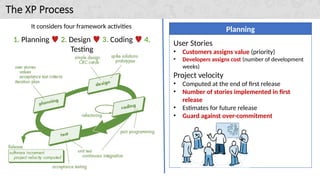
Extreme Programming (XP) is a popular agile software development approach that emphasizes communication, simplicity, feedback, courage, and respect among team members. The XP process consists of four main activities: planning, design, coding, and testing, with techniques like user story prioritization, unit testing, and pair programming to ensure quality and adaptability. An industrial variant, known as Industrial XP (IXP), is aimed at large organizations while still incorporating object-oriented development practices.