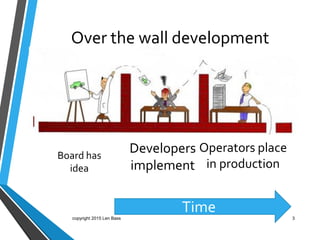
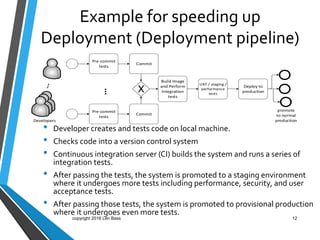
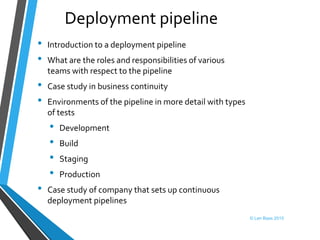
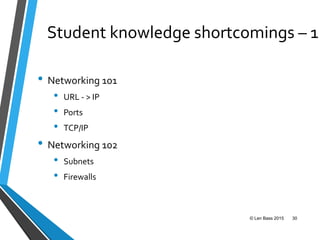
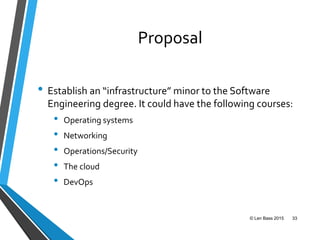
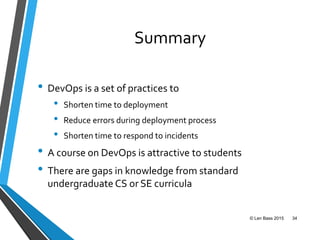
This document discusses Len Bass's experience teaching a DevOps course. It begins with an overview of DevOps and what it aims to accomplish. It then describes the structure and content of the course, which combines lectures, readings, discussions, and hands-on assignments using open source DevOps tools. The document notes that students often lack fundamental knowledge in areas like networking, security, and operations. It proposes establishing an "infrastructure minor" to address gaps in students' undergraduate education.