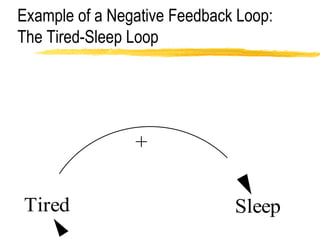
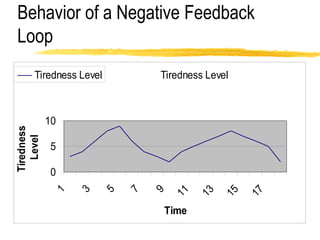
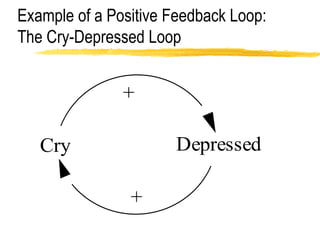
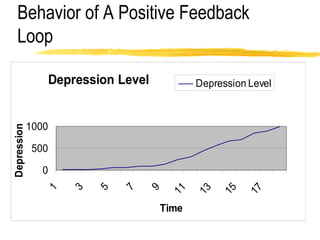
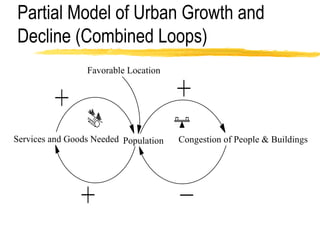
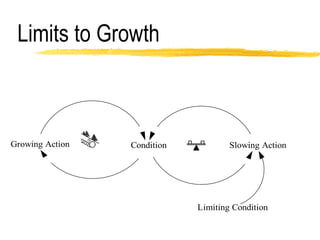
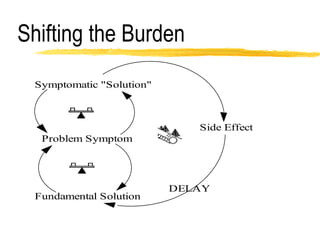
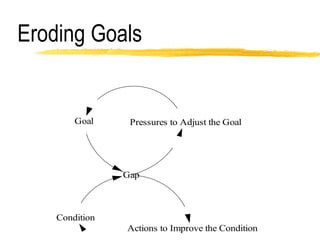
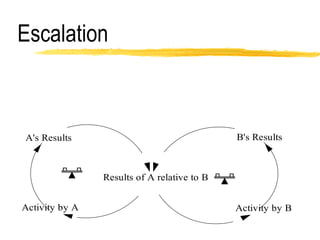
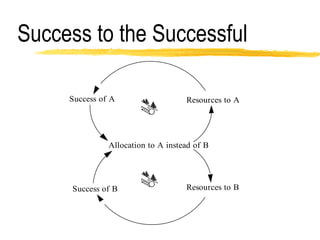
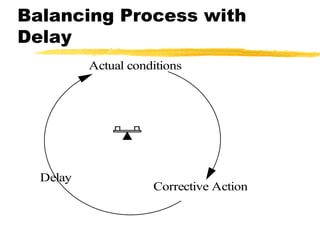
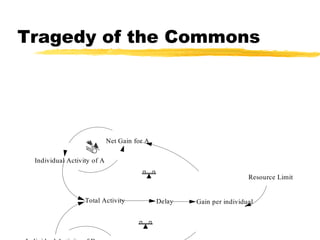
This document discusses key concepts in system dynamics modeling including feedback loops, causal loop diagrams, system archetypes, and an example production management problem. Positive feedback loops are reinforcing, while negative feedback loops aim to reduce discrepancies between a current state and a target or goal. Causal loop diagrams show causal links and influences between variables in a system. Common system archetypes include limits to growth, shifting the burden, eroding goals, escalation, success to the successful, and more. An example problem describes a company managing production and raw material inventory levels while facing unpredictable customer orders.