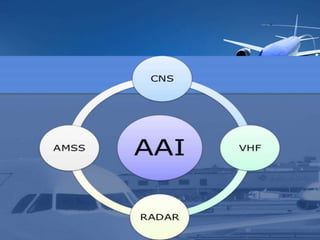
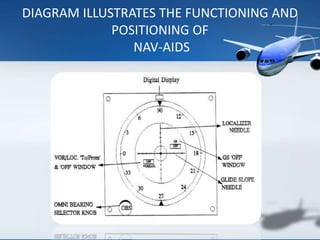
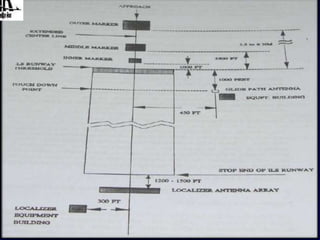
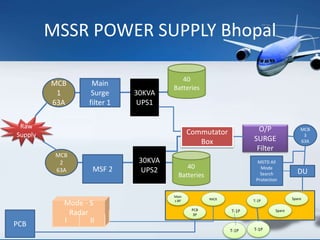
The Airports Authority of India (AAI) is responsible for managing airports and providing air traffic control services across India. It generates revenue through airport development, landing/parking fees, and air traffic control services. Key responsibilities include controlling airspace, installing and maintaining communications and navigation equipment, developing and managing terminals, and providing air traffic control, rescue and fire services, and security. AAI oversees air traffic control, sets air routes, and provides area flight information, notices to airmen, and communications, navigation, and surveillance services through technologies like radar, VHF radio, and navigation aids.