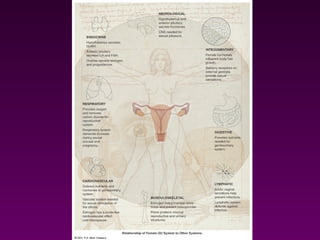
This document provides information on assessing the female genitourinary system, including:
- The structures that make up the system and their functions
- How to take a history, examine patients, and identify normal vs abnormal findings
- Cultural and developmental variations
- A case study of a patient complaining of scant midcycle bleeding, and the relevant history, exam findings, and potential nursing diagnoses for this patient