Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

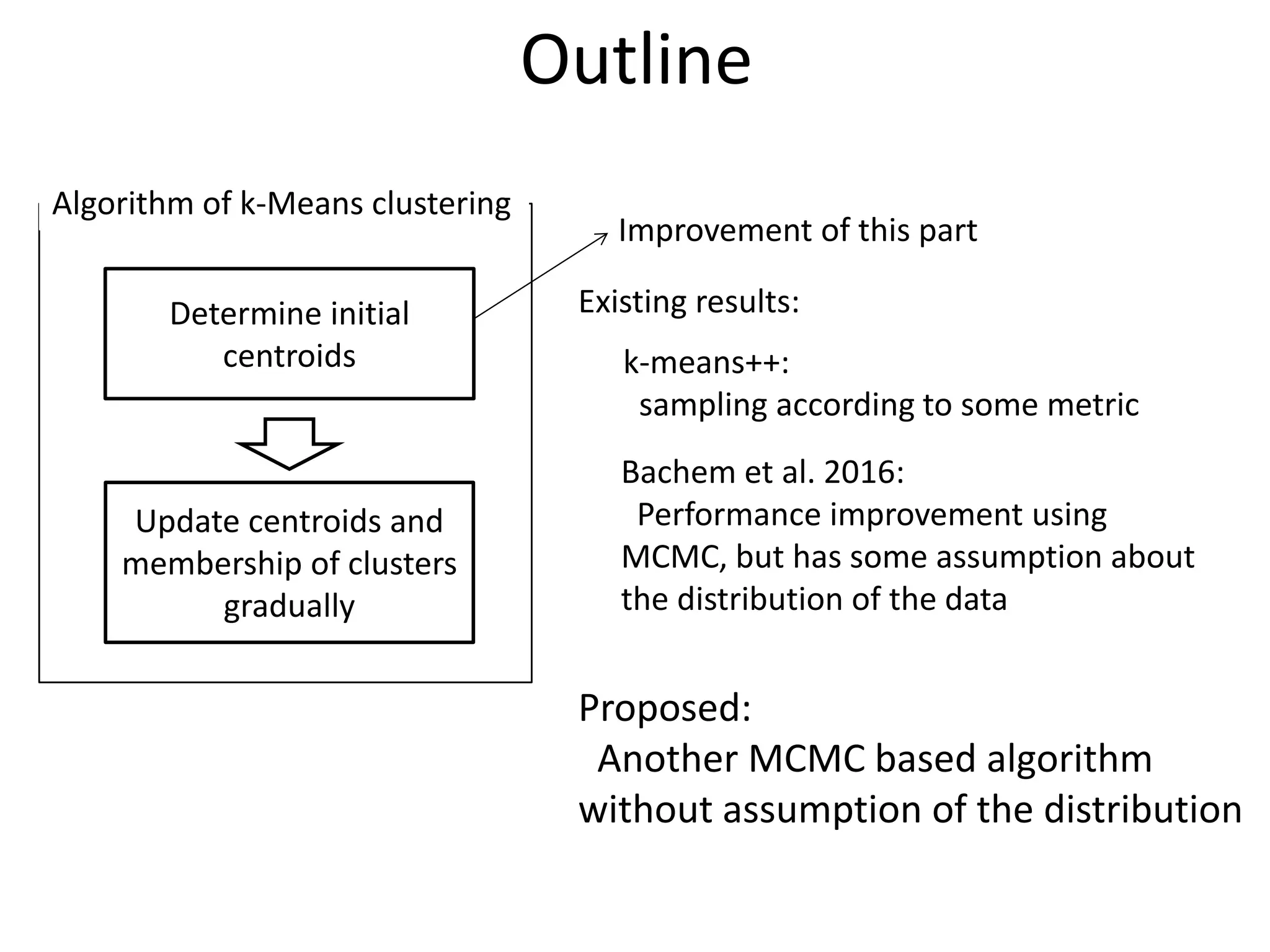
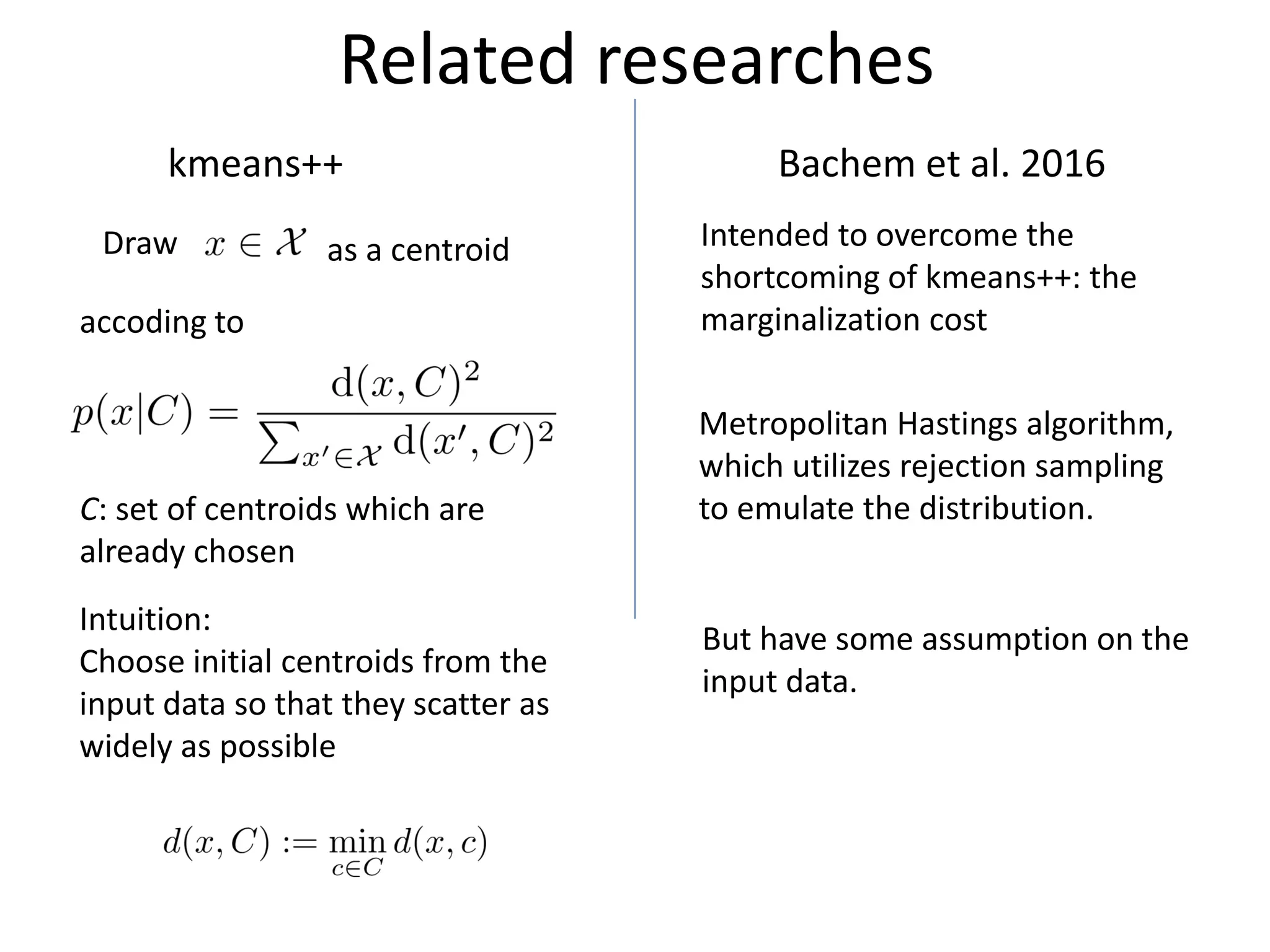
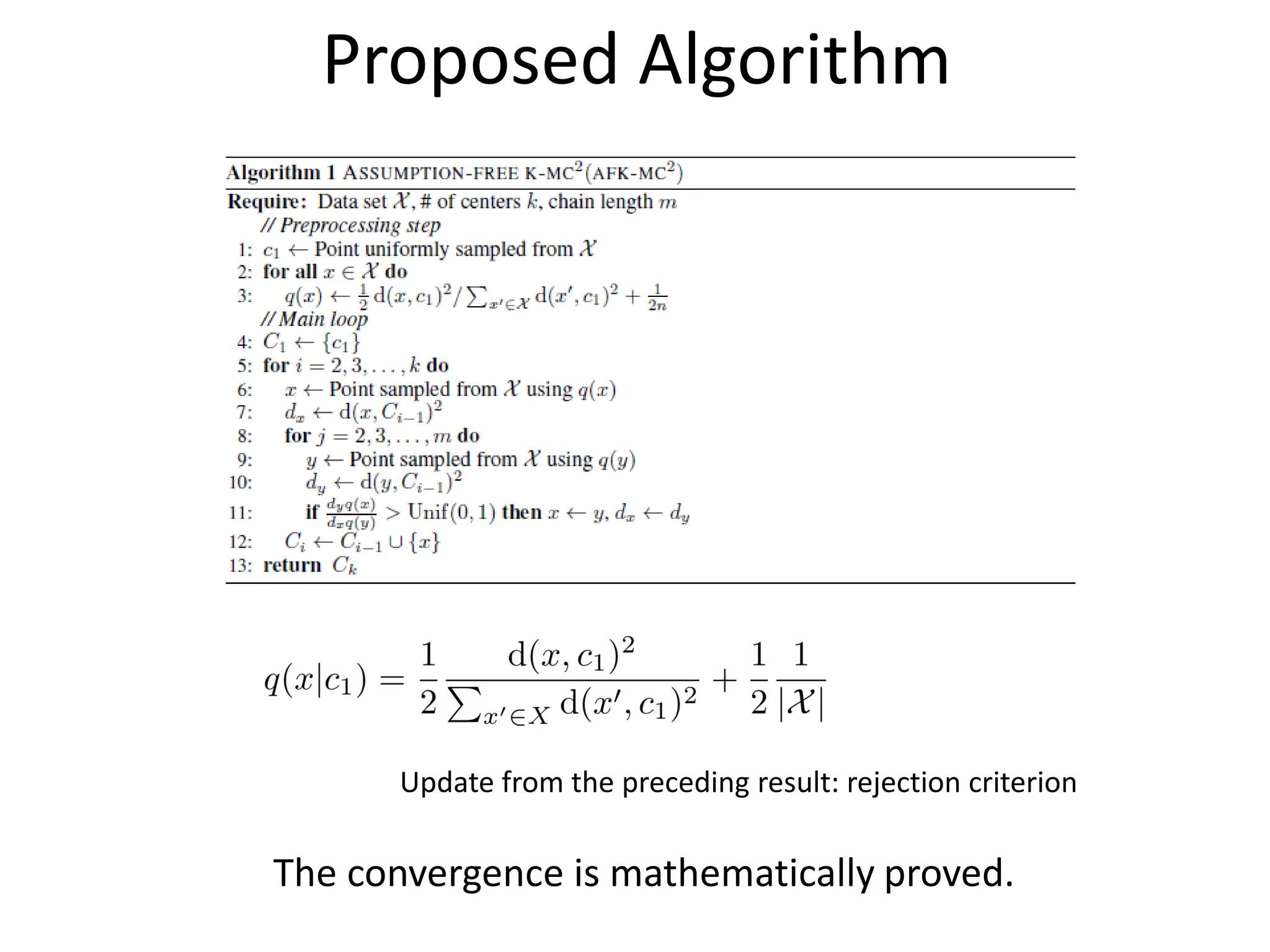
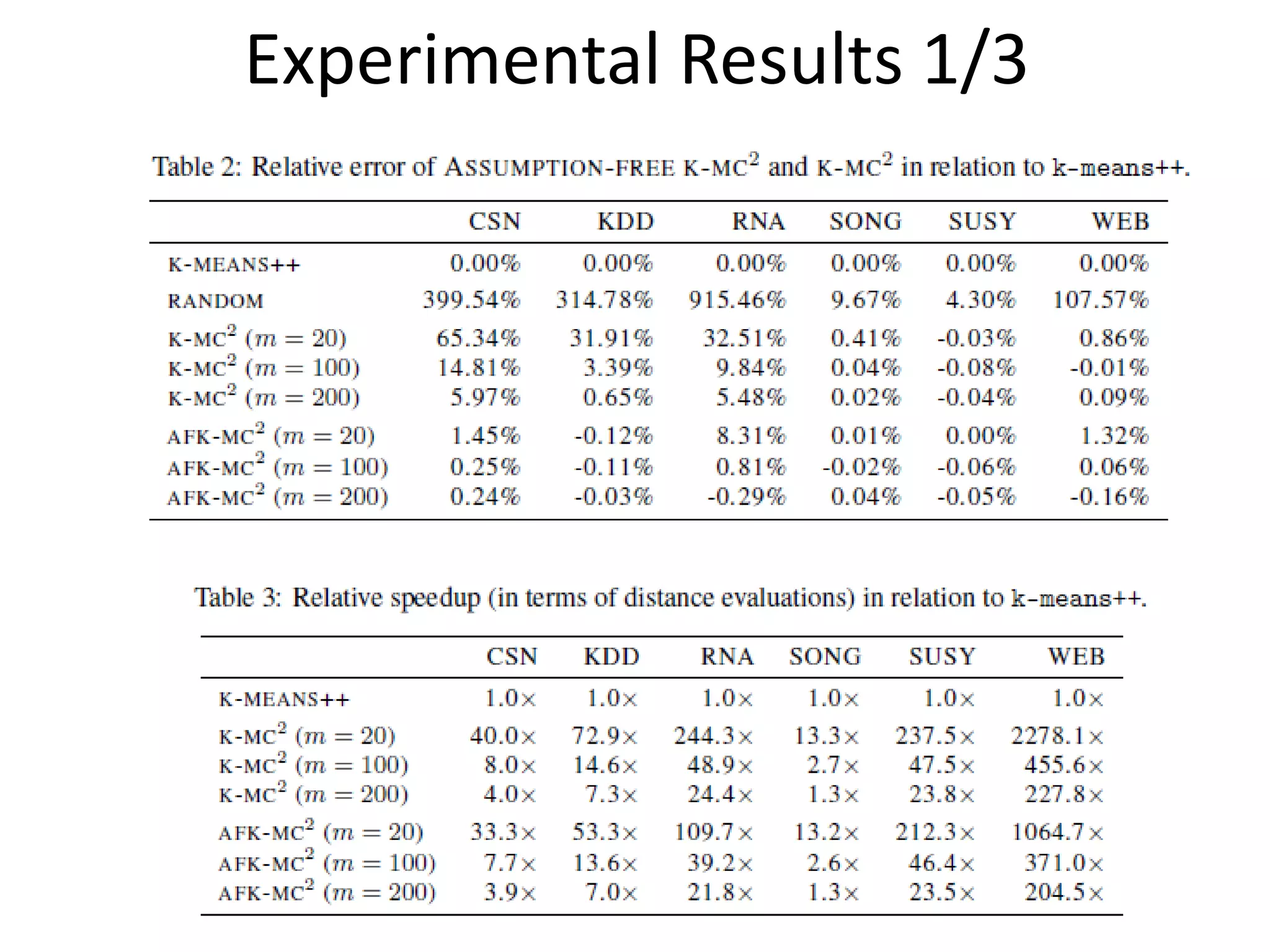
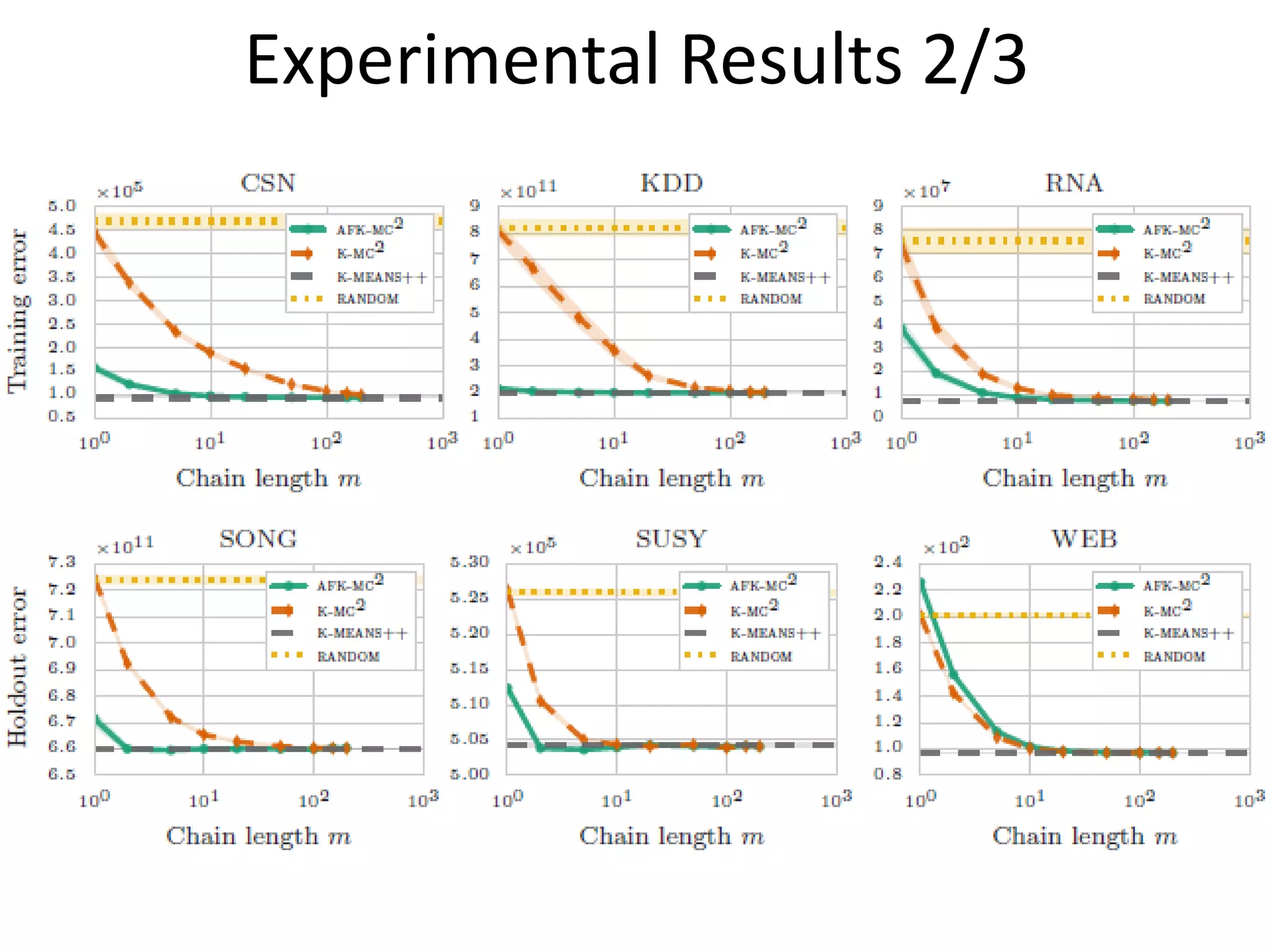
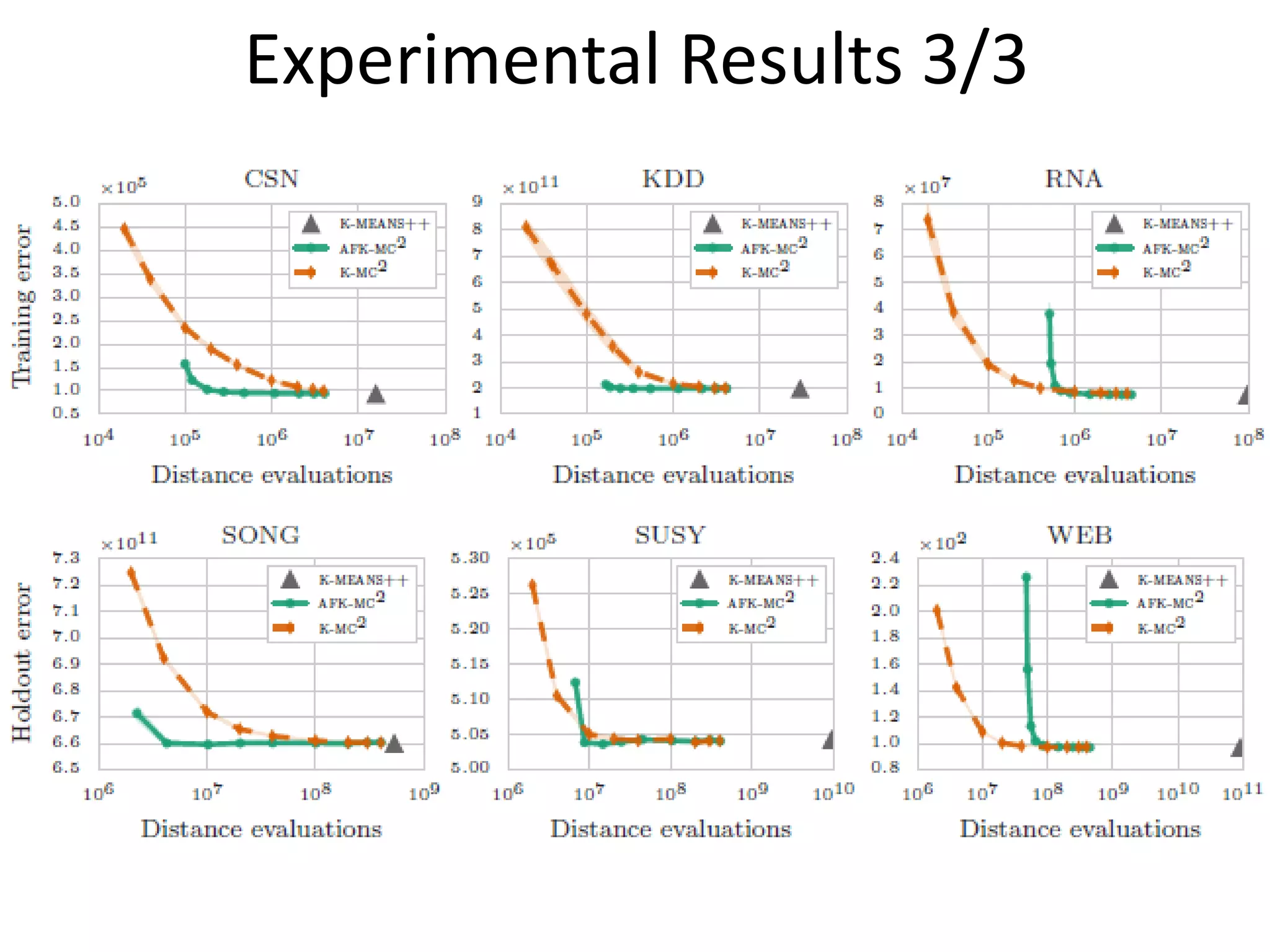


The document proposes a new MCMC-based algorithm for initializing centroids in k-means clustering that does not assume a specific distribution of the input data, unlike previous work. It uses rejection sampling to emulate the distribution and select initial centroids that are widely scattered. The algorithm is proven mathematically to converge. Experimental results on synthetic and real-world datasets show it performs well with a good trade-off of accuracy and speed compared to existing techniques.







