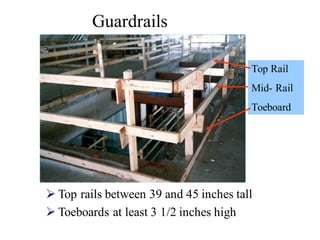
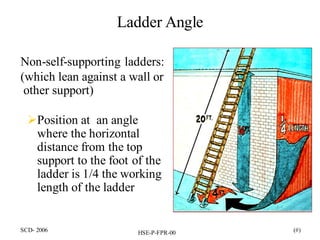
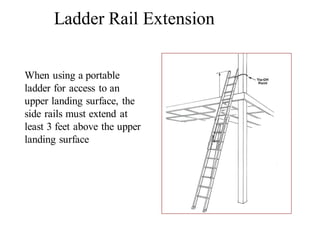
This document discusses fall protection on construction sites. It notes that falls are the leading cause of death in construction and most fatal falls occur from open-sided floors or through floor openings. It provides guidance on fall protection options like guardrails, safety nets, and personal fall arrest systems. Fall protection is required for any work from heights over 6 feet, including on walkways, ramps, open sides/edges, holes, roofs, excavations, wall openings, and residential construction. Ladders must be properly secured, inspected for defects, and climbed safely to prevent falls.