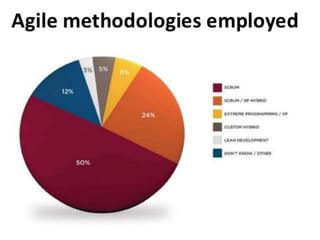
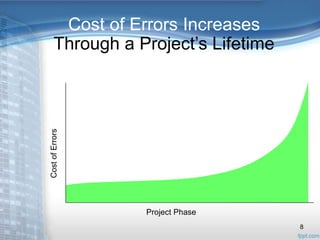
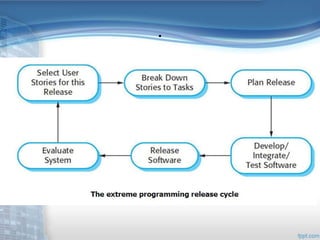
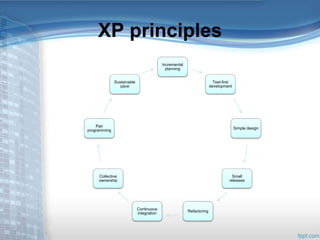
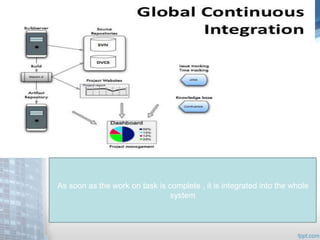
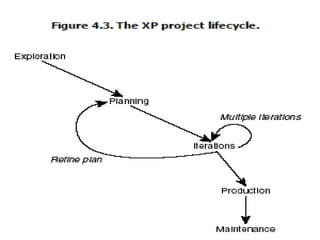
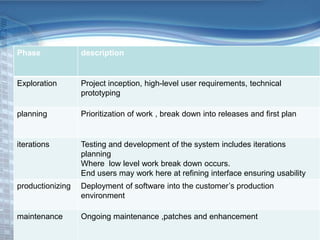
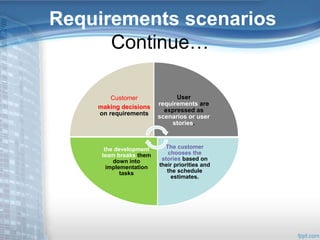
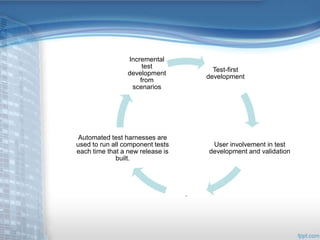
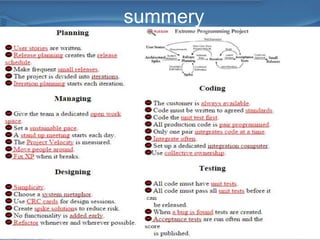
This document provides an overview of Extreme Programming (XP), an agile software development methodology. It discusses XP's history and features, which include short 2-week development cycles, pair programming, test-driven development, and frequent refactoring. The core principles of XP are also examined, such as incremental planning, small releases, simple design, and sustainable pace. Various phases of the XP process are outlined, from exploration to productionizing. Requirements are captured as scenarios and prioritized by the customer. Automated testing is a key practice in XP. Both advantages like collective code ownership and disadvantages like its unsuitability for large projects are noted.