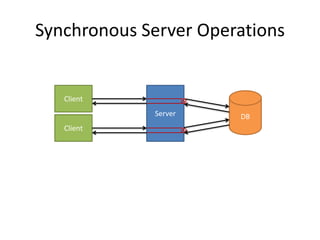
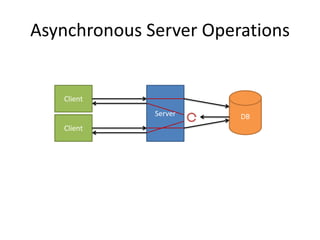
This document provides an overview of Node.js and Express. It discusses that Node.js is a JavaScript runtime for building asynchronous and event-driven servers. It allows JavaScript to run outside browsers for IO operations. The document also covers key aspects of the Node.js ecosystem like NPM, Connect middleware, and the popular web framework Express. It includes demos of building asynchronous servers, routing, templates, and integrating data models in Express apps.