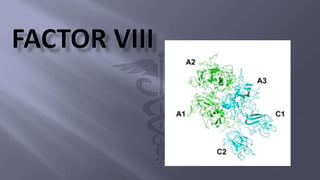
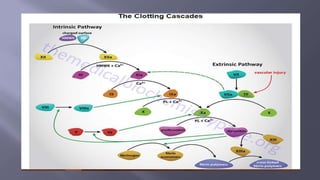
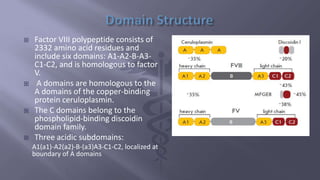
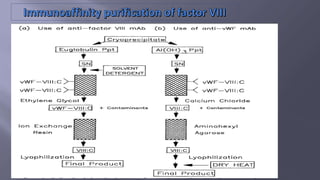
This document summarizes information about factor VIII, which is involved in the intrinsic pathway of coagulation. It discusses that factor VIII is produced in liver sinusoidal cells and endothelial cells lining blood vessels. It consists of six domains and undergoes proteolytic processing. The document also describes the production and purification process of recombinant factor VIII from human embryonic kidney cells for use in treatments like Nuwiq, which has advantages over plasma-derived factor VIII.