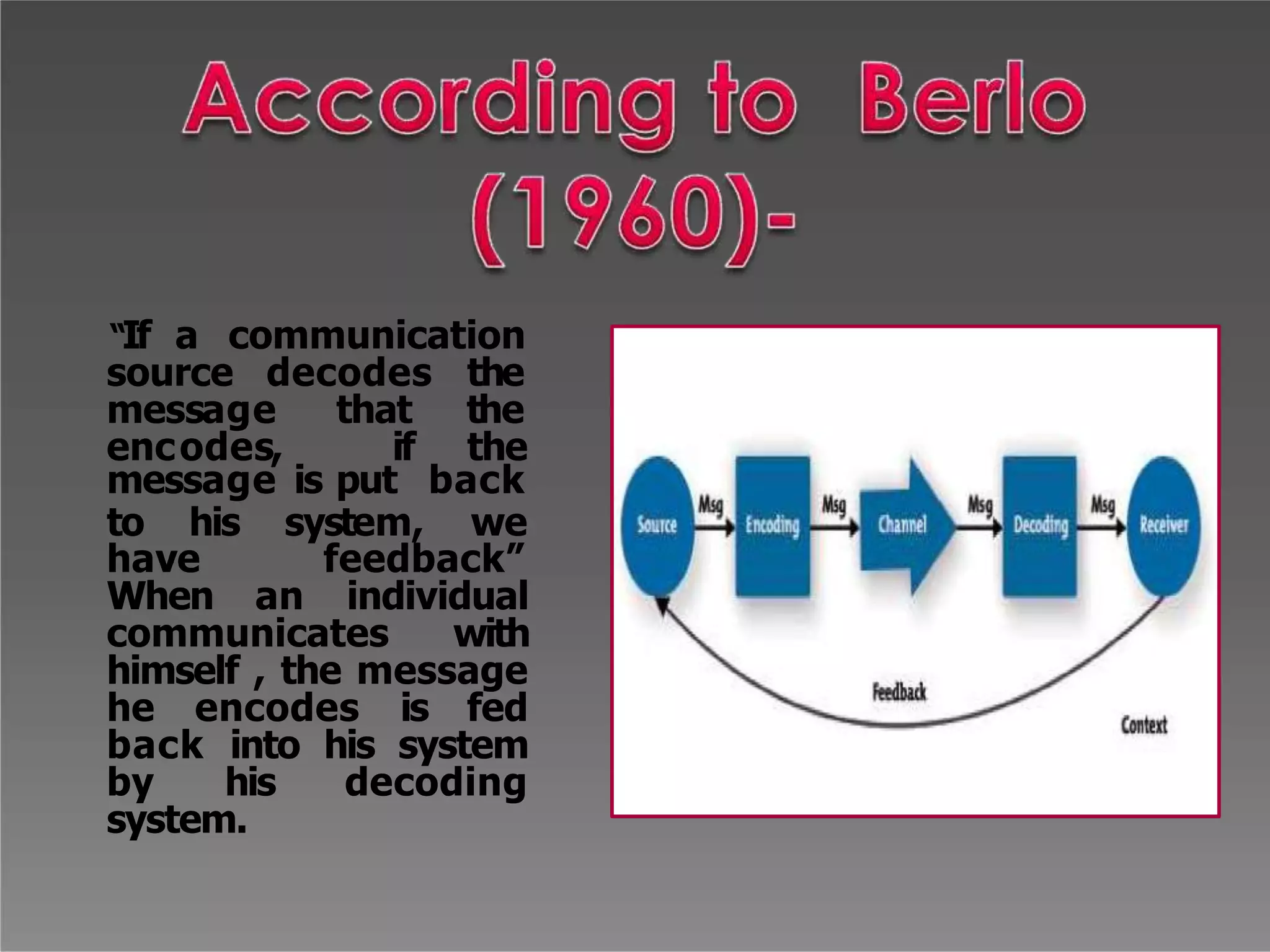
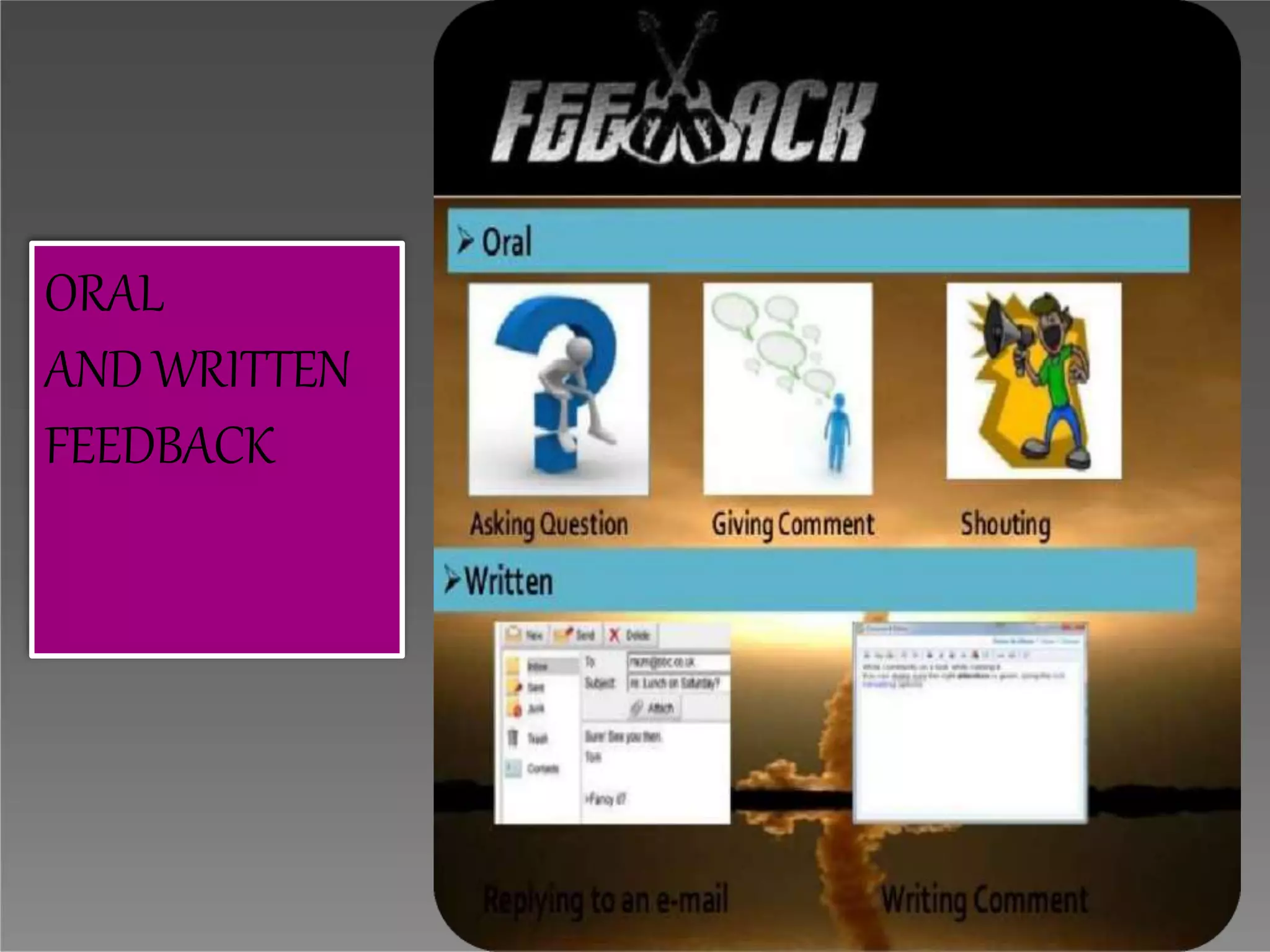
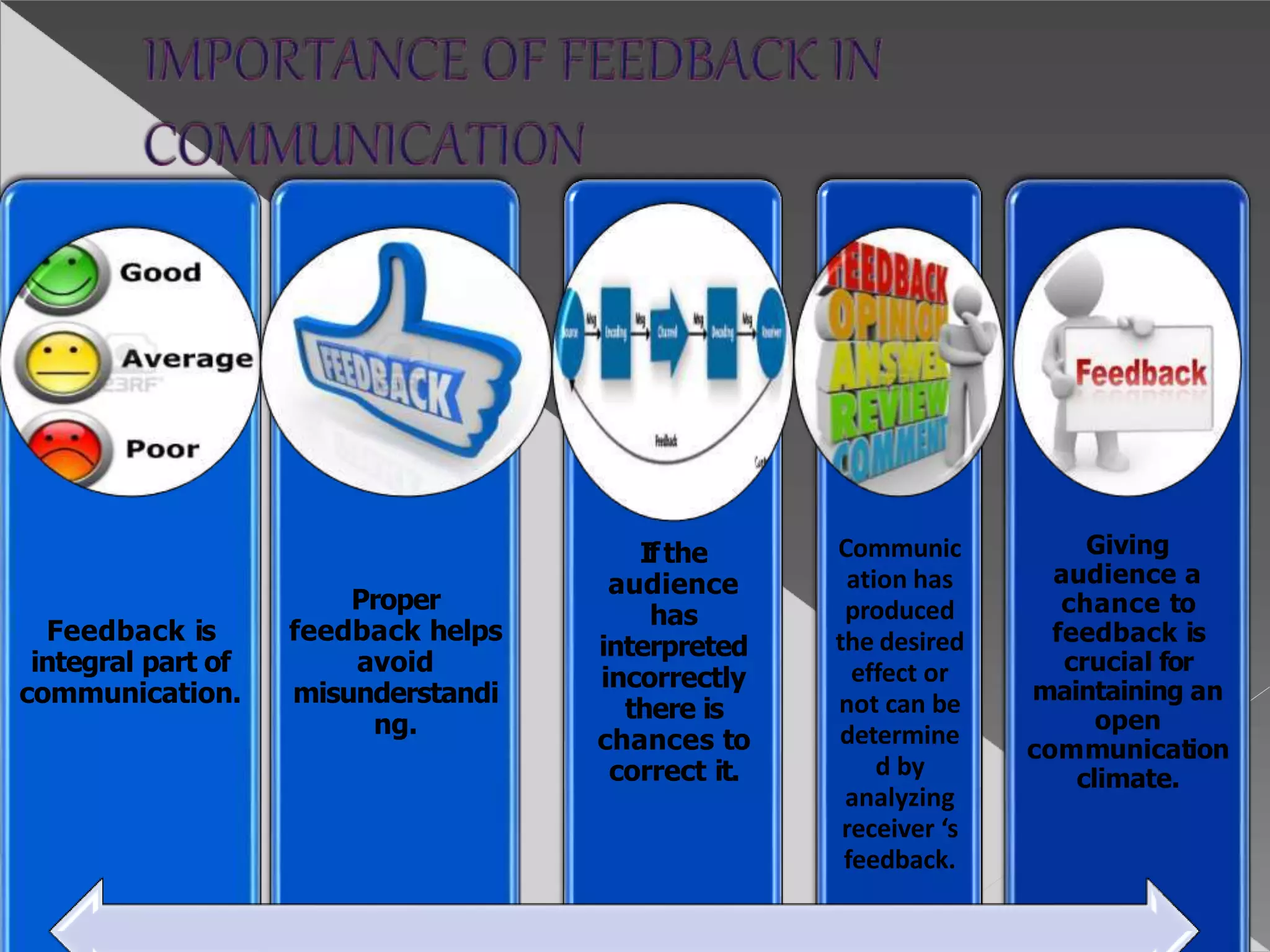
The document discusses the importance of feedback in communication. It defines feedback as the audience's response that allows the communicator to evaluate how well the message was received. Effective communication is only achieved when the intended message is understood. Feedback is crucial as it completes the communication cycle and helps determine if the desired effect was produced. It also enables corrections to misunderstandings and helps plan future communication. While feedback faces some barriers, understanding them can help improve clarification and receipt of proper feedback.