This document summarizes key aspects of labor and delivery, including:
1. The definition and classification of labor, including premature, term, and post-term labor.
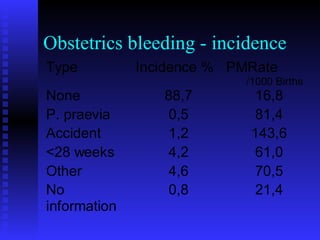
2. The stages of labor, including dilation of the cervix, expulsion of the fetus and placenta, and potential complications like postpartum hemorrhage.
3. Fetal monitoring methods during labor and delivery like cardiotocography and ultrasound to evaluate fetal well-being and presentation.
4. Factors that influence labor like fetal position, maternal exertion, and medical interventions like induction or Cesarean section if complications arise.