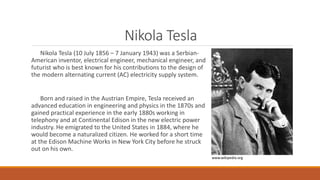
The document summarizes information on 10 famous scientists: Albert Einstein, Isaac Newton, Galileo Galilei, Stephen Hawking, Nikola Tesla, Charles Darwin, Archimedes, Marie Curie, Leonardo da Vinci, and their contributions to fields like physics, astronomy, mathematics, biology, and engineering. It provides brief biographies of 2-3 sentences for each scientist extracted from their Wikipedia pages.