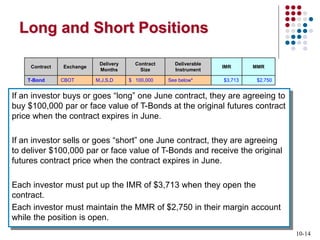
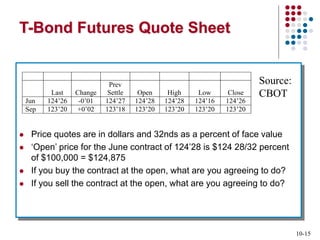
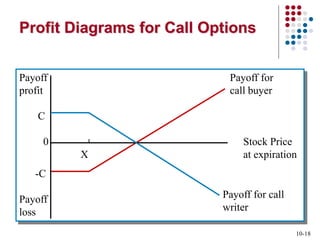
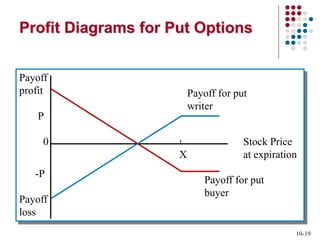
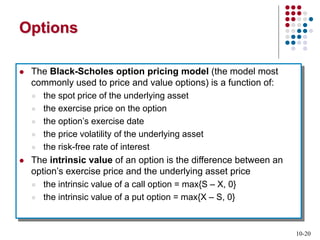
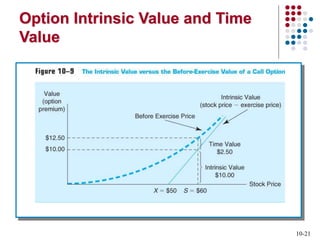
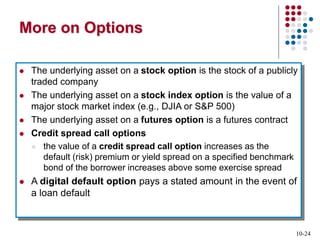
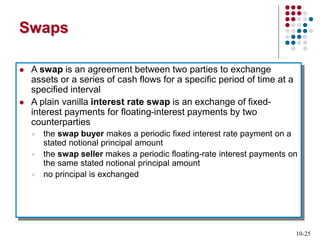
Derivatives are financial contracts whose value is based on an underlying asset or condition. The two main types are futures and options. Futures obligate the buyer and seller to exchange a standardized asset at a predetermined price and date. Options provide the right, but not obligation, to buy or sell the underlying asset at a strike price by expiration. Derivatives are used for speculation and hedging risk. Major derivatives exchanges include the Chicago Board of Trade and Chicago Board Options Exchange. The Commodity Futures Trading Commission regulates futures and some options while the Securities and Exchange Commission regulates stock options.