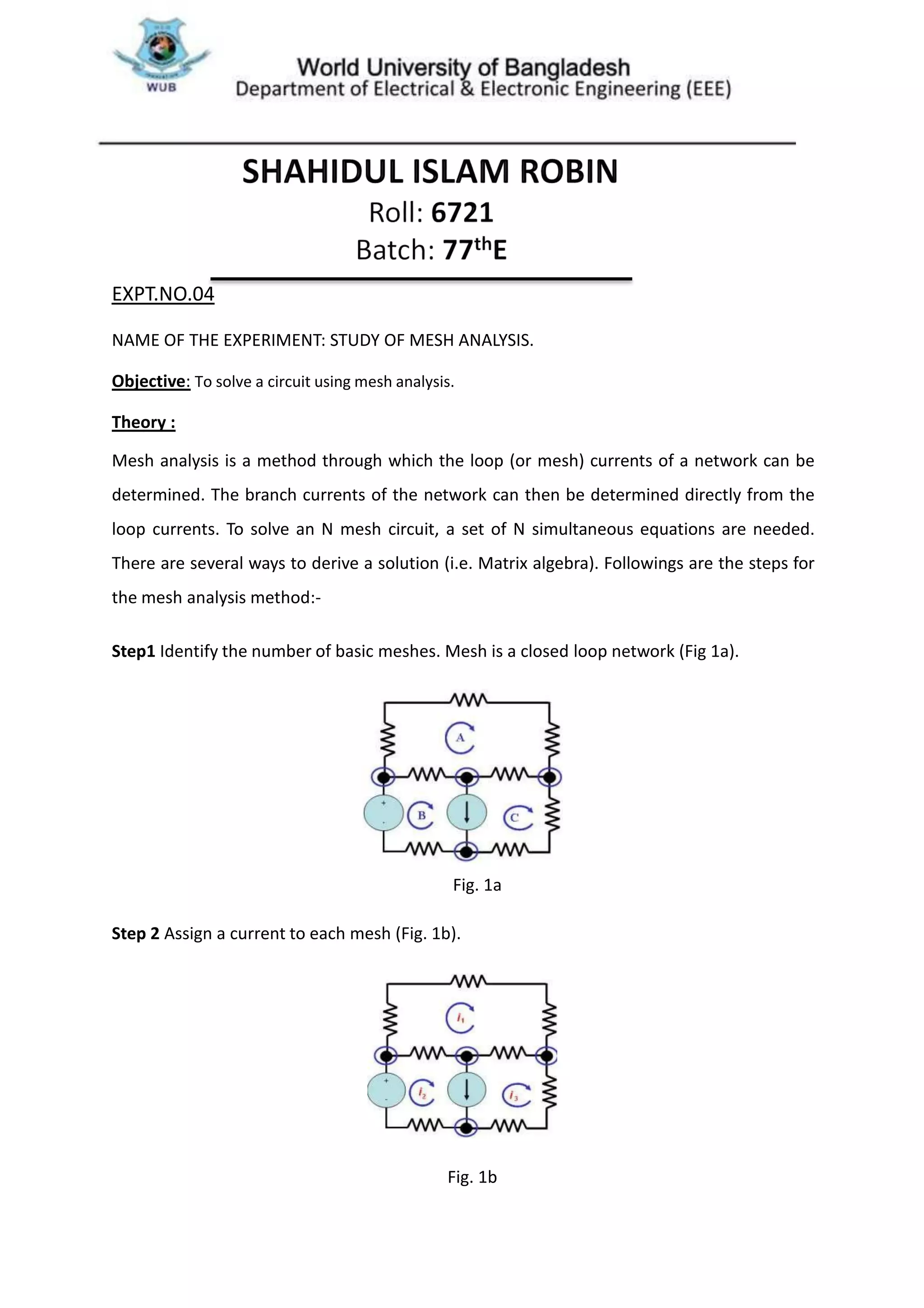
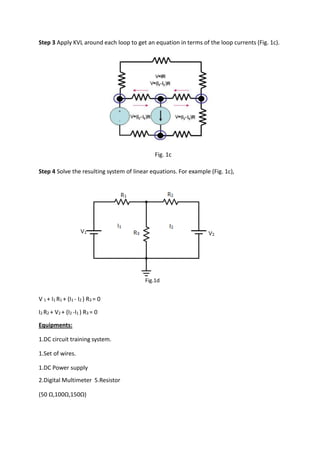
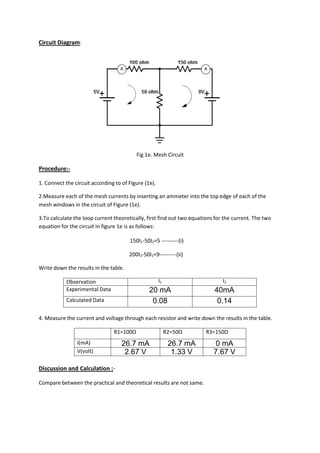
This document describes an experiment to solve an electrical circuit using mesh analysis. The key steps of mesh analysis are: 1) identify the number of meshes in the circuit, 2) assign a current to each mesh, and 3) apply Kirchhoff's voltage law around each loop to generate equations that can be solved for the mesh currents. The experiment uses a DC circuit board to build a 2-mesh circuit and measures the mesh currents experimentally and theoretically to compare the results.