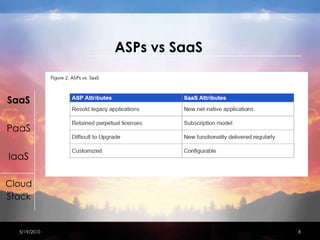
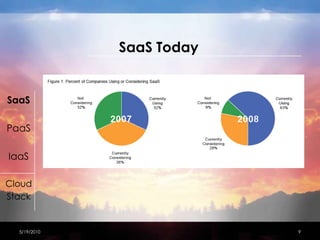
This document discusses network security considerations for cloud computing. It begins with an introduction to different cloud deployment models including Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). It then covers each model in more detail, describing features and benefits. The document also discusses virtualization techniques, risks of cloud computing including loss of control and operational risks, and security best practices such as host hardening and securing inter-host communication. Standard organizations developing cloud computing security standards are also mentioned.