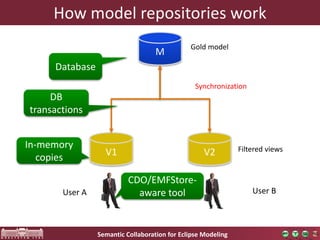
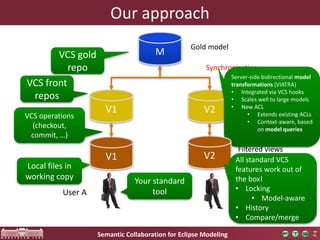
This document discusses a new framework for semantic collaboration on Eclipse modeling projects. It aims to provide fine-grained access control for modeling assets while retaining compatibility with traditional version control systems. The framework uses model queries and transformations to filter models on the server-side according to access rules. This allows for rule-based, context-aware access policies without modifying modeling tools or infrastructure. A demonstration of the framework showed how standard version control features like locking, history and merging still work while providing improved security and flexibility over file-based access control. The framework was presented at MODELS 2016 and the authors are looking for contributors to help bring it to Eclipse.