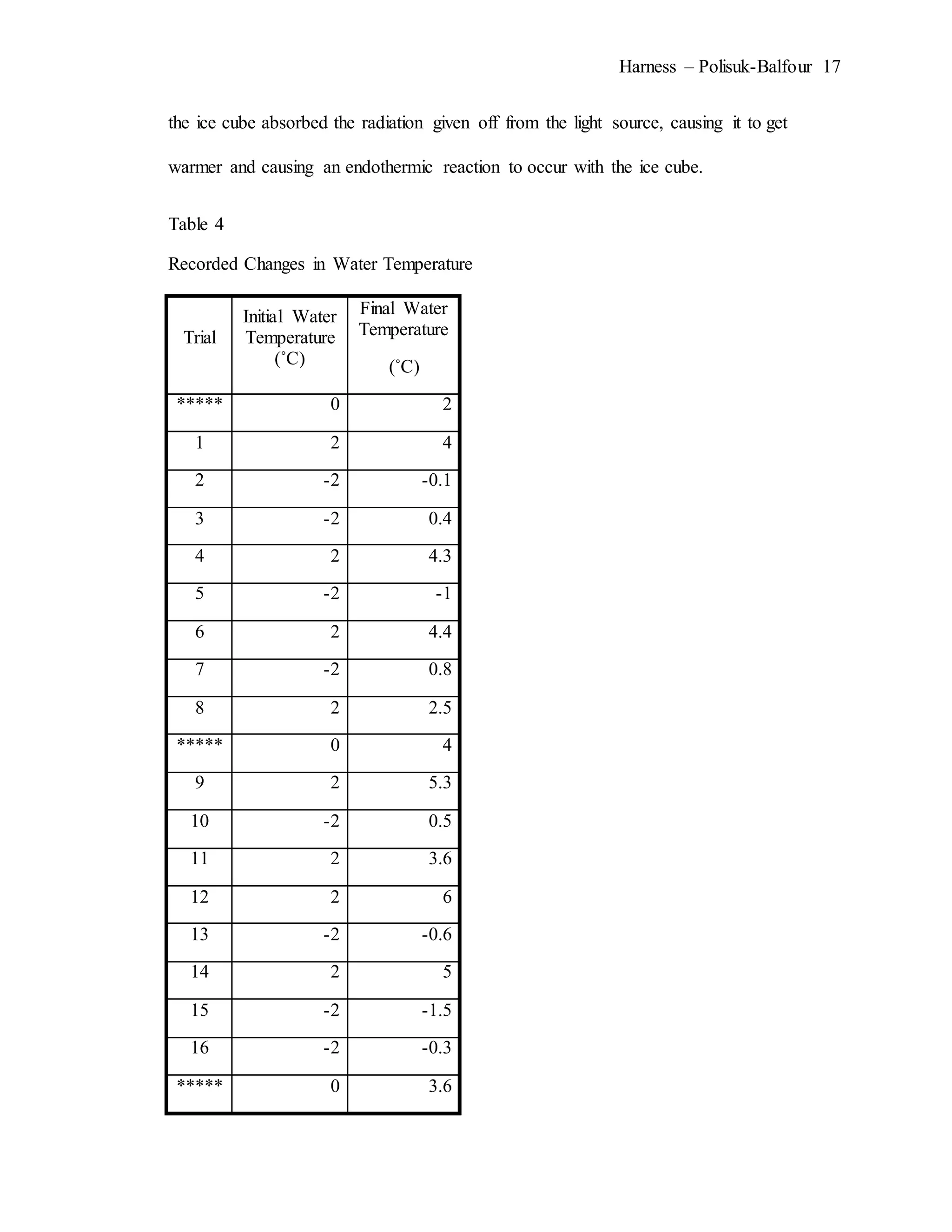
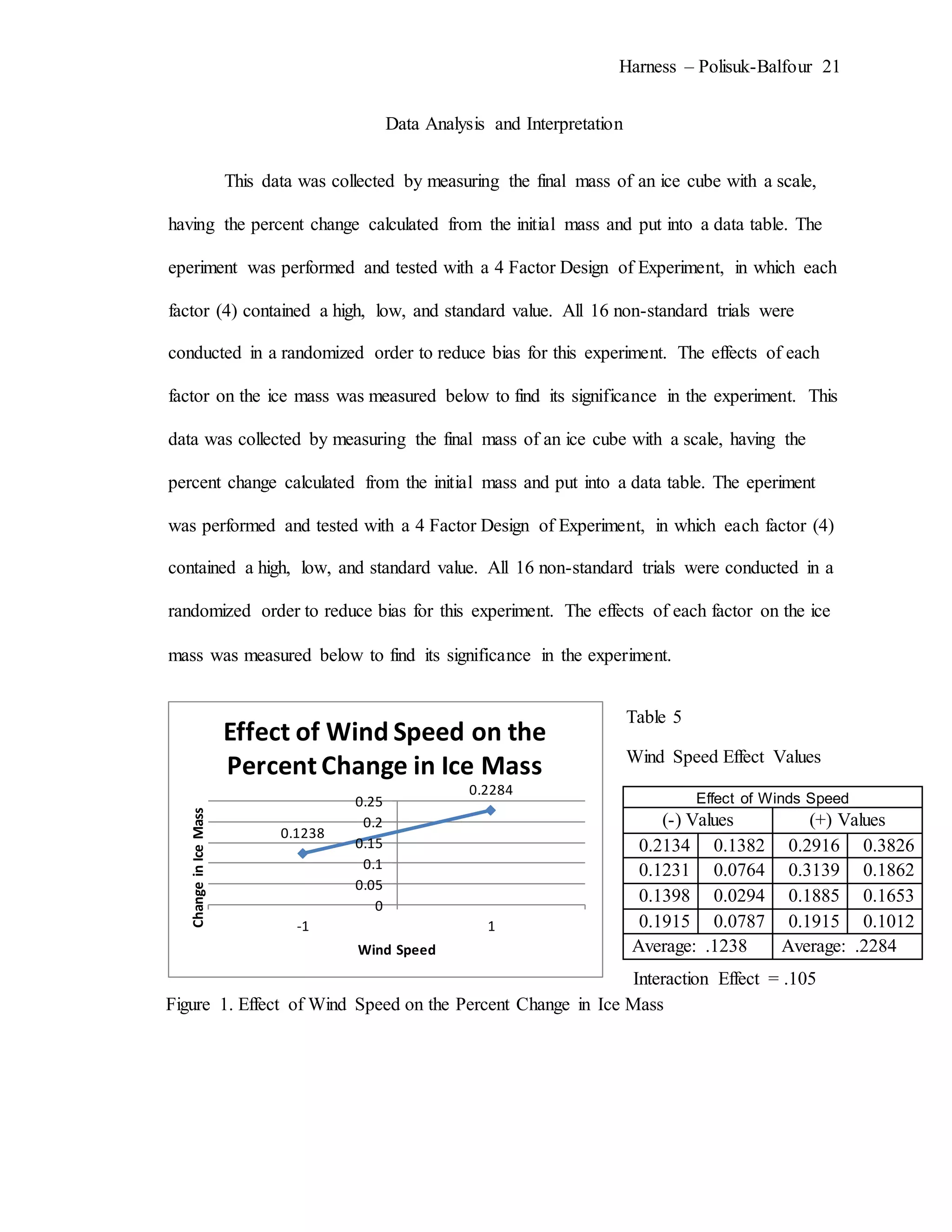
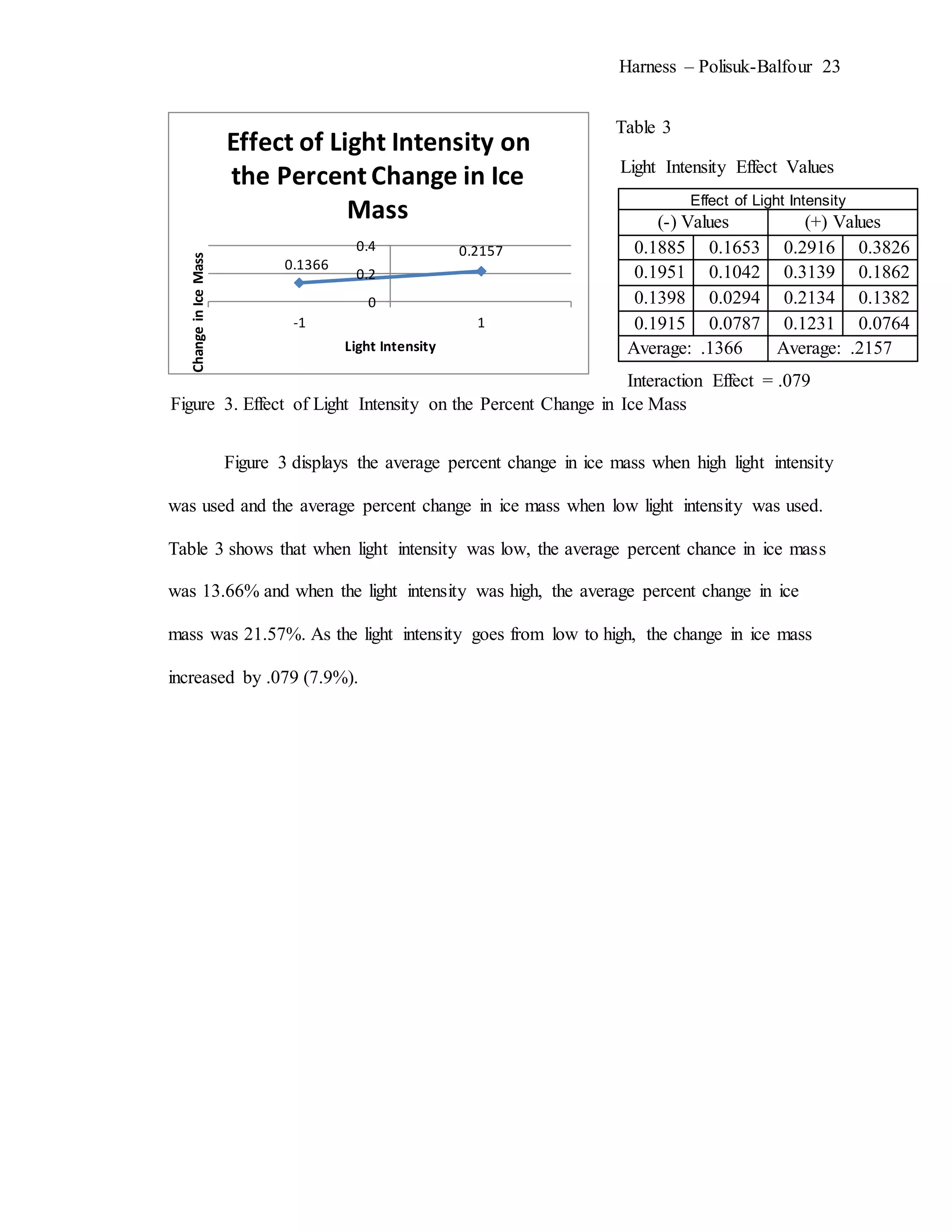
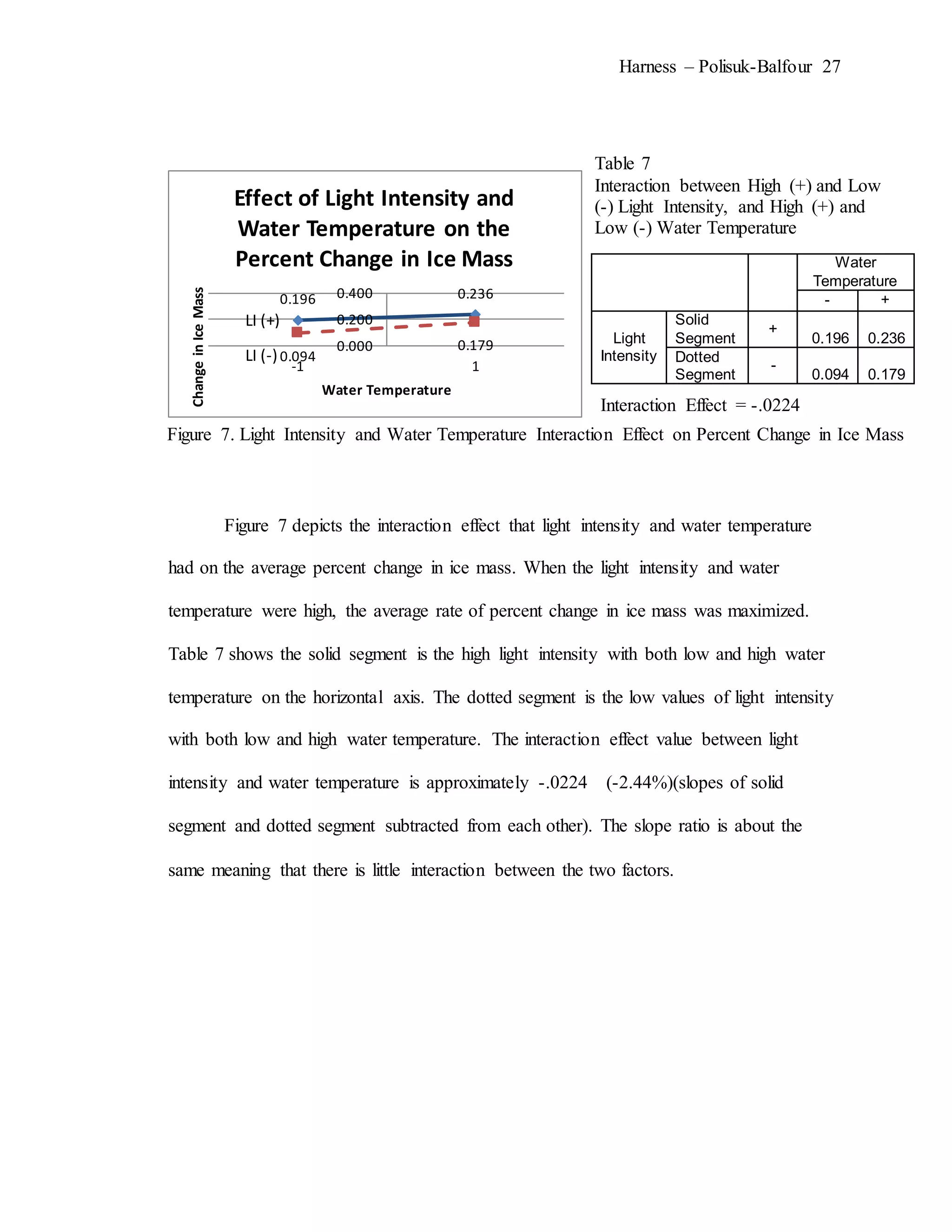
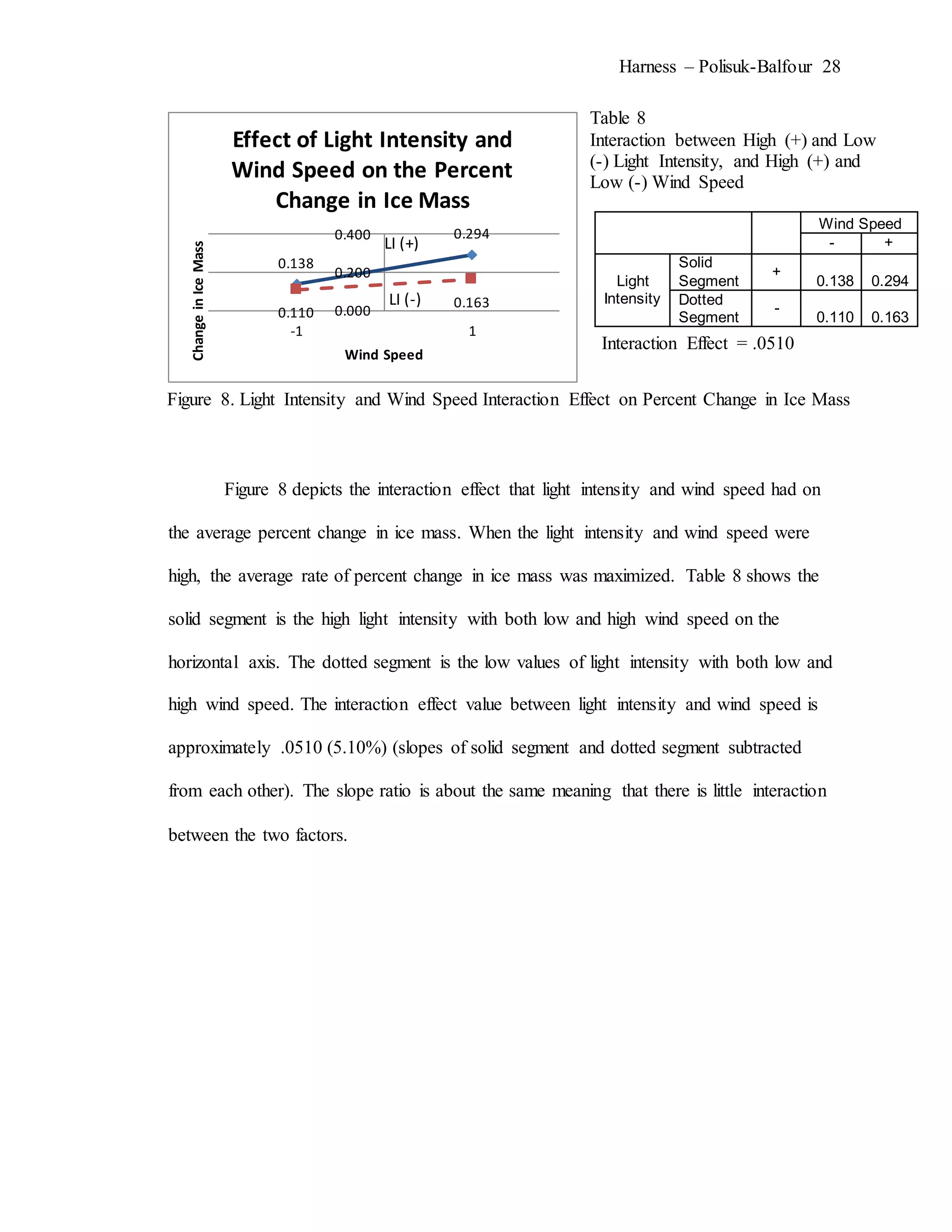
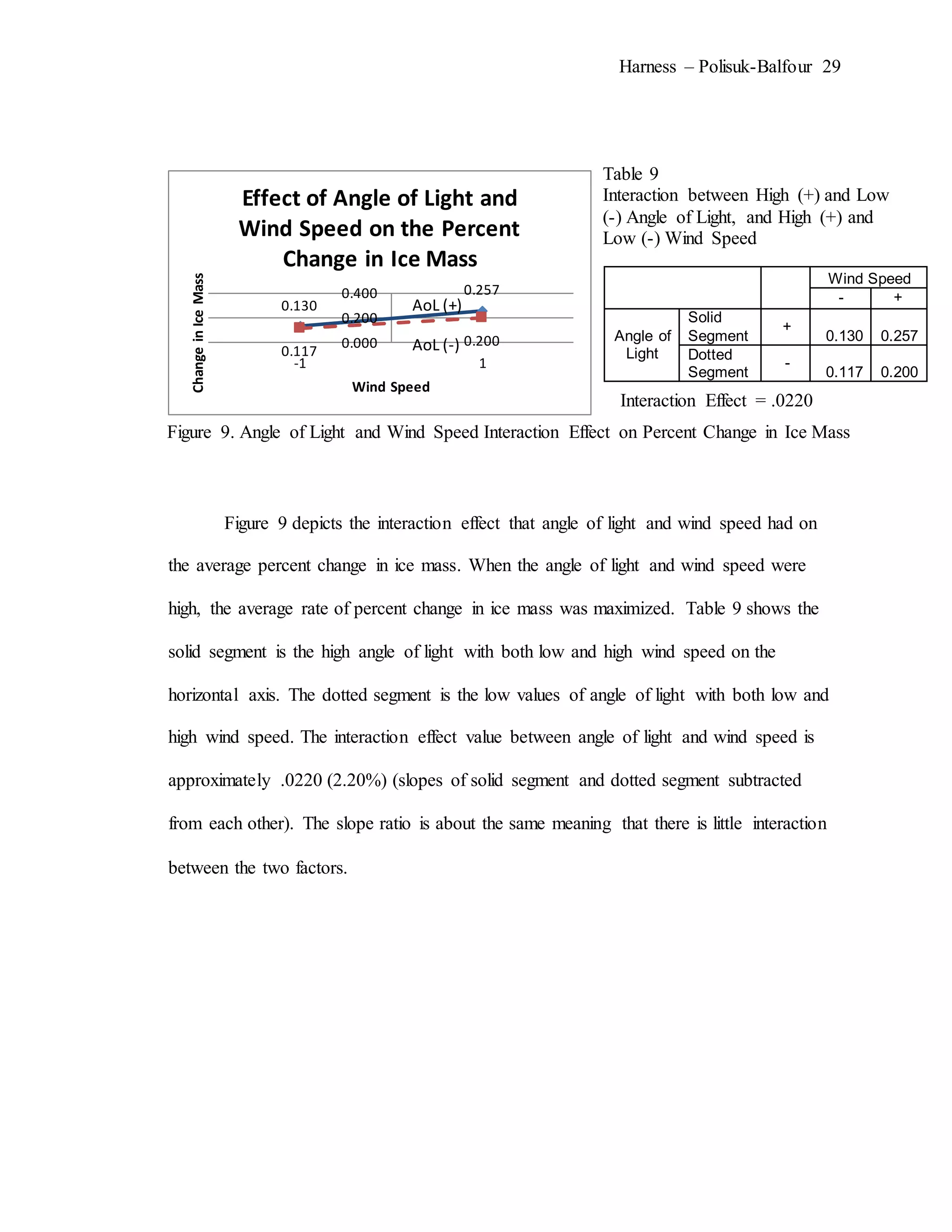
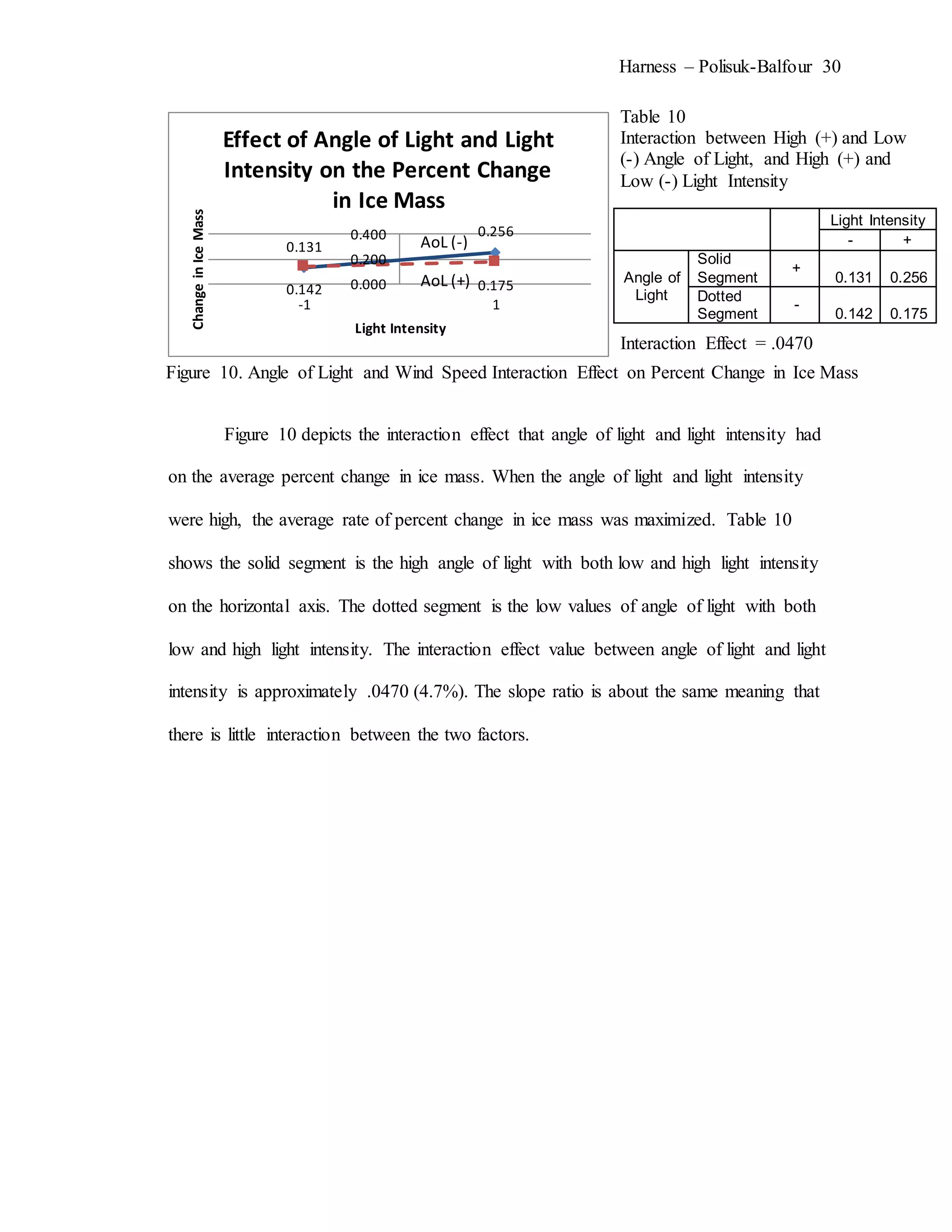
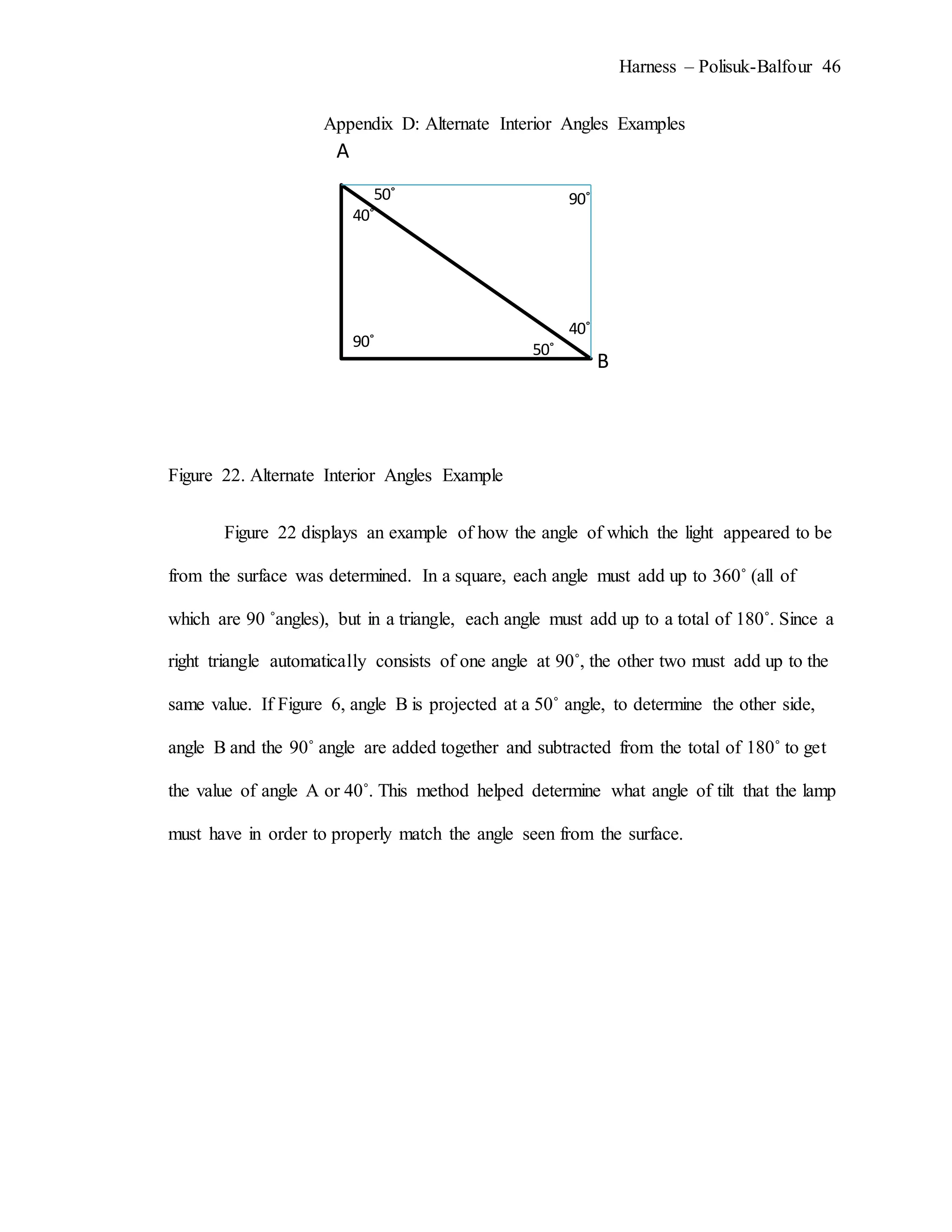
The document describes an experiment that simulated conditions in the Arctic environment to study how wind speed, water temperature, light angle, and light intensity affect the mass of an ice cube over time. Ice cubes were exposed to different combinations of these four factors for two minutes before measuring the percent change in mass. The results showed that higher water temperatures and more intense exposure to light and wind led to greater ice mass loss, with a maximum change of 38.26%. Lower levels of the factors resulted in less melting, with a minimum change of 2.94%. The goal was to better understand how the Arctic reacts to climate changes like rising temperatures.