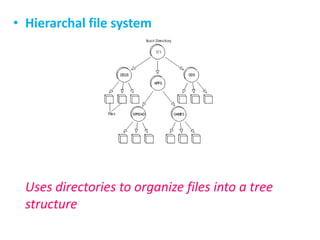
File management refers to the system an operating system uses to organize and track files. It provides facilities to create, move, and delete files and directories in a hierarchical tree structure. There are different types of file systems designed for various storage devices like disks, flash memory, and networks, as well as database and transactional file systems. File management involves assigning file names, storing metadata like modification times, and securing access to files.