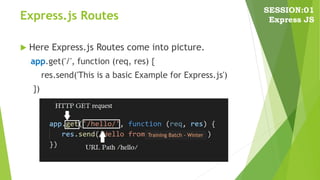
The document discusses Express.js, a web framework for Node.js. It provides an overview of Express.js and how it can be used to start an application server listening on a port, handle HTTP requests asynchronously with methods like GET and POST. It also includes code samples of setting up a basic Express server with a "Hello World" route, installing Express, and using routes to define how the app responds to different URIs and HTTP methods.