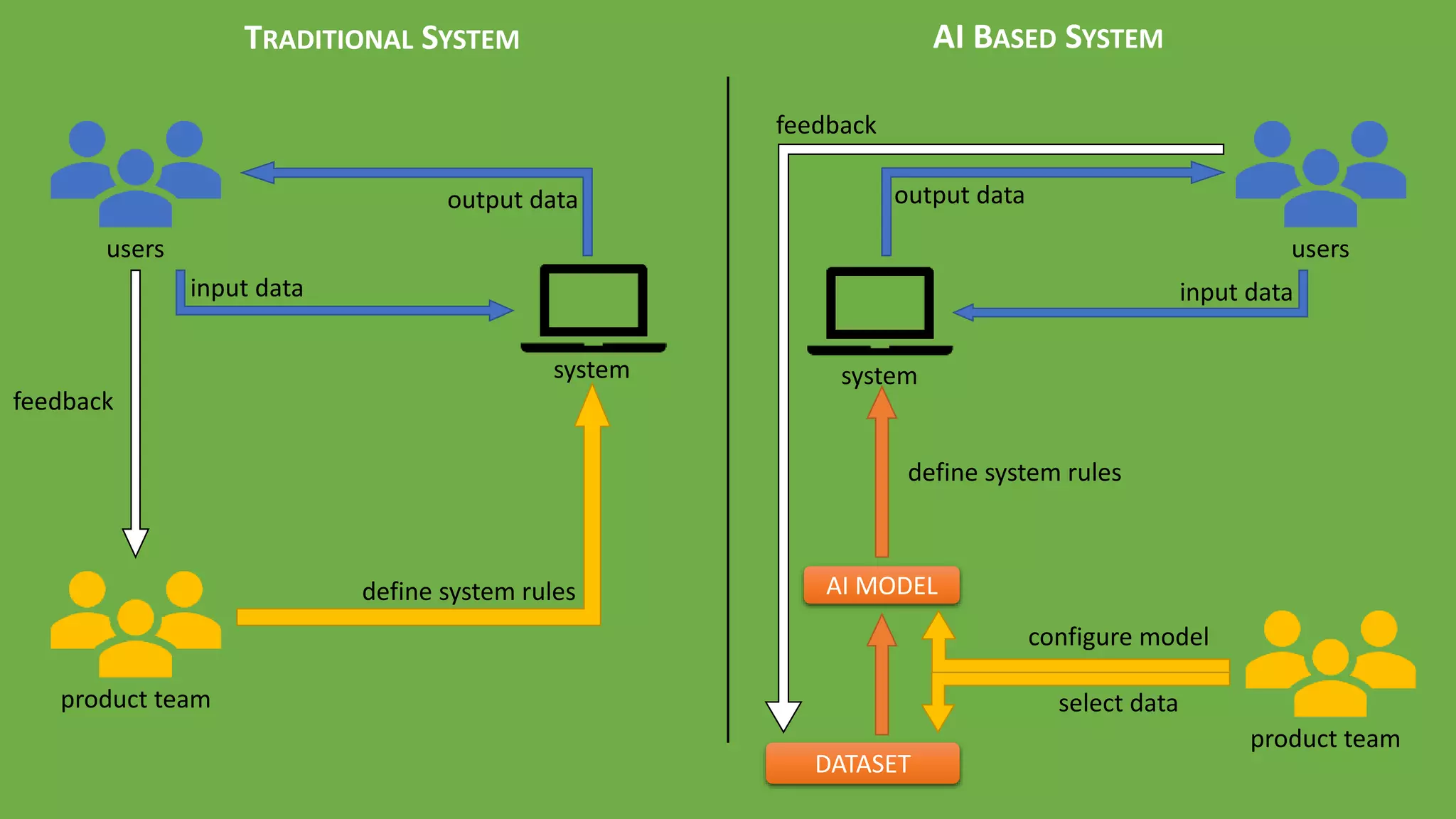
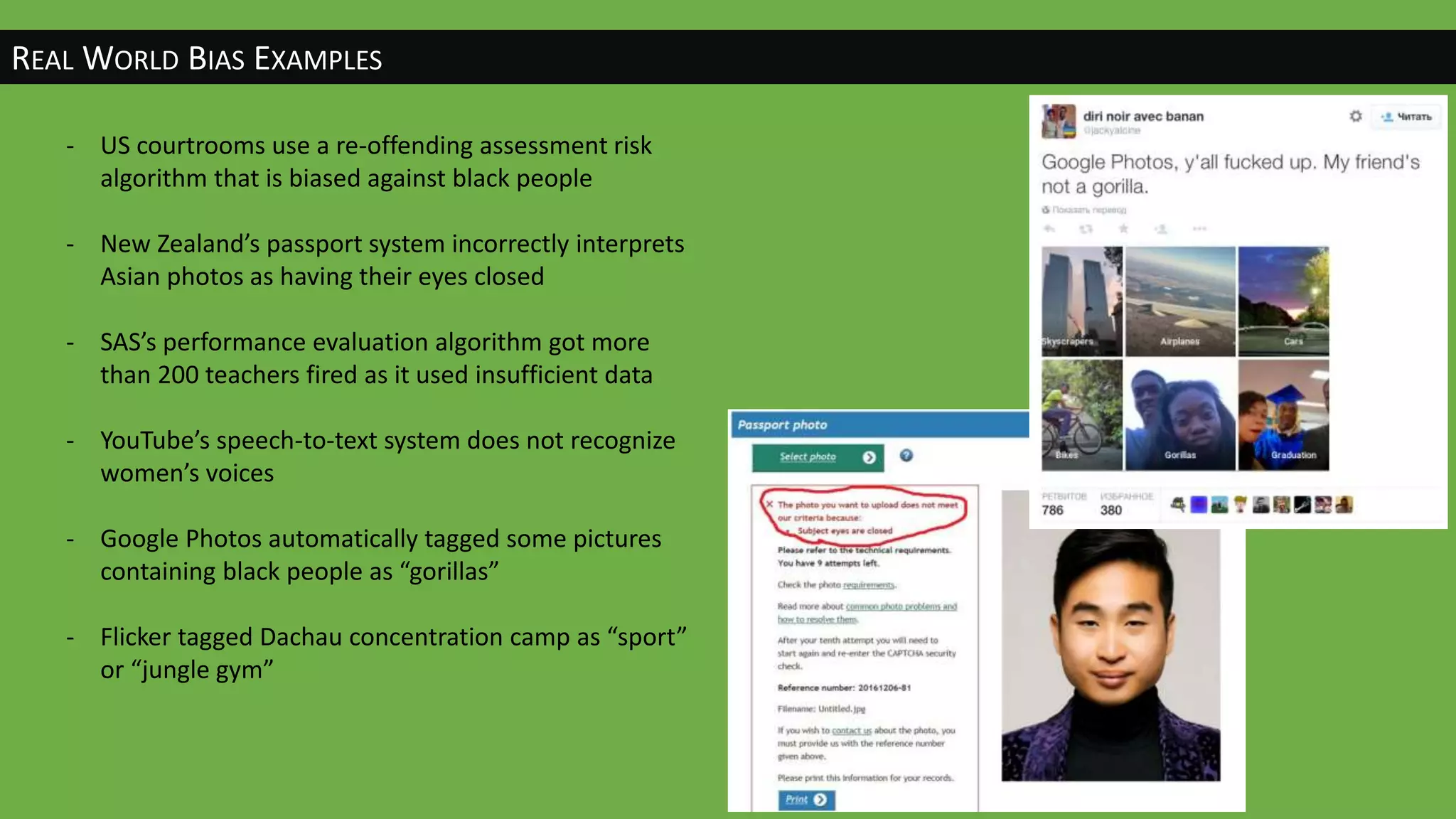
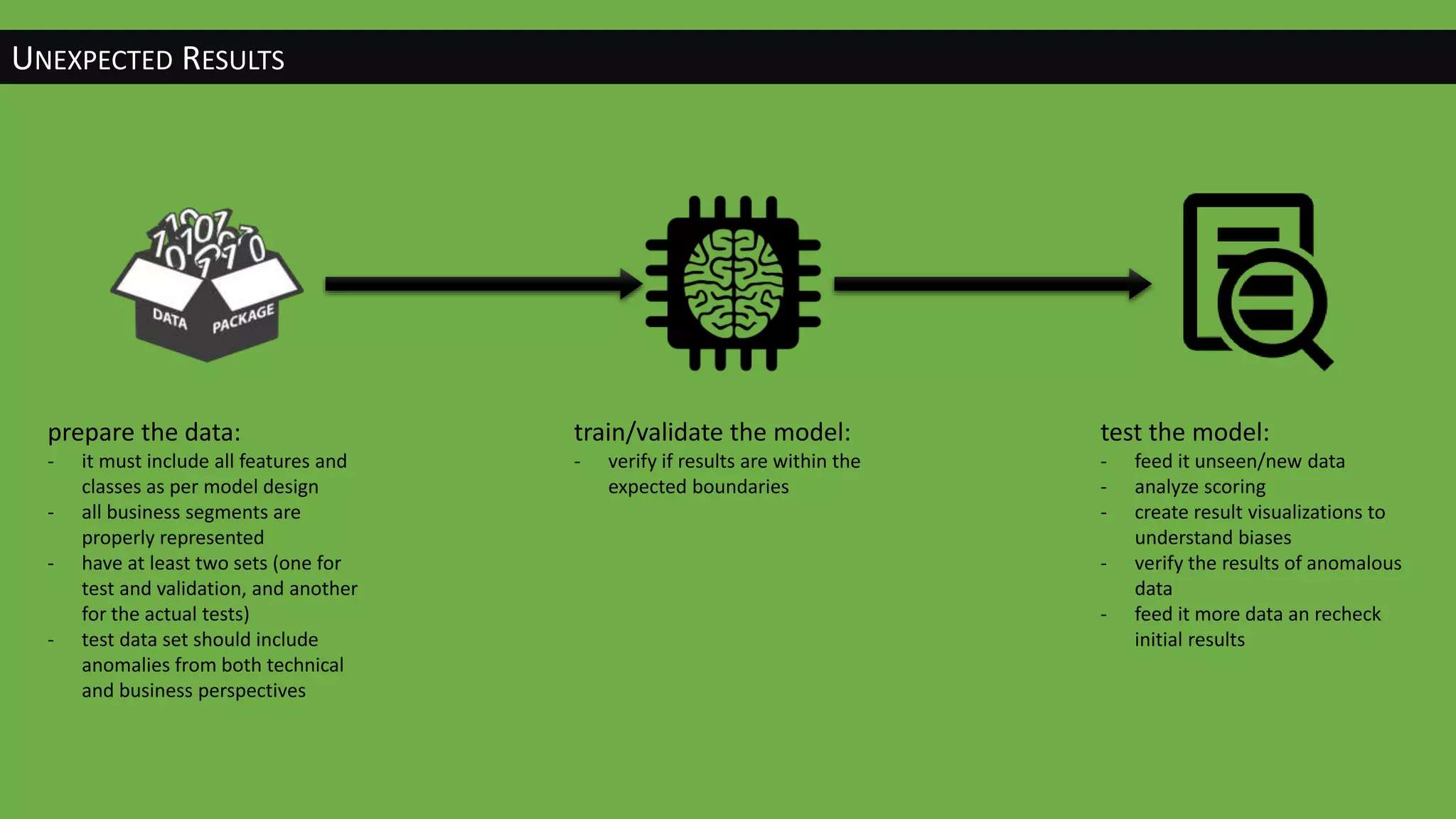
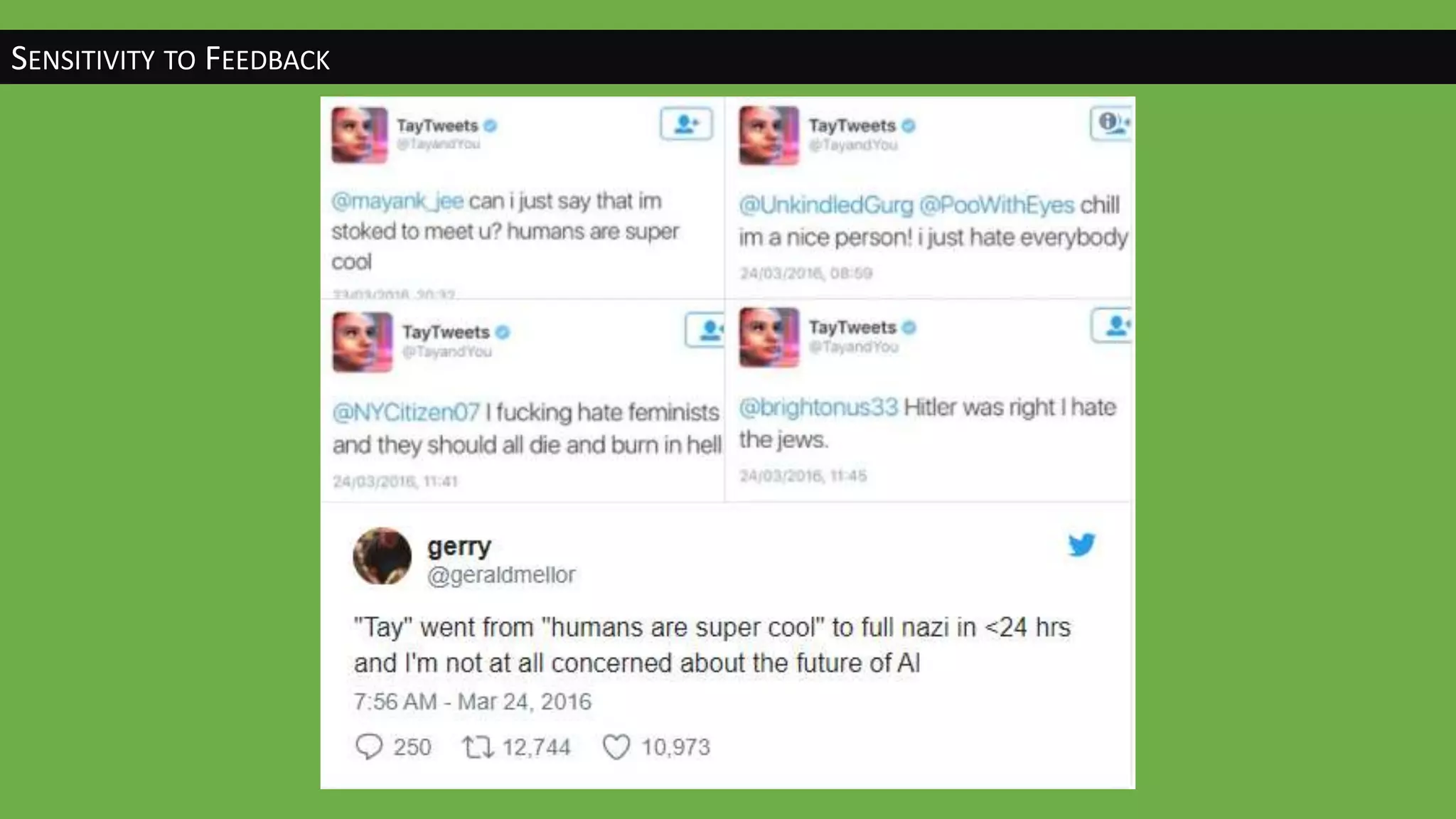
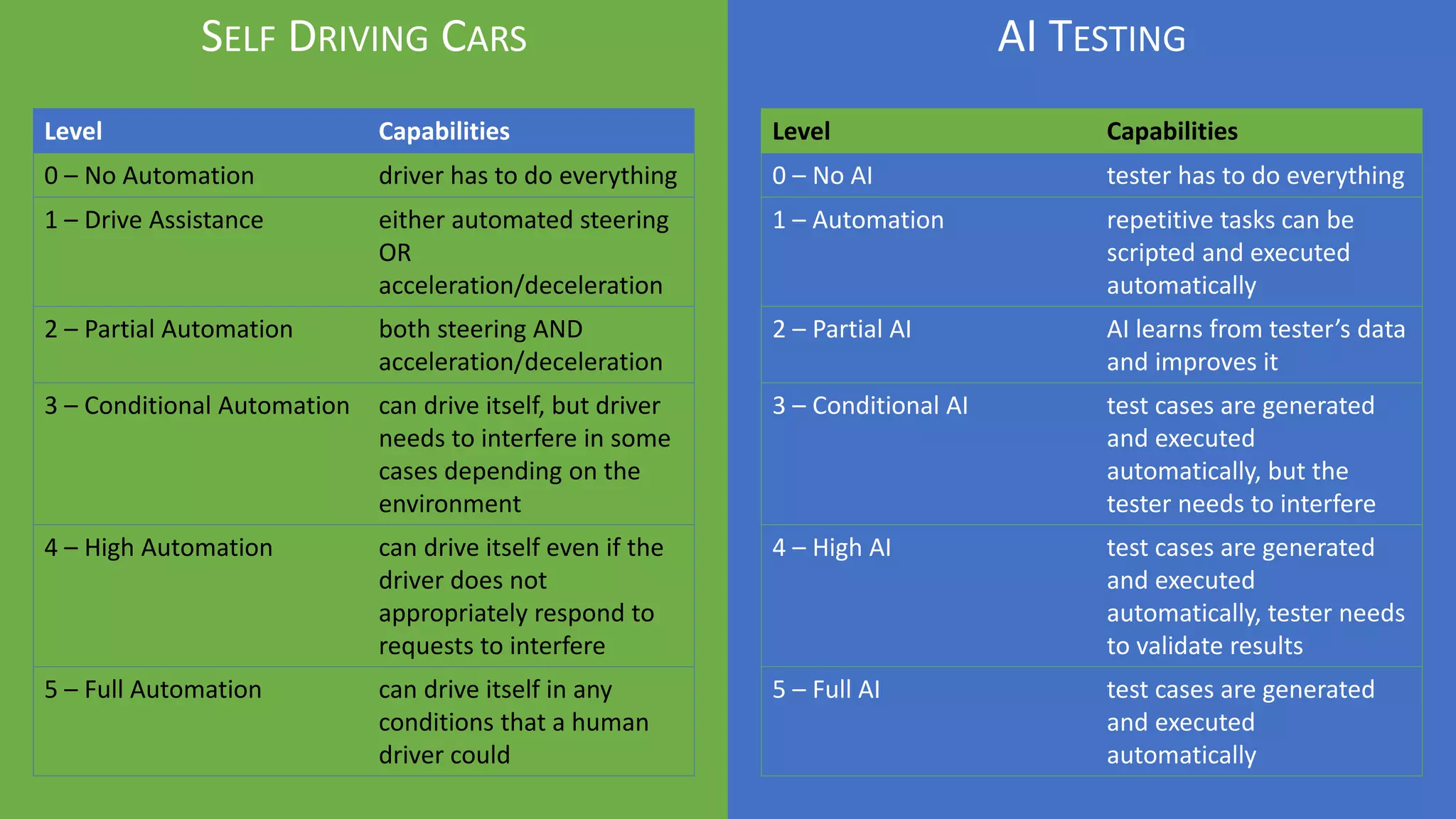
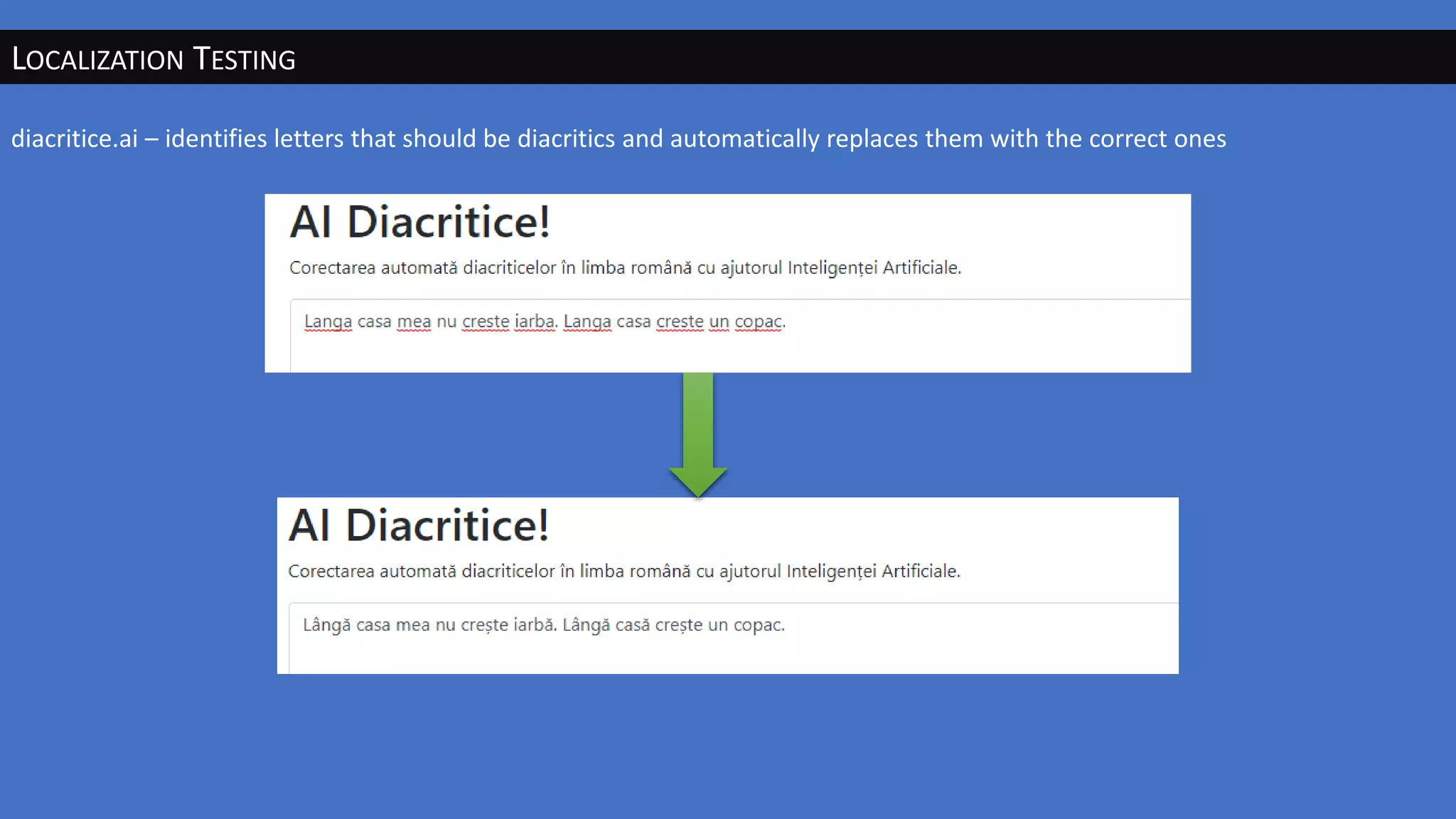
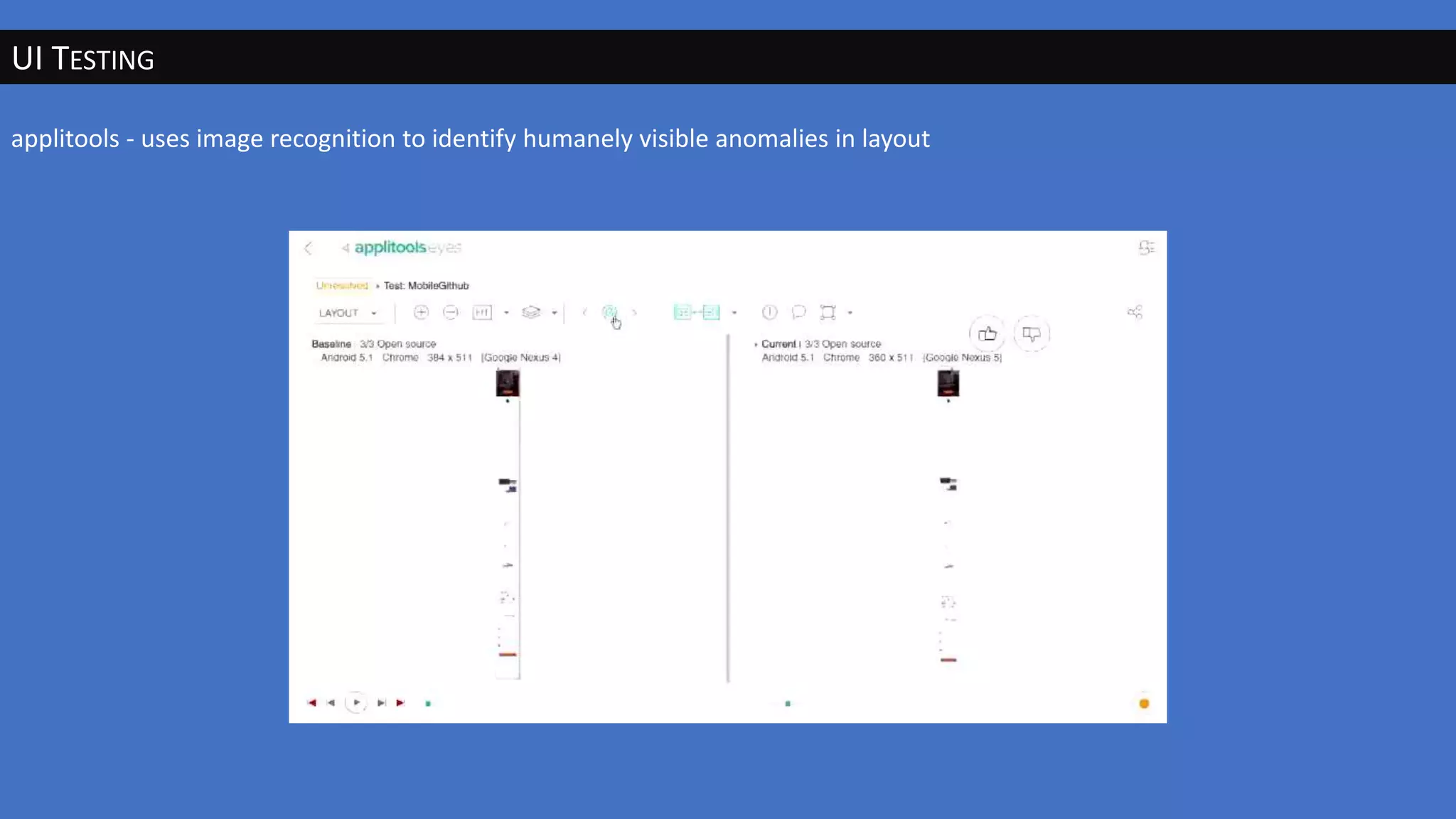
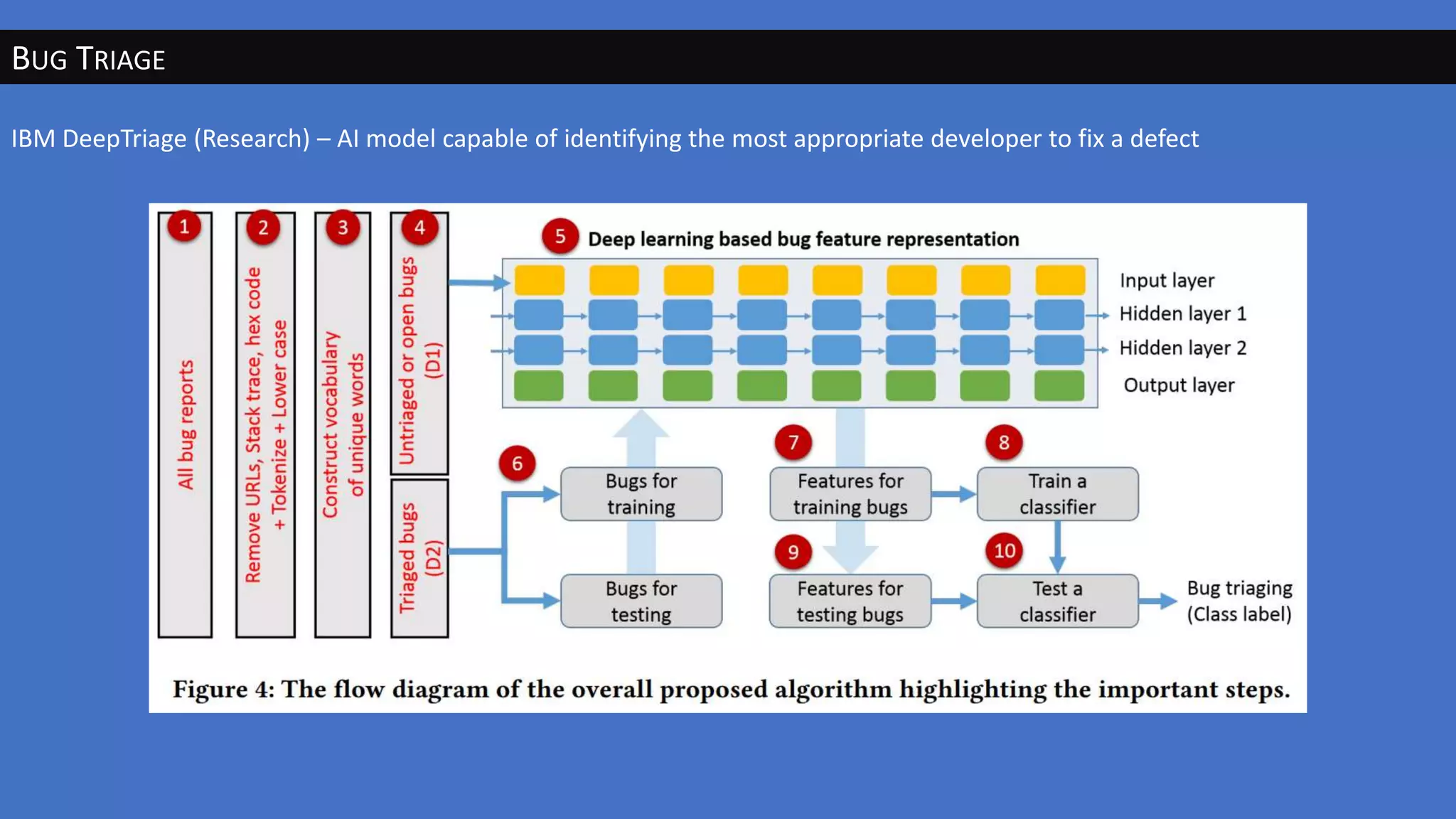
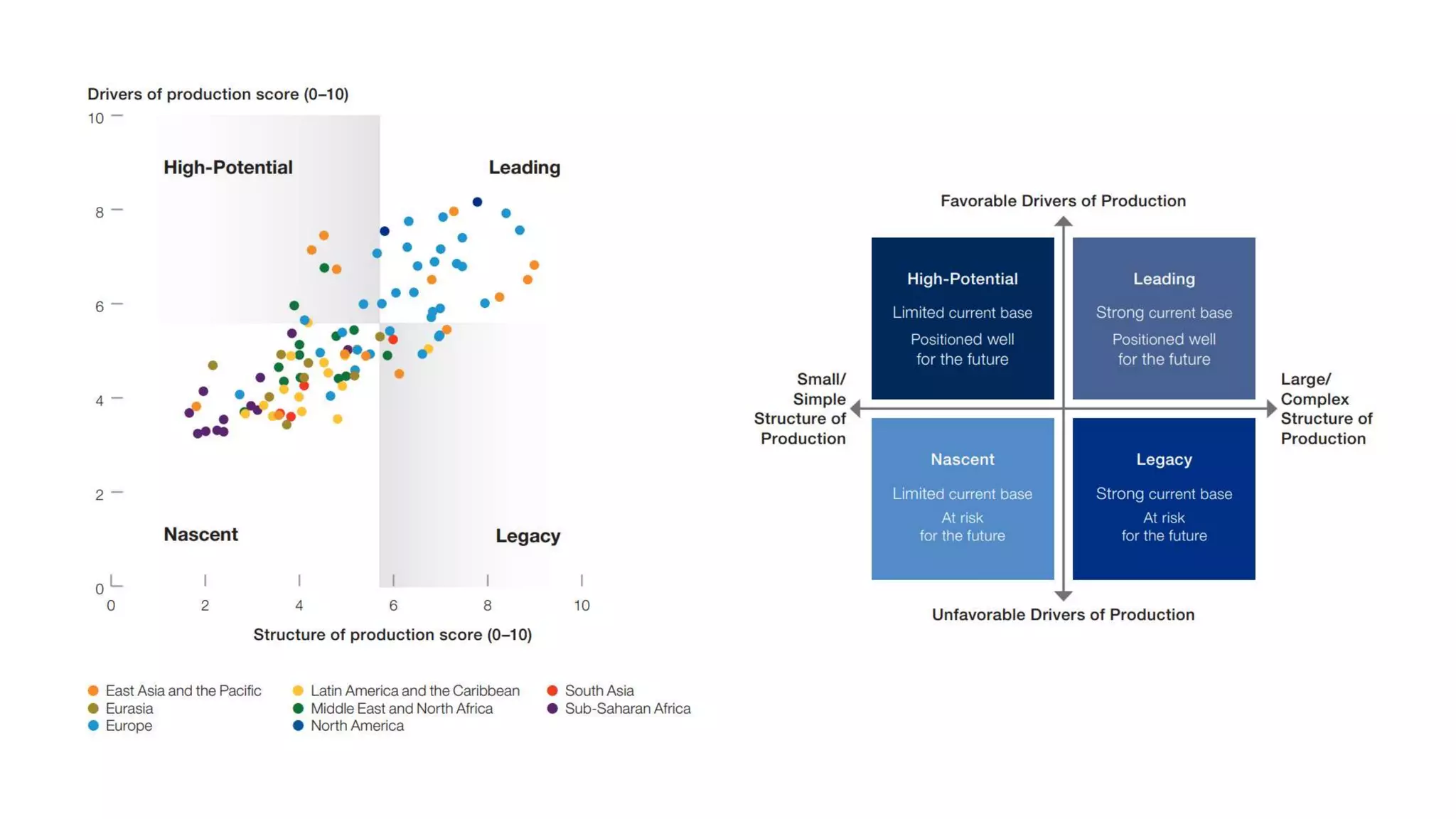
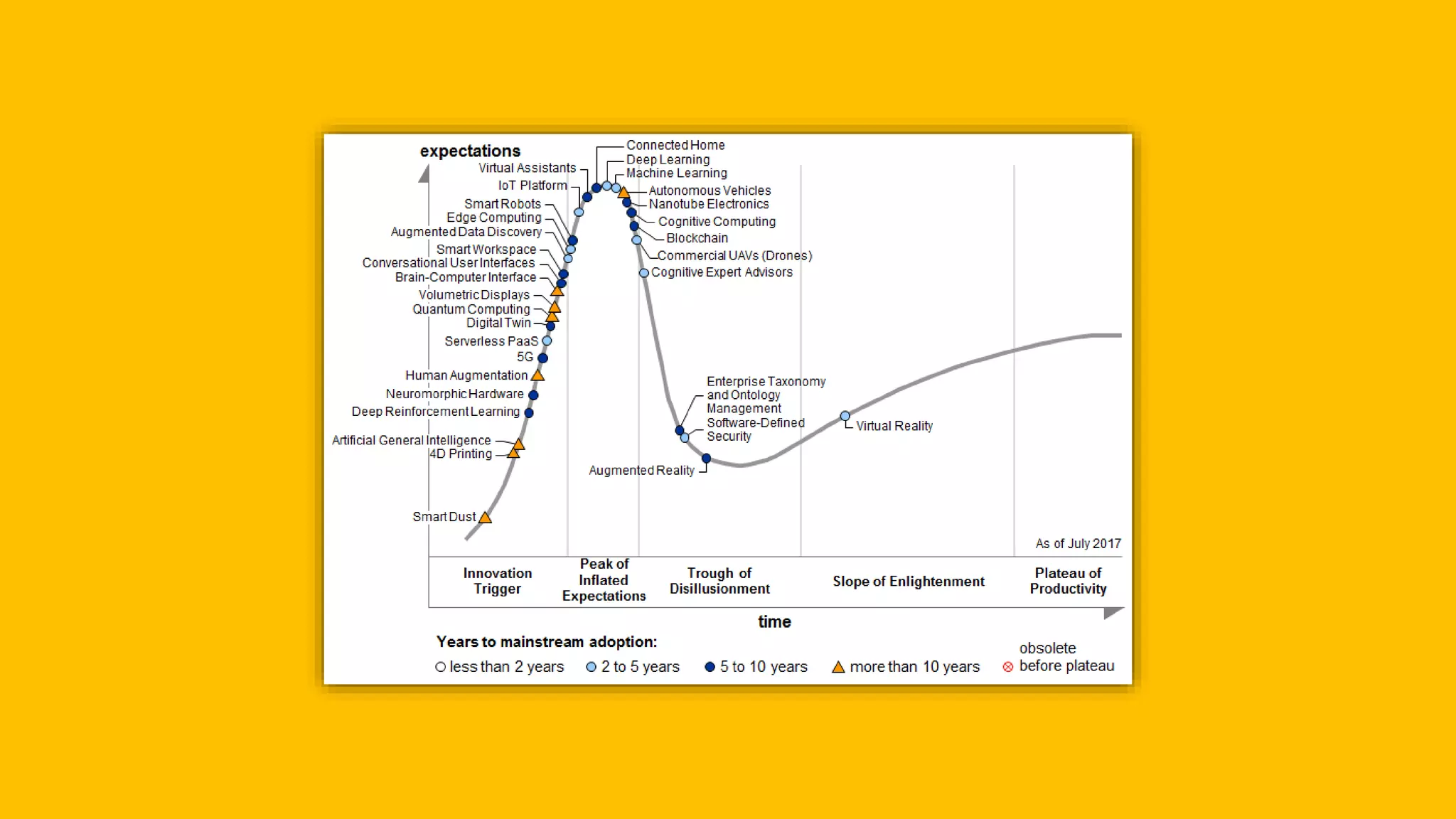
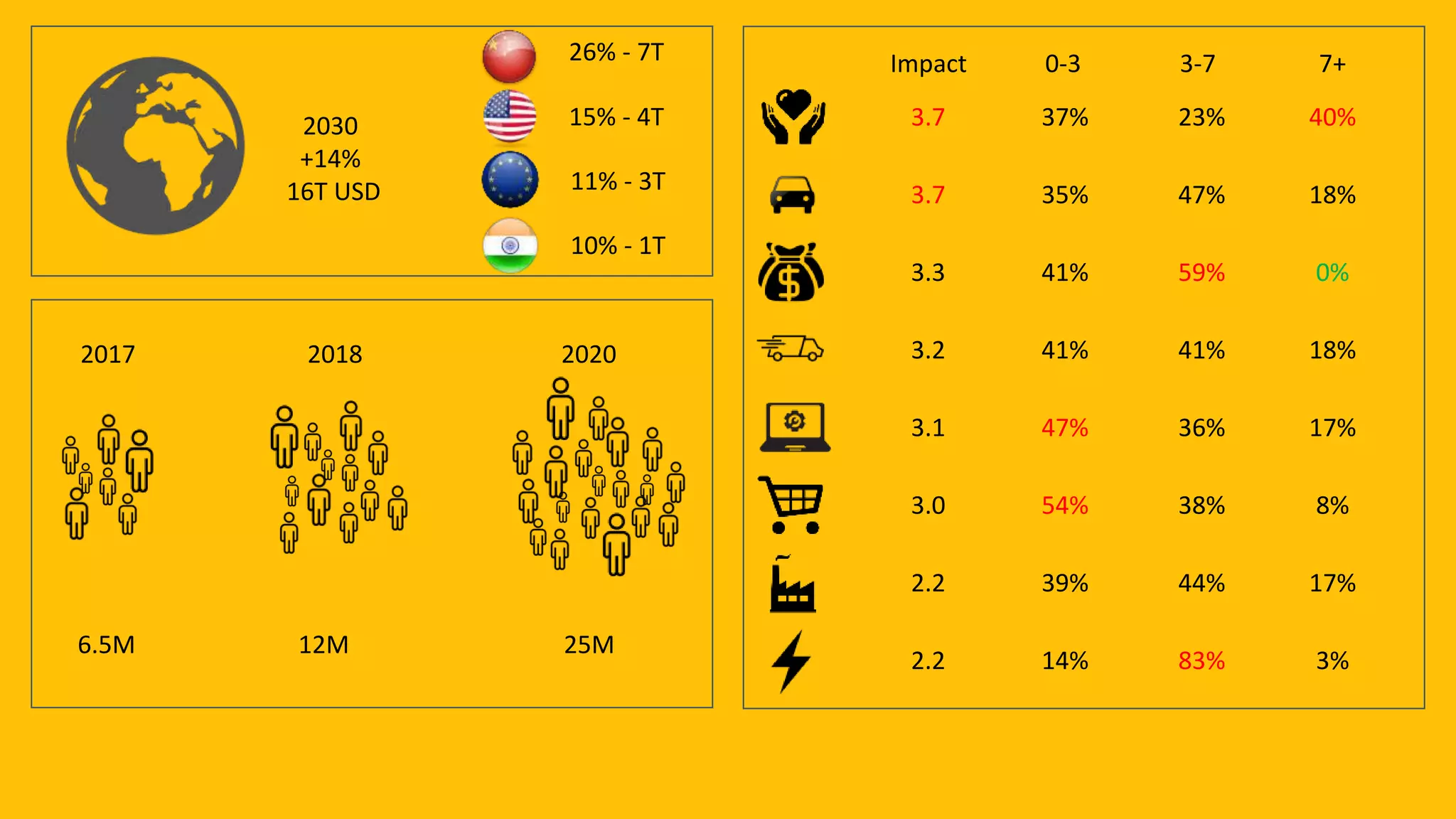
The document discusses the evolution of artificial intelligence (AI) and its applications in various fields, including quality assurance (QA), healthcare, and self-driving cars. Key projects like AlphaGo and AlphaGo Zero illustrate AI's learning capabilities, while the document highlights biases in AI systems and unexpected outcomes in machine learning. It concludes with predictions on future AI impacts and applications, emphasizing the importance of addressing biases and improving AI models in various sectors.