This document discusses India's family planning program, including its history, objectives, methods, and implementation. The key points are:
- India launched its national family planning program in 1952 to control population growth and promote reproductive health. Over time the program's goals have expanded.
- The objectives are to meet population stabilization goals, reduce maternal and child mortality, and address unmet needs for contraception and healthcare.
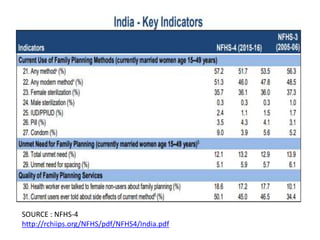
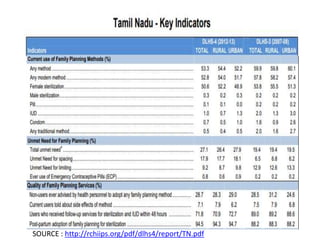
- The document outlines various national policies from 2000 and 2017 that set targets for fertility rates and increasing access to family planning services.
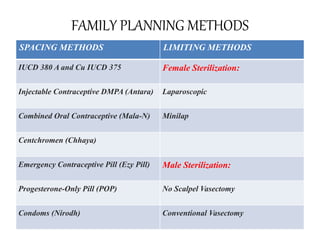
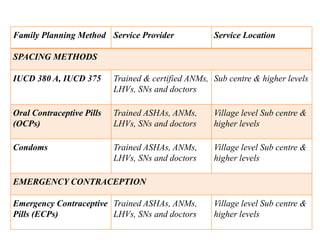
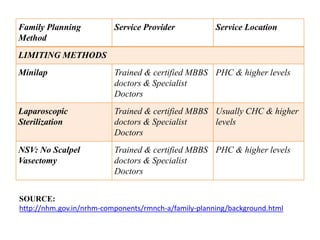
- It describes common family planning methods in India including IUDs, oral contraceptives, sterilization procedures, and condoms, and who provides these services.