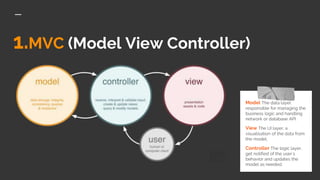
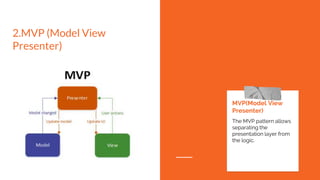
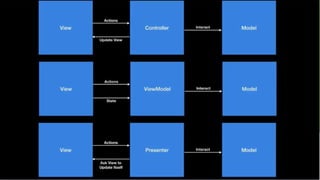
This document discusses design patterns used in Android development. It defines design patterns as reusable object-oriented code between projects. The most common patterns used in Android are MVC, MVP, and MVVM. MVC separates an app into a model, view, and controller. MVP is similar but the presenter updates the passive view. MVVM uses a view model to send data streams between the model and view. Design patterns help make code more maintainable, manage complexity, and improve readability and testability.