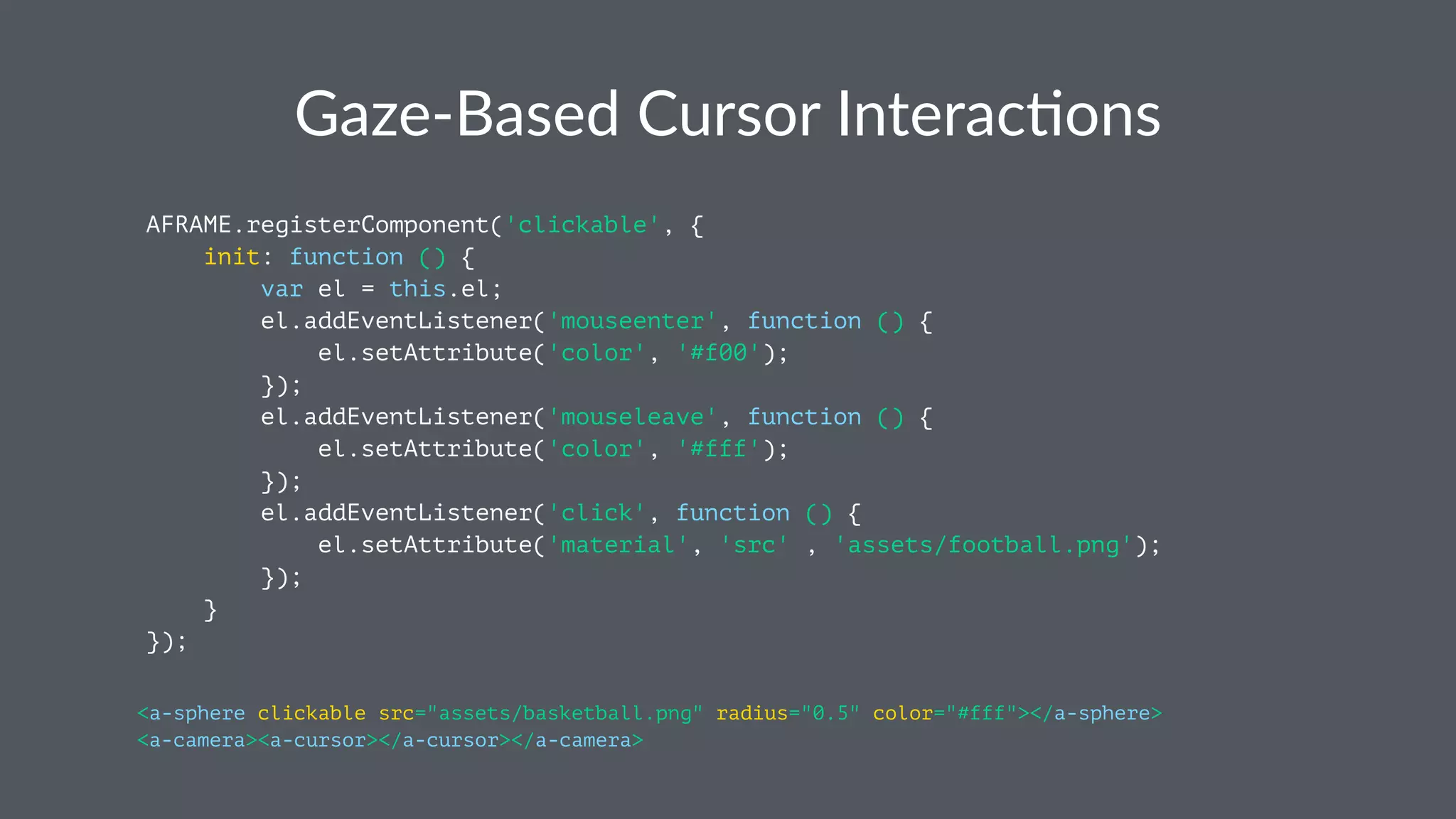
The document provides an introduction to WebVR, covering VR setup, user experience considerations, and various VR devices and programming frameworks. It discusses the evolution of virtual reality on the web, including WebVR's goals, non-goals, and frameworks such as A-Frame and ReactVR. The content emphasizes the importance of creating comfortable and compelling VR experiences while utilizing existing web technologies.

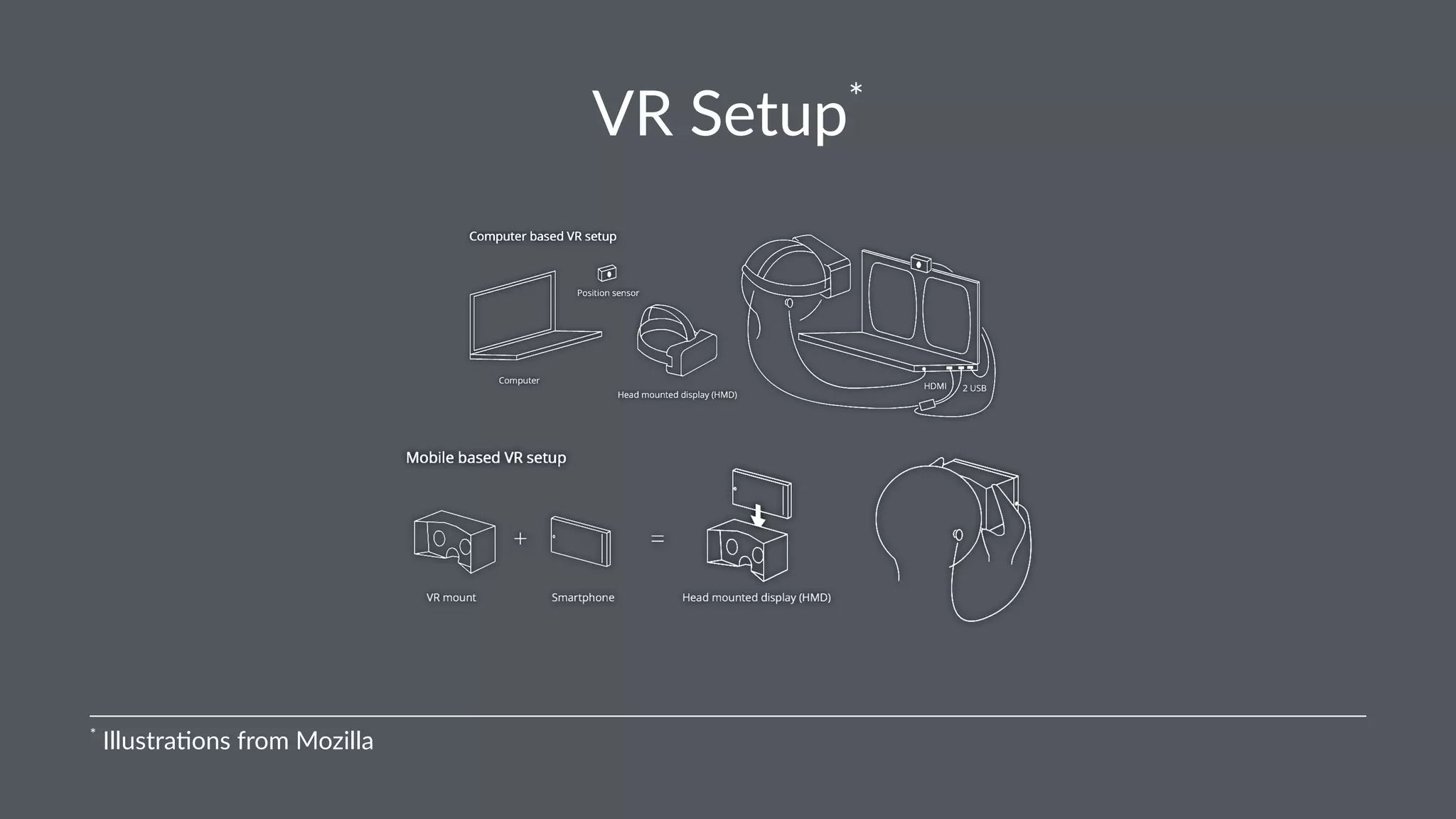

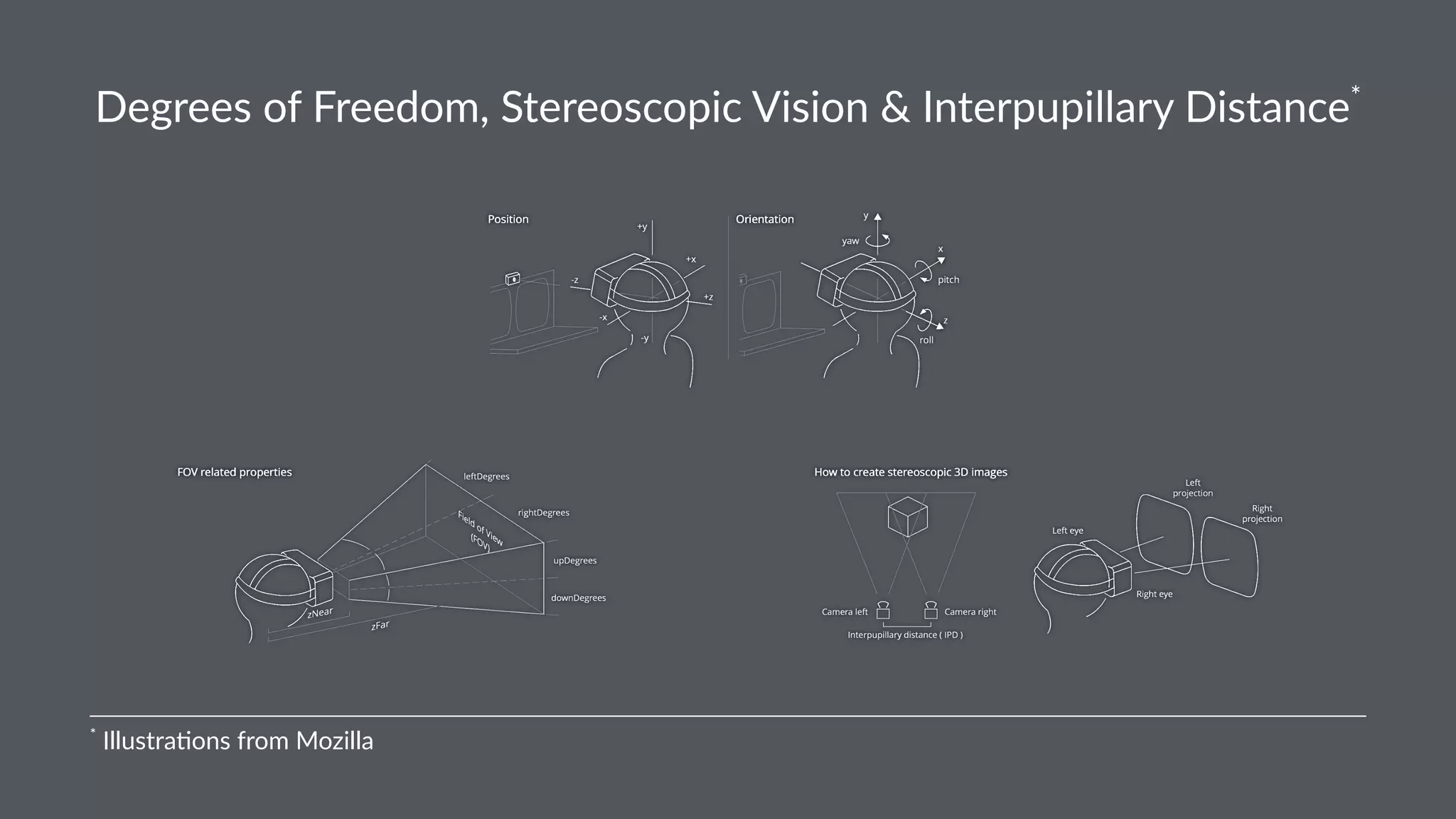









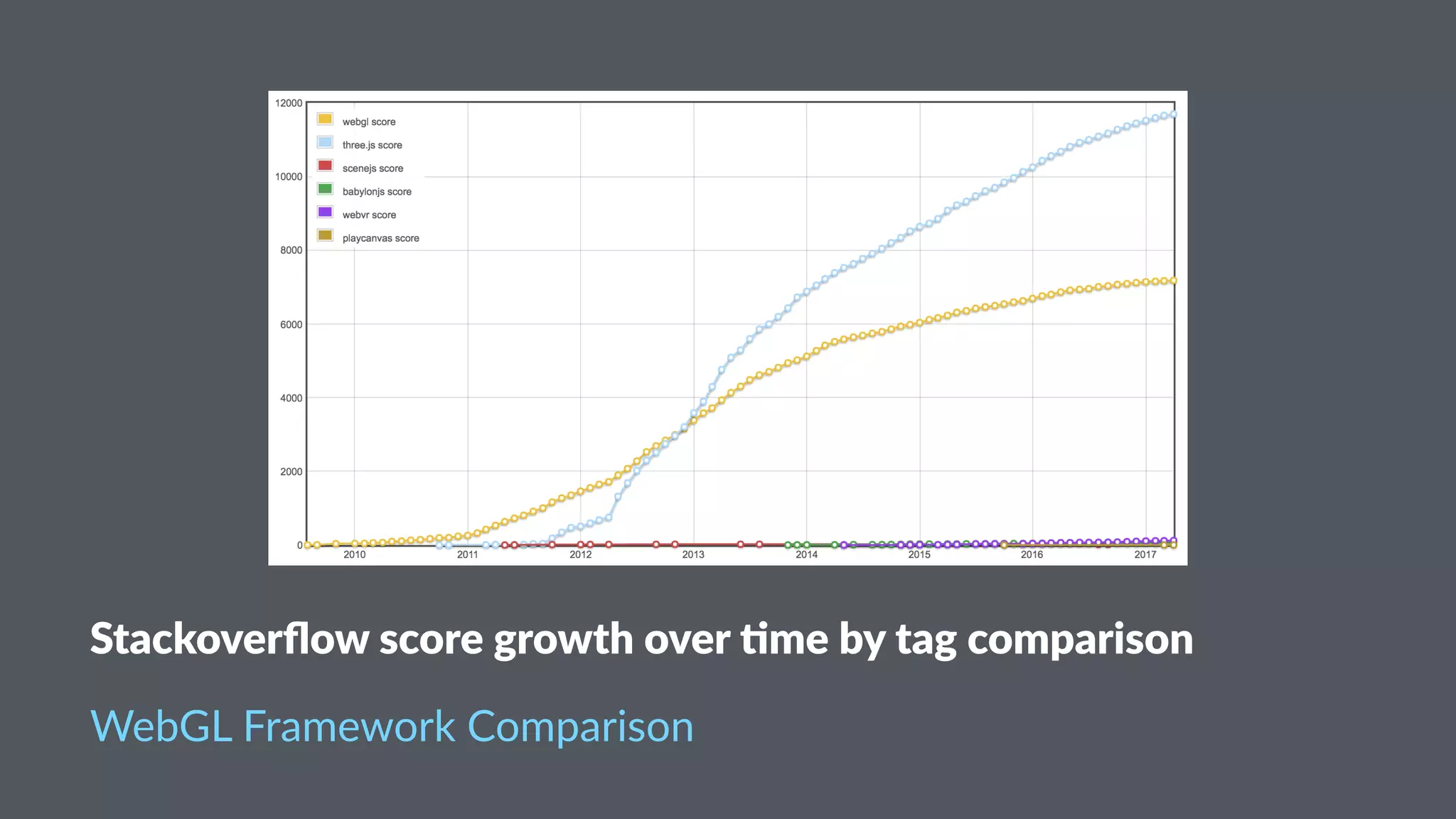








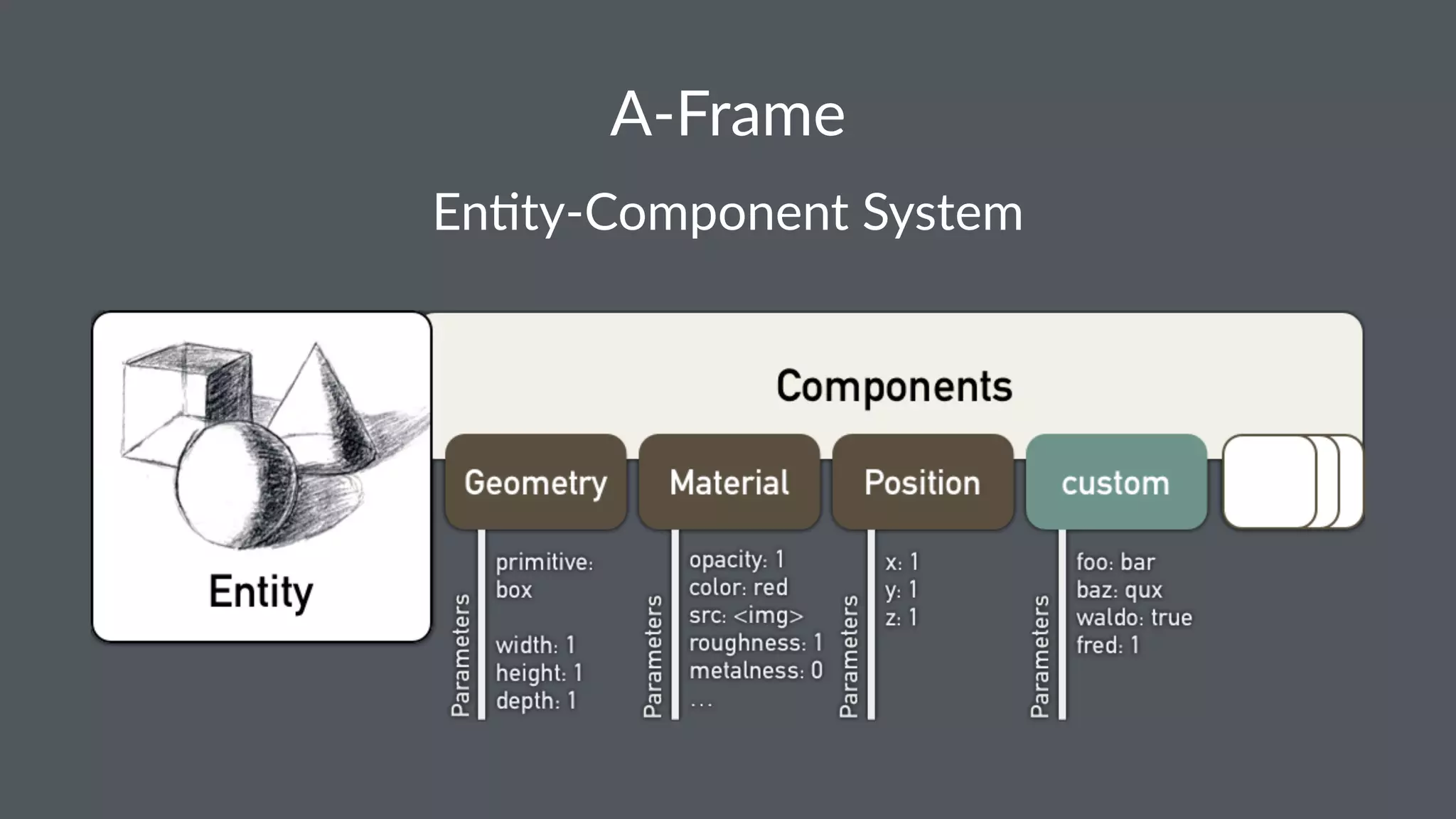








![A-Frame Inspector
[control]+[option]+[i]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ferguson-vr-hackathon-170509192617/75/Ferguson-VR-Hackathon-May-6-2017-33-2048.jpg)


