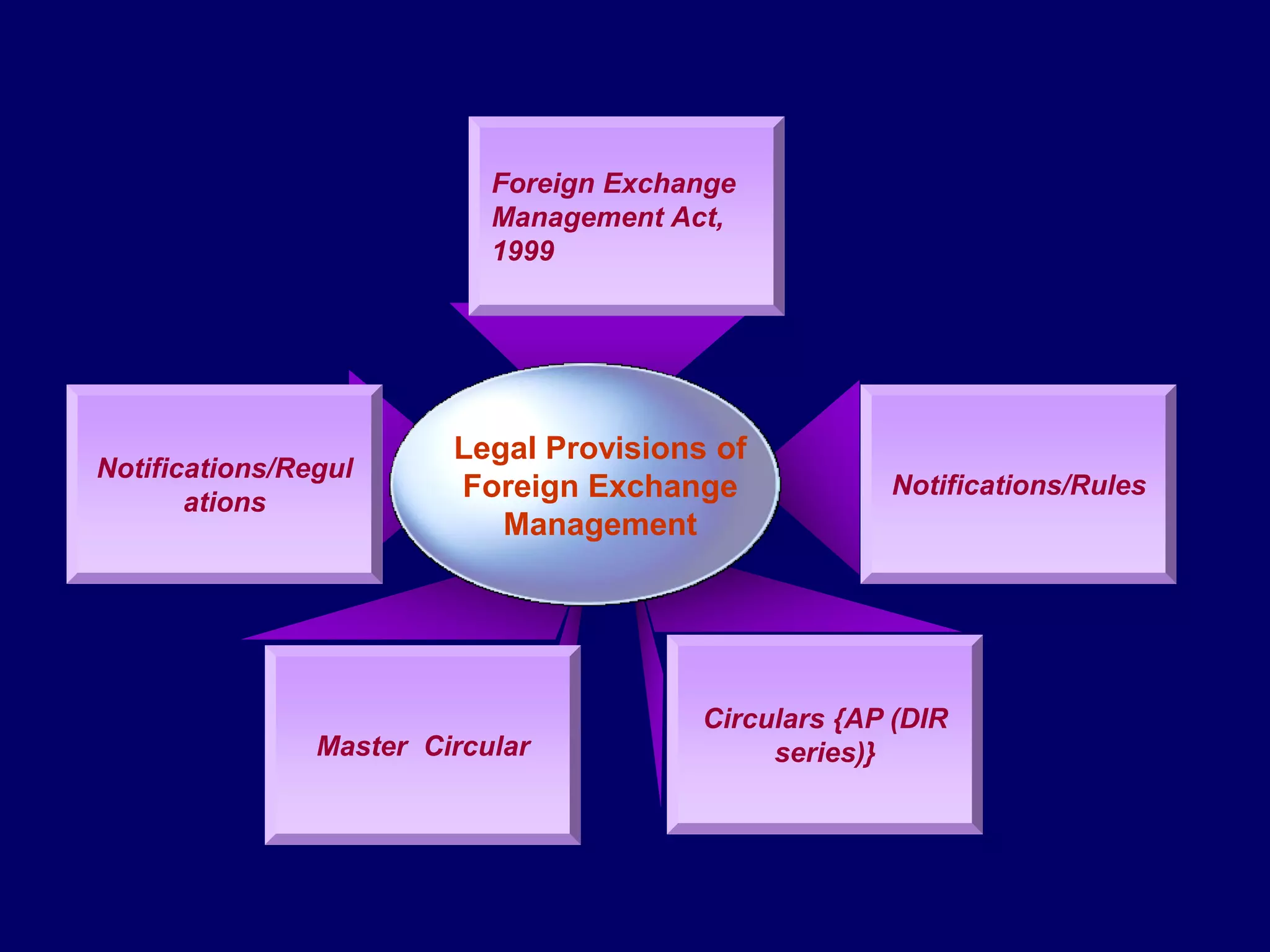
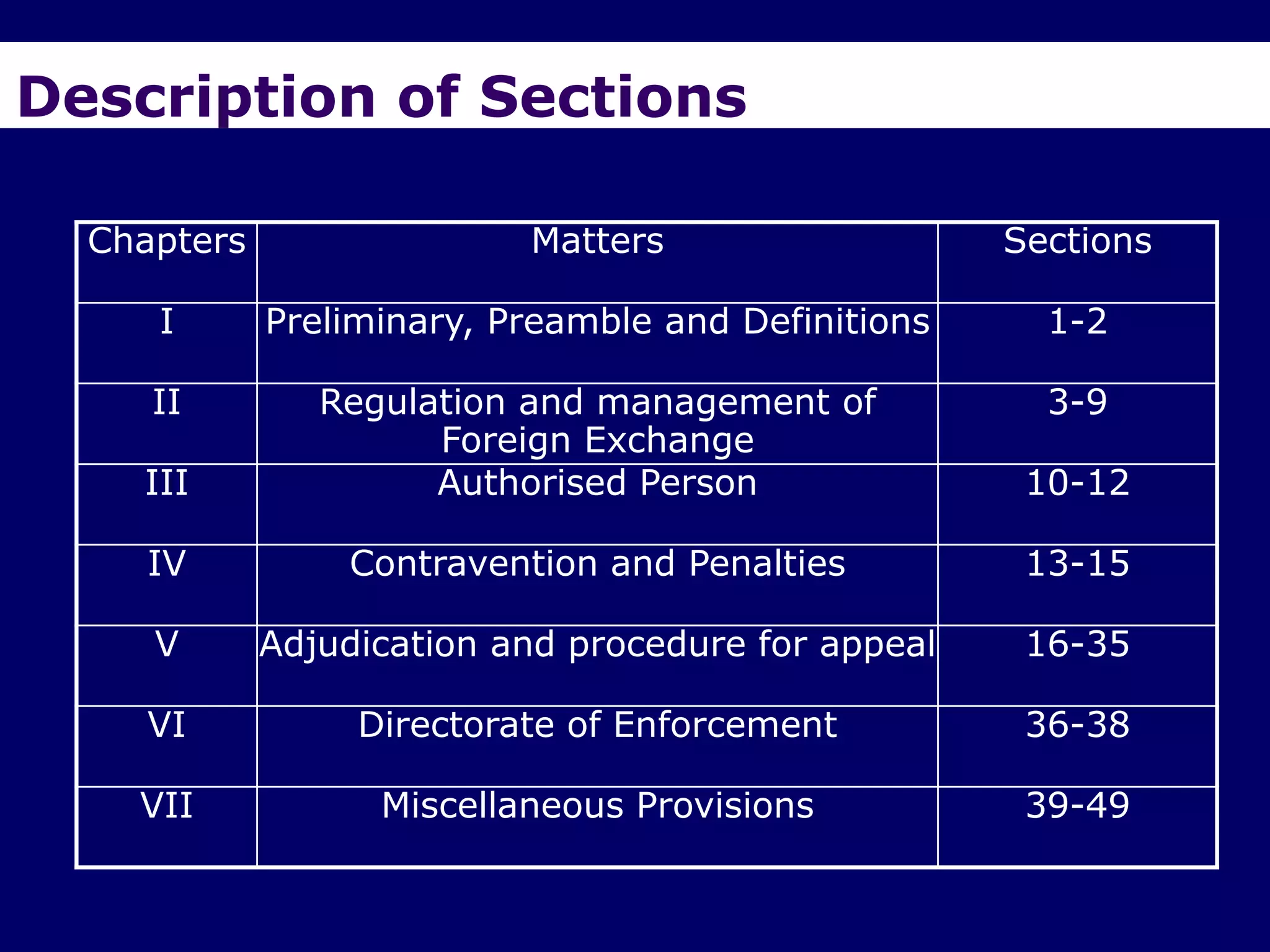
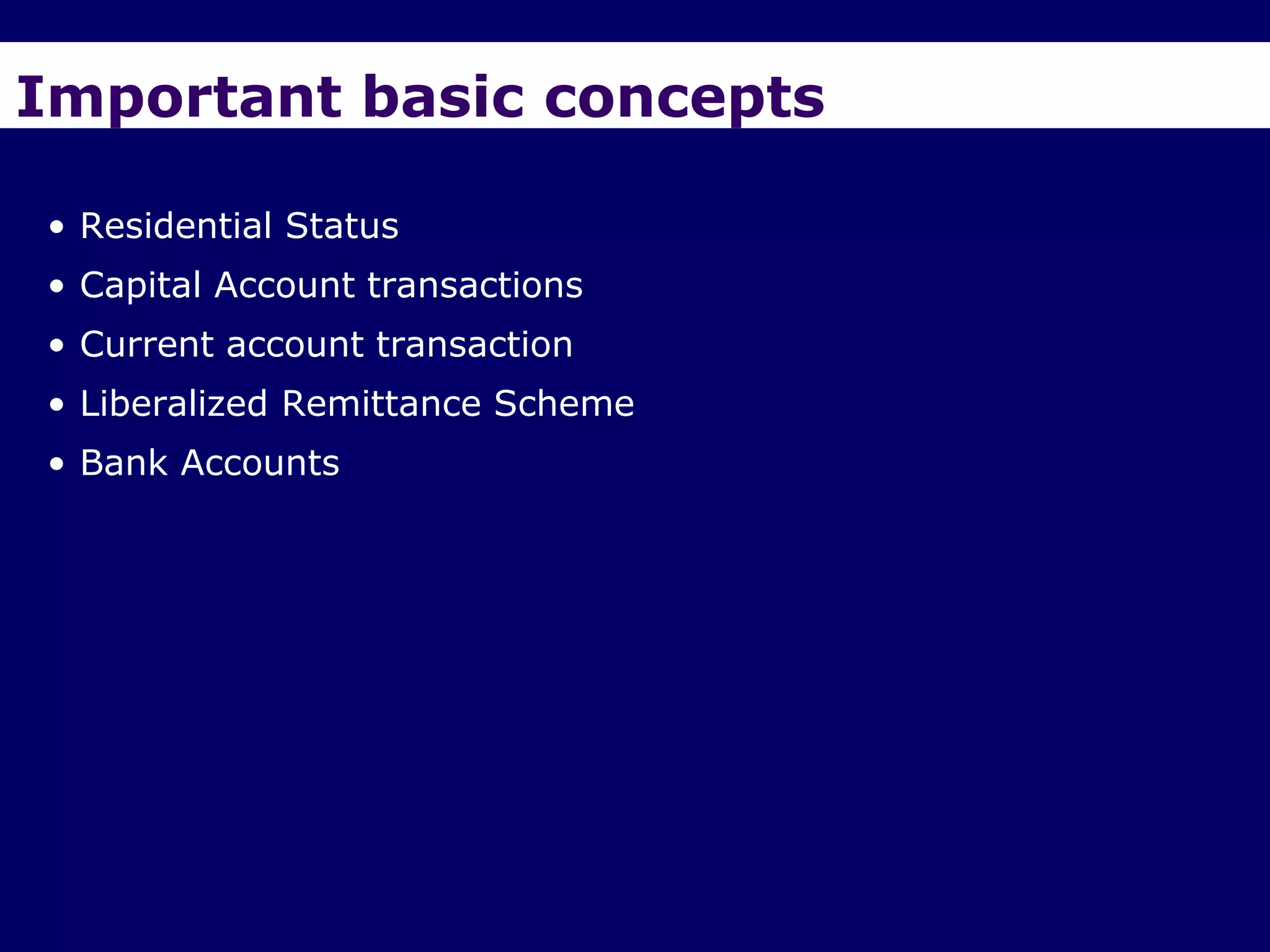
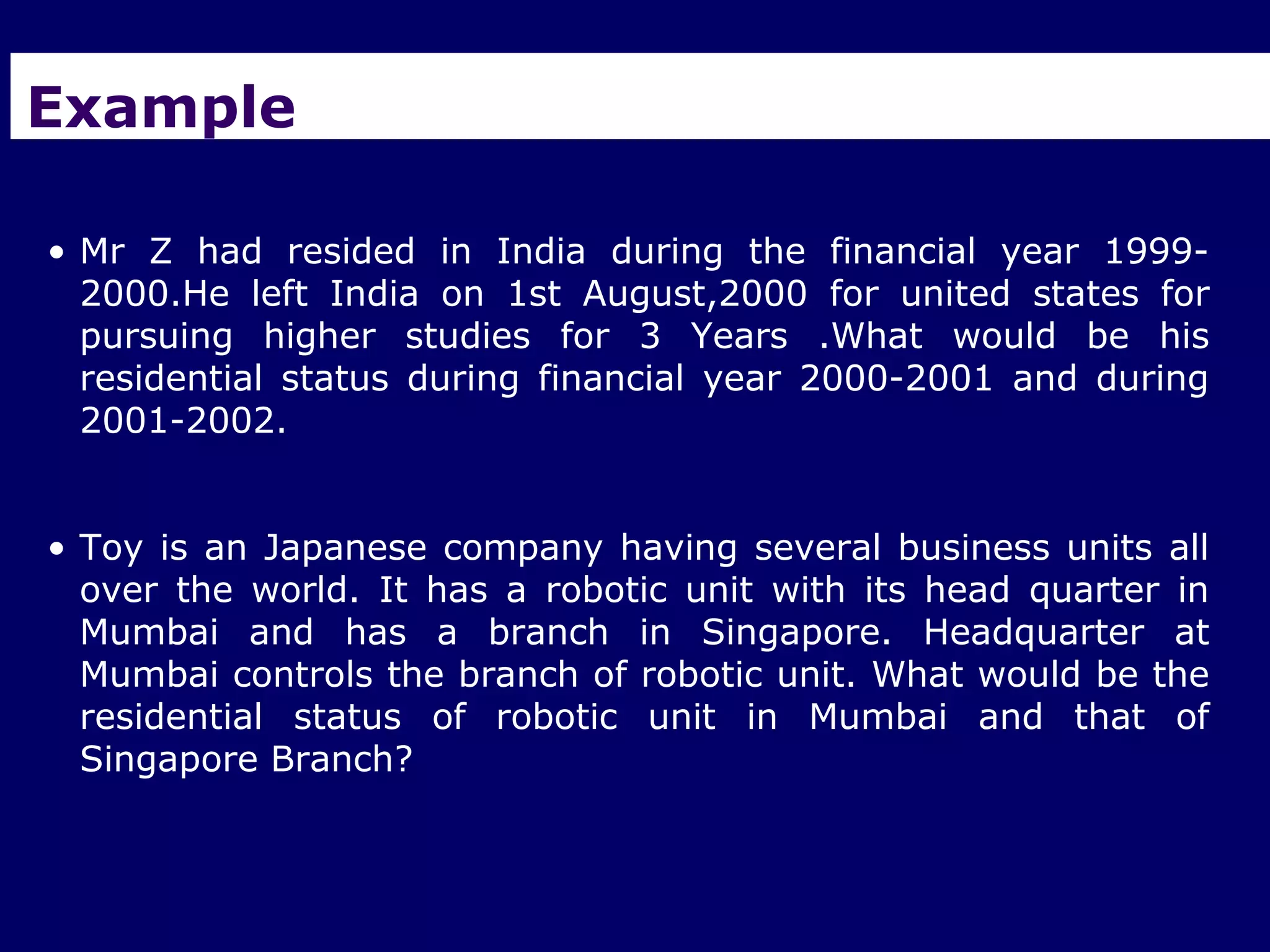
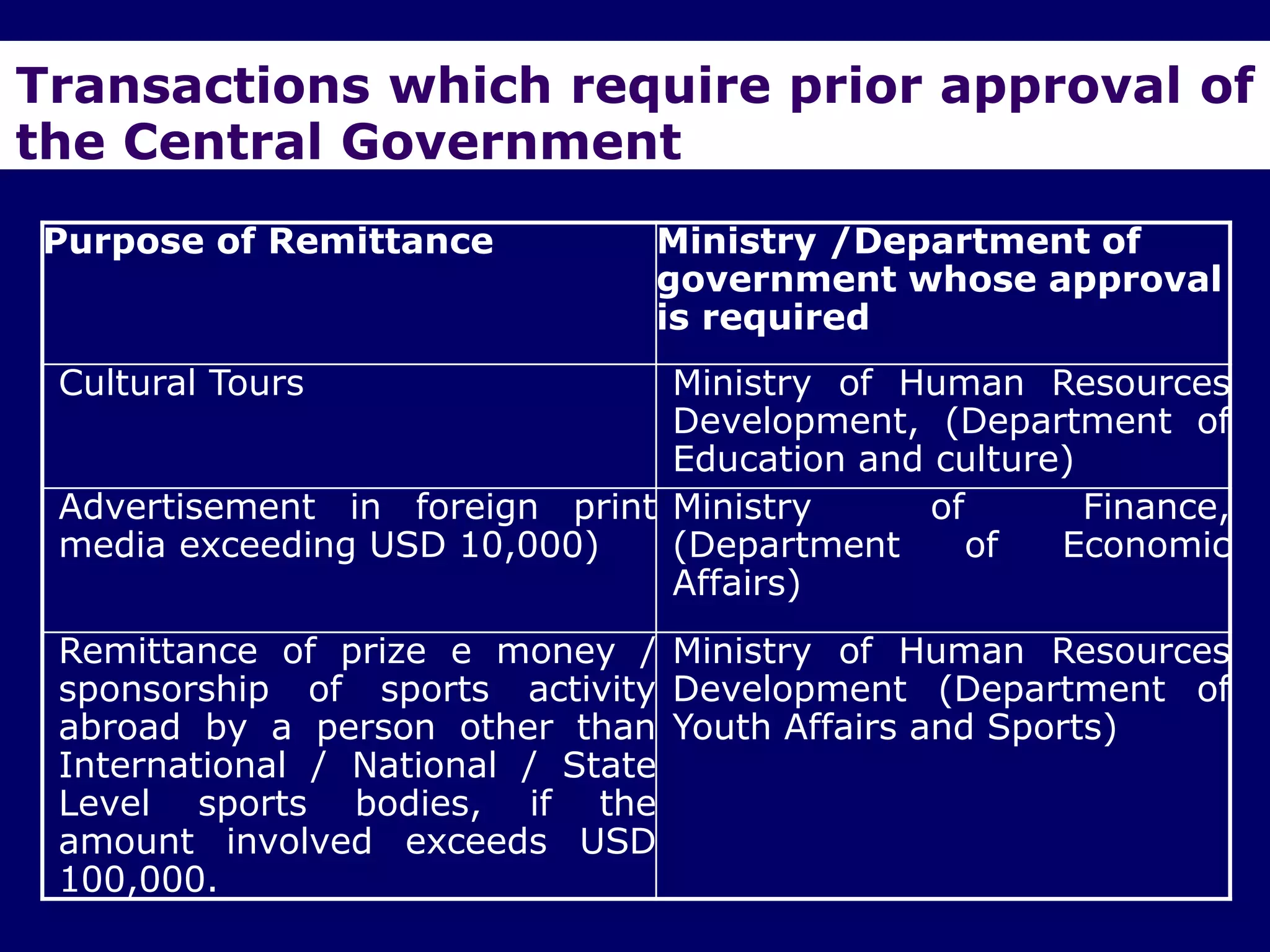
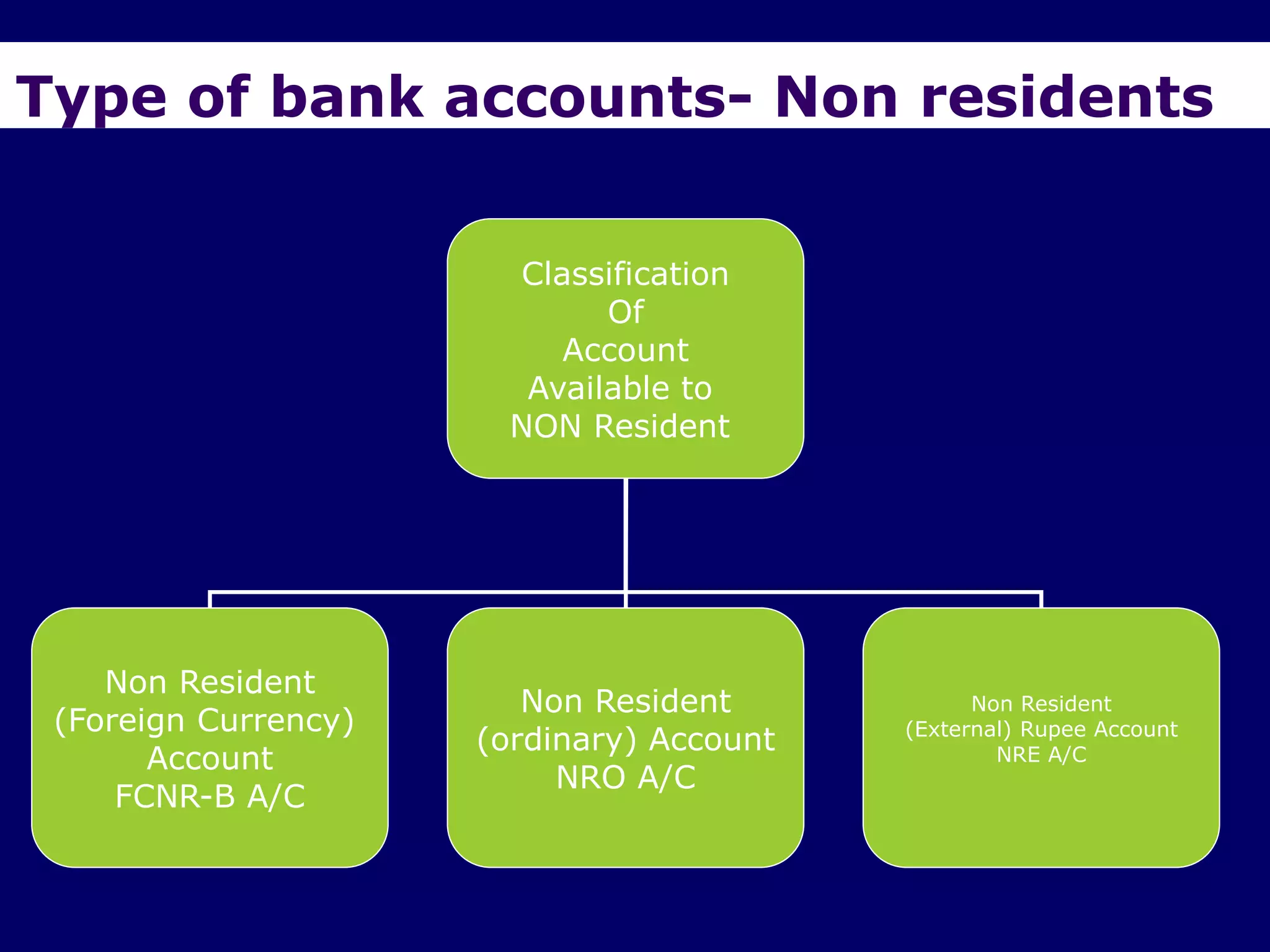
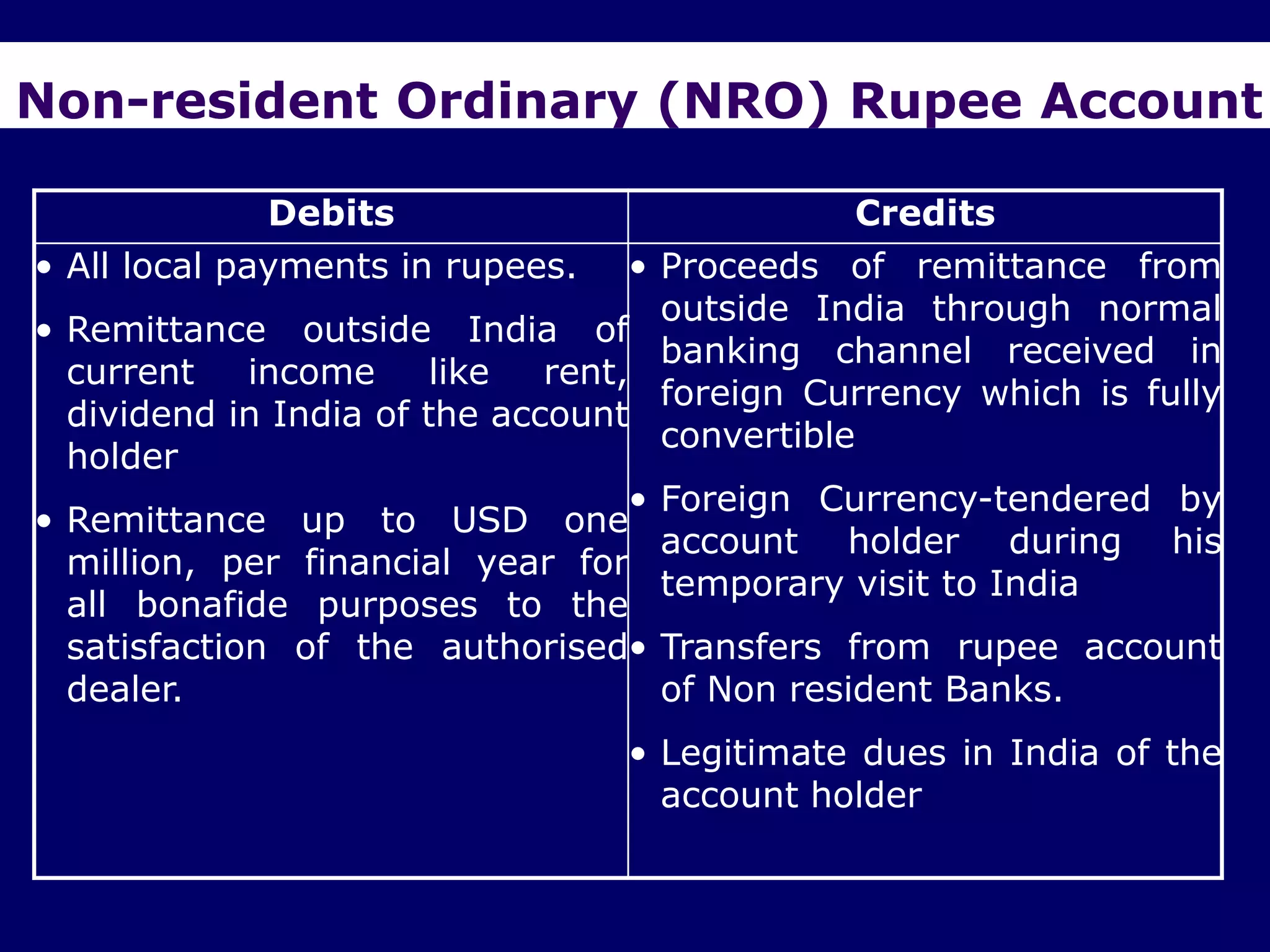
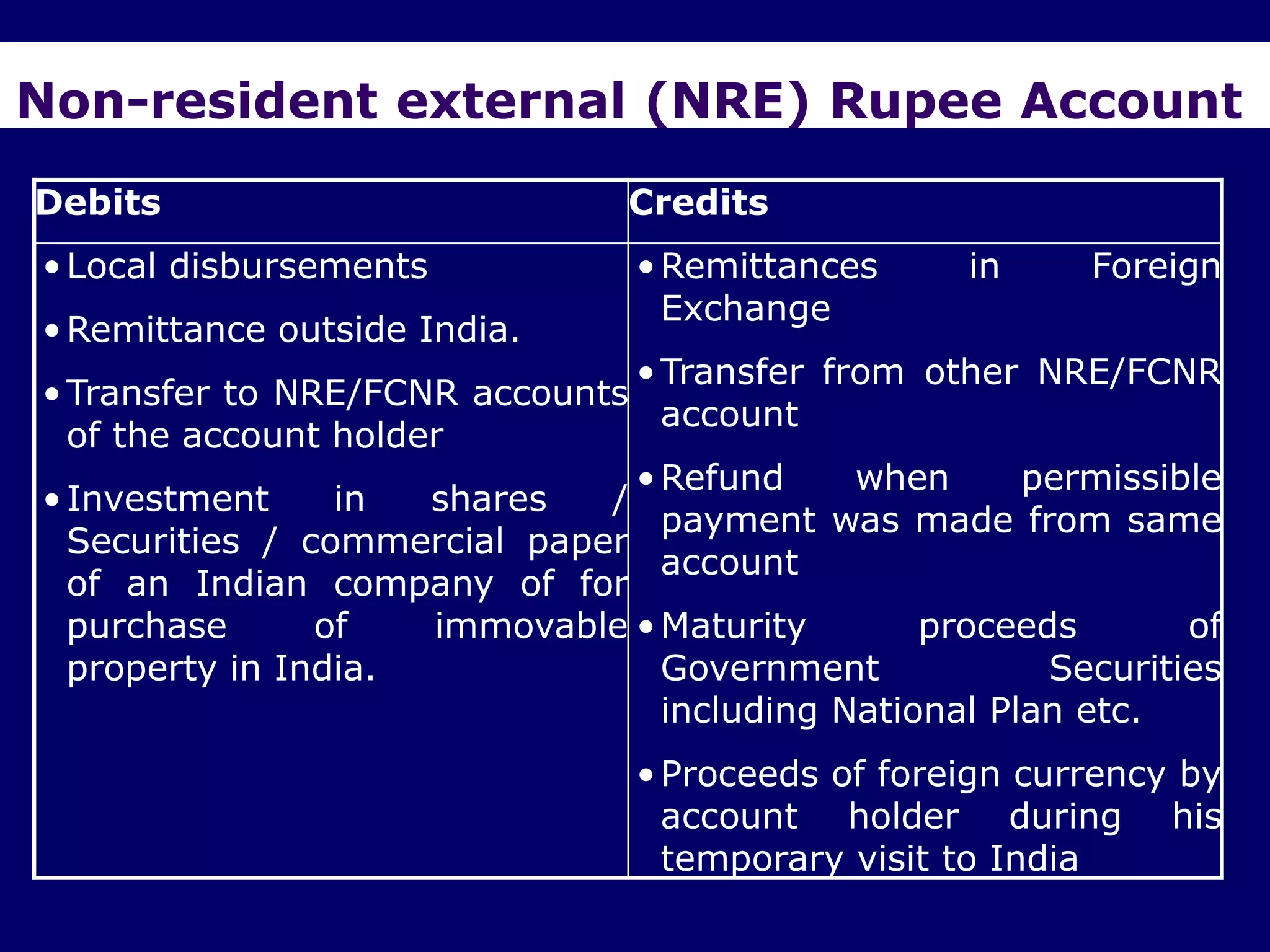
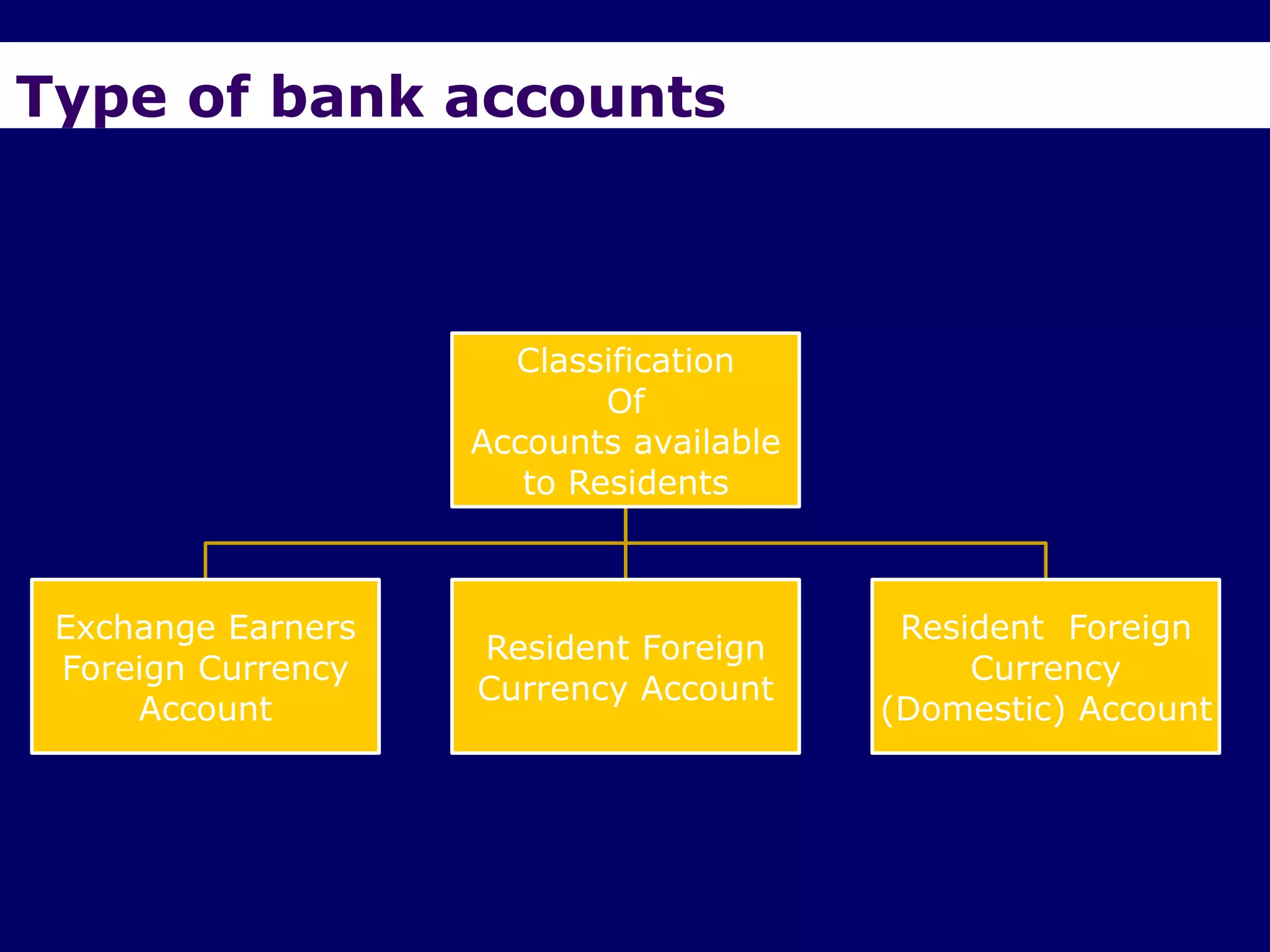
The document provides an overview of the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) 1999 in India. The key objectives of FEMA are to consolidate and amend laws related to foreign exchange to facilitate external trade and payments. It introduces important concepts like residential status, capital account transactions, current account transactions, and the liberalized remittance scheme. It describes the legal provisions and chapters/sections of FEMA. It also provides examples to illustrate residential status and the difference between capital and current account transactions.