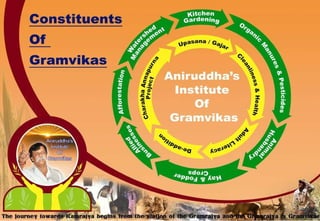
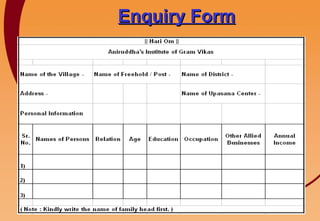
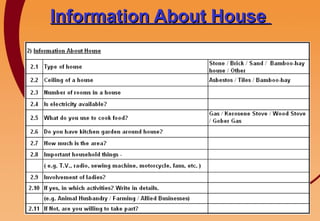
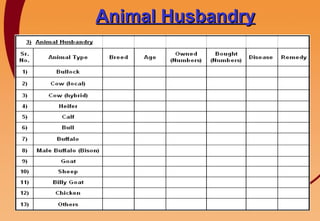
1) The document outlines the principles and components of Gram Vikas (village development) as envisioned by the Shree Aniruddha Upasana Foundation.
2) The goal is to develop neglected classes in villages by making optimal use of available resources and lowering production costs, not making people rich.
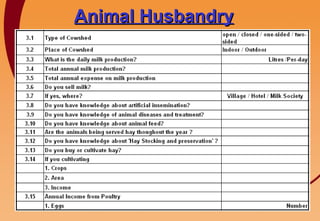
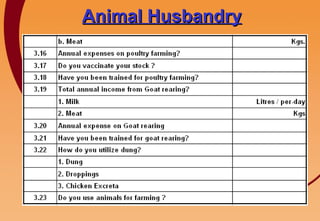
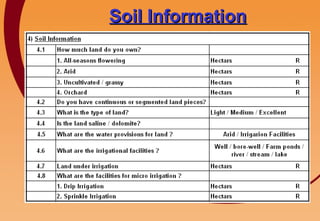
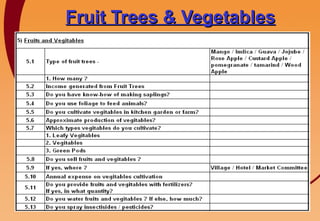
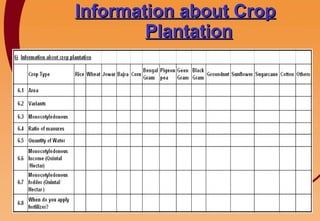
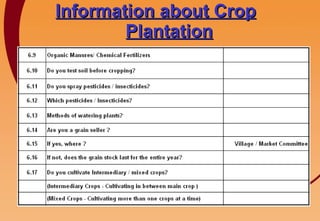
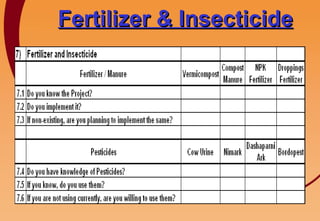
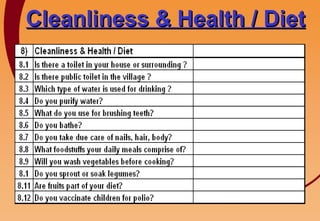
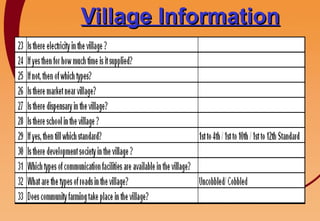
3) Key components include training in organic farming, kitchen gardening, animal husbandry, social forestry, water harvesting, and allied small businesses. Hygiene, health, and literacy programs are also discussed.
4) The work will start in villages where the Foundation has centers, and then expand to other districts in a decentralized manner with local volunteer leaders.