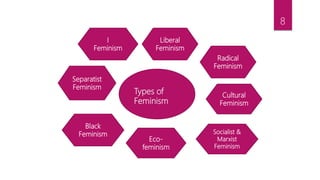
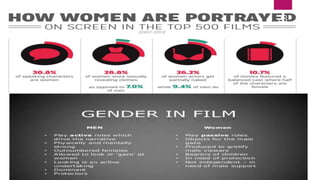
This document provides an overview of feminism and its evolution. It discusses the basic definition of feminism as believing in social, political, and economic equality between men and women. It outlines some common misconceptions about feminism. It then discusses the evolution of feminism in three waves - the first wave focused on legal rights, the second wave focused on expanding opportunities, and the third wave focuses on individual experiences and continuing progress. The document also summarizes different types of feminism such as liberal, radical, cultural, black, eco-feminism, and others. Finally, it discusses portrayals of women in media like magazines, advertisements, movies, and news reporting.