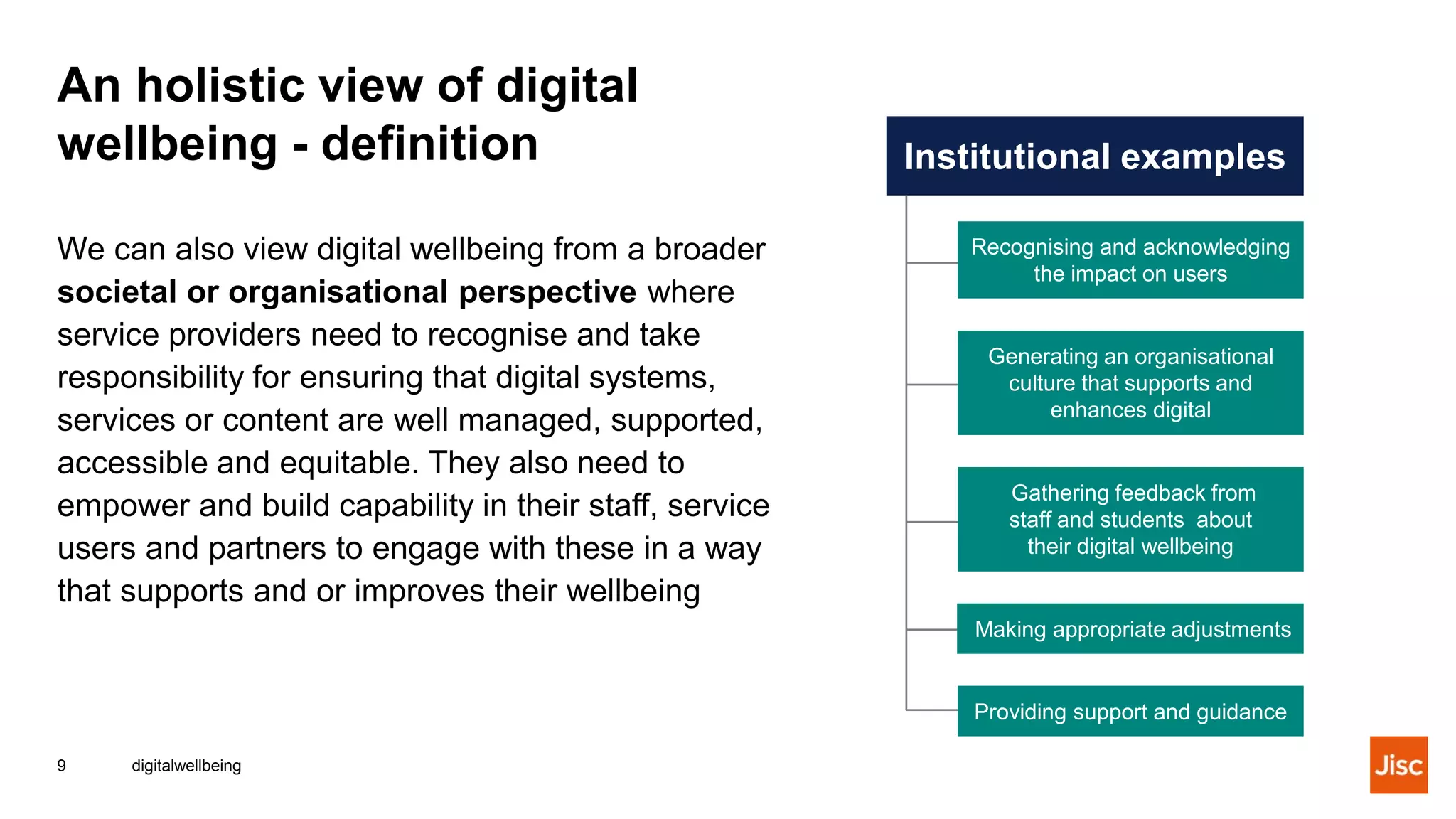
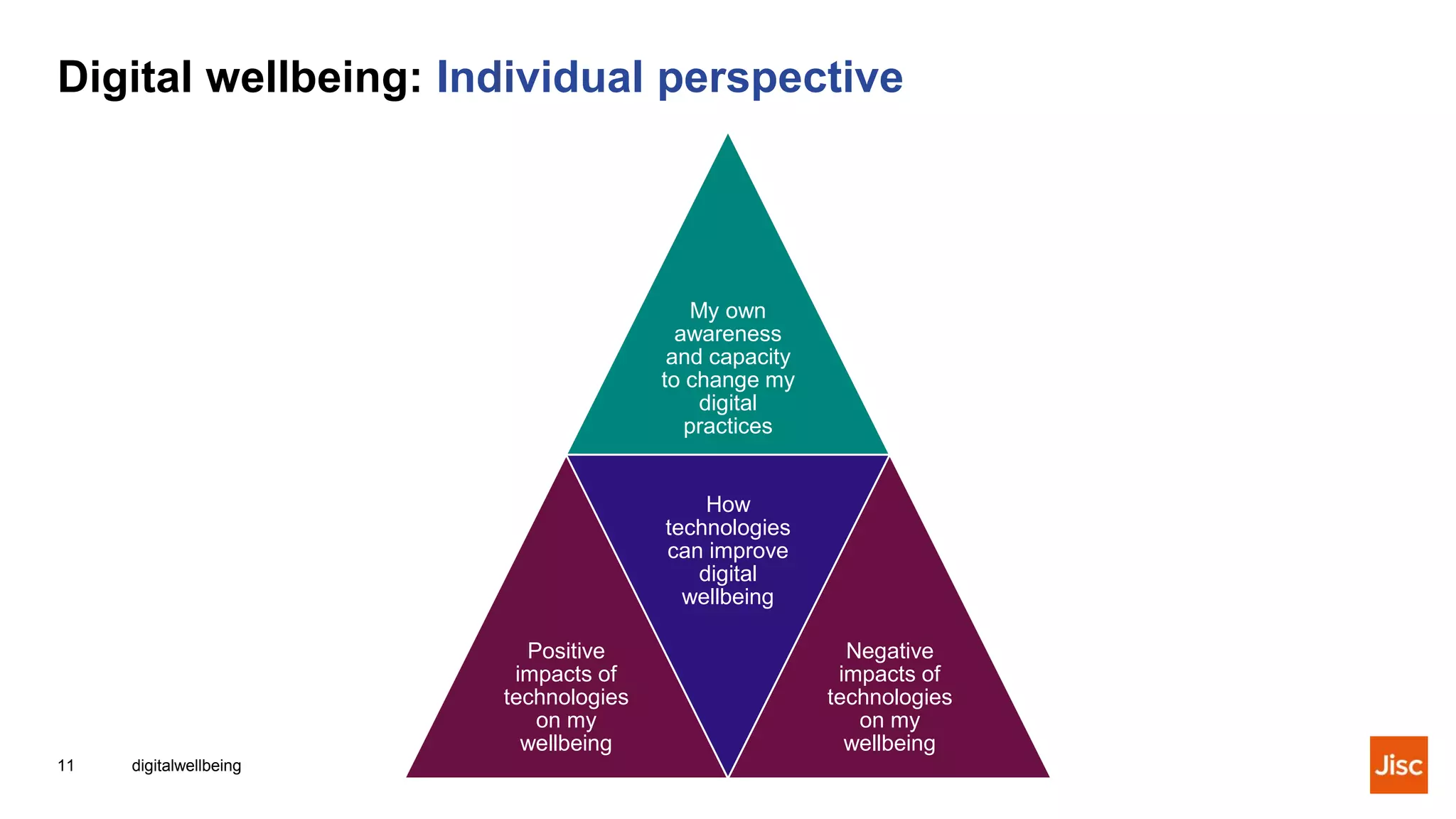
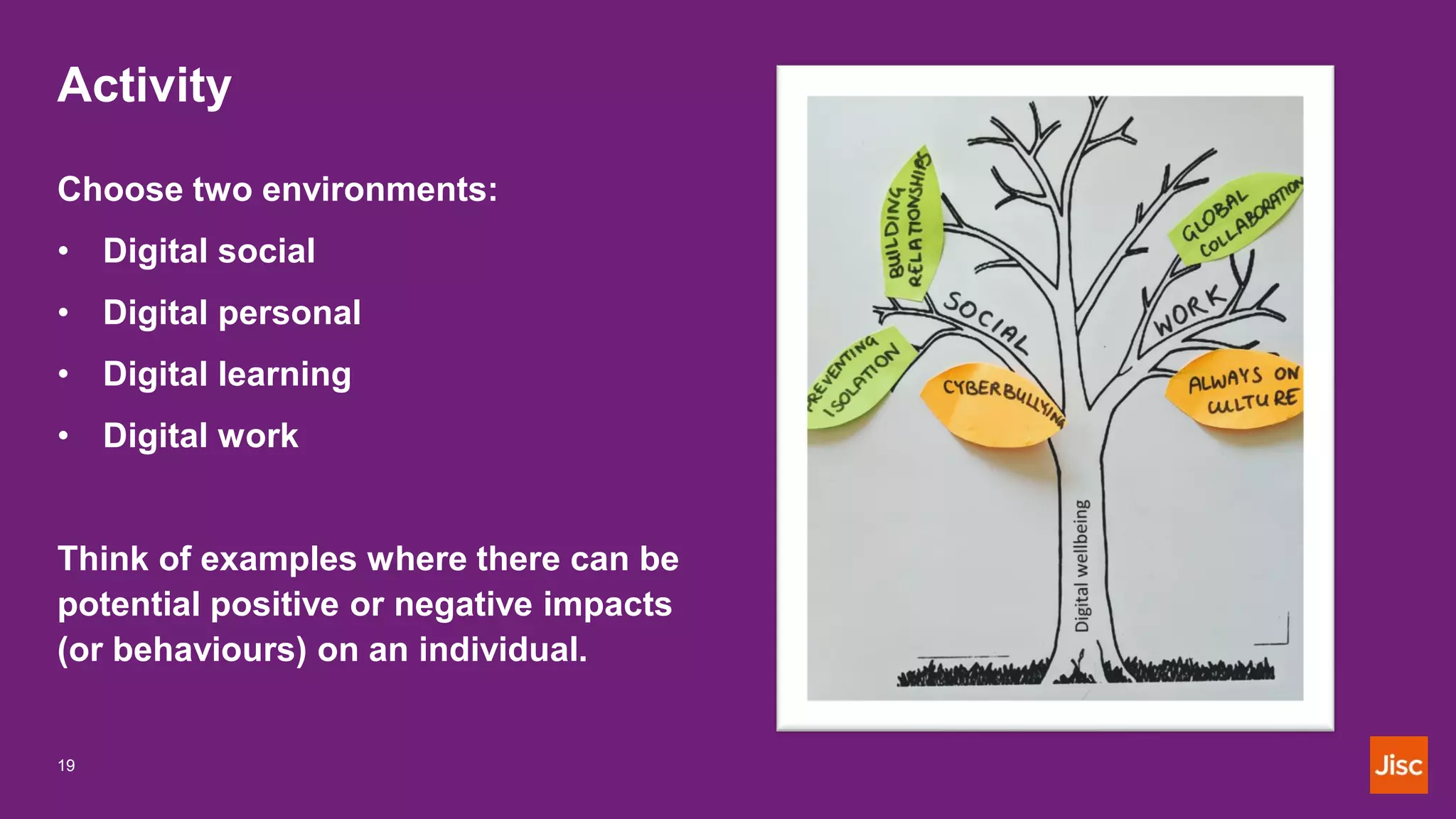
This document discusses digital wellbeing and defines it as considering the impact of technologies and digital services on people's mental, physical, and emotional health. It can be viewed from individual, organizational, and societal perspectives, and includes emotional, social, physical, and mental aspects within personal, work, learning, and community contexts. The document provides examples of positive and negative impacts on digital wellbeing and discusses supporting digital wellbeing from both individual and institutional perspectives.