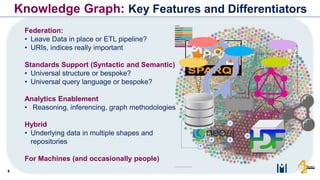
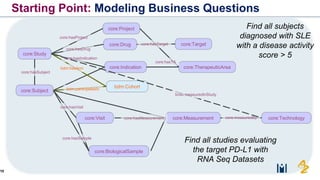
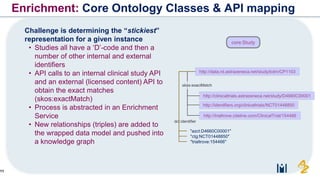
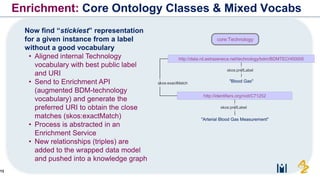
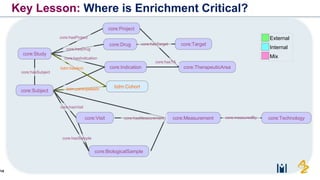
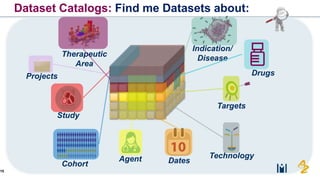
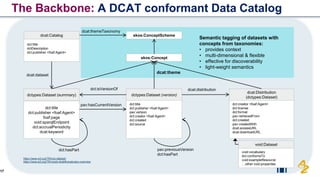
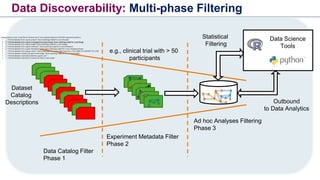
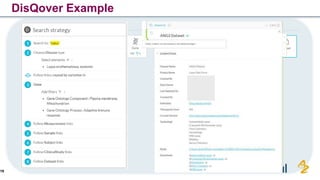
The document discusses the need for FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) data principles in R&D to enhance the understanding of disease mechanisms and improve drug discovery processes. It outlines the challenges faced by researchers, such as fragmented data silos and bottlenecks in bioinformatics, and proposes the use of knowledge graphs to integrate and enrich biomedical data. A dataset catalog is emphasized as a crucial tool for ensuring data discoverability and supporting enterprise strategies.