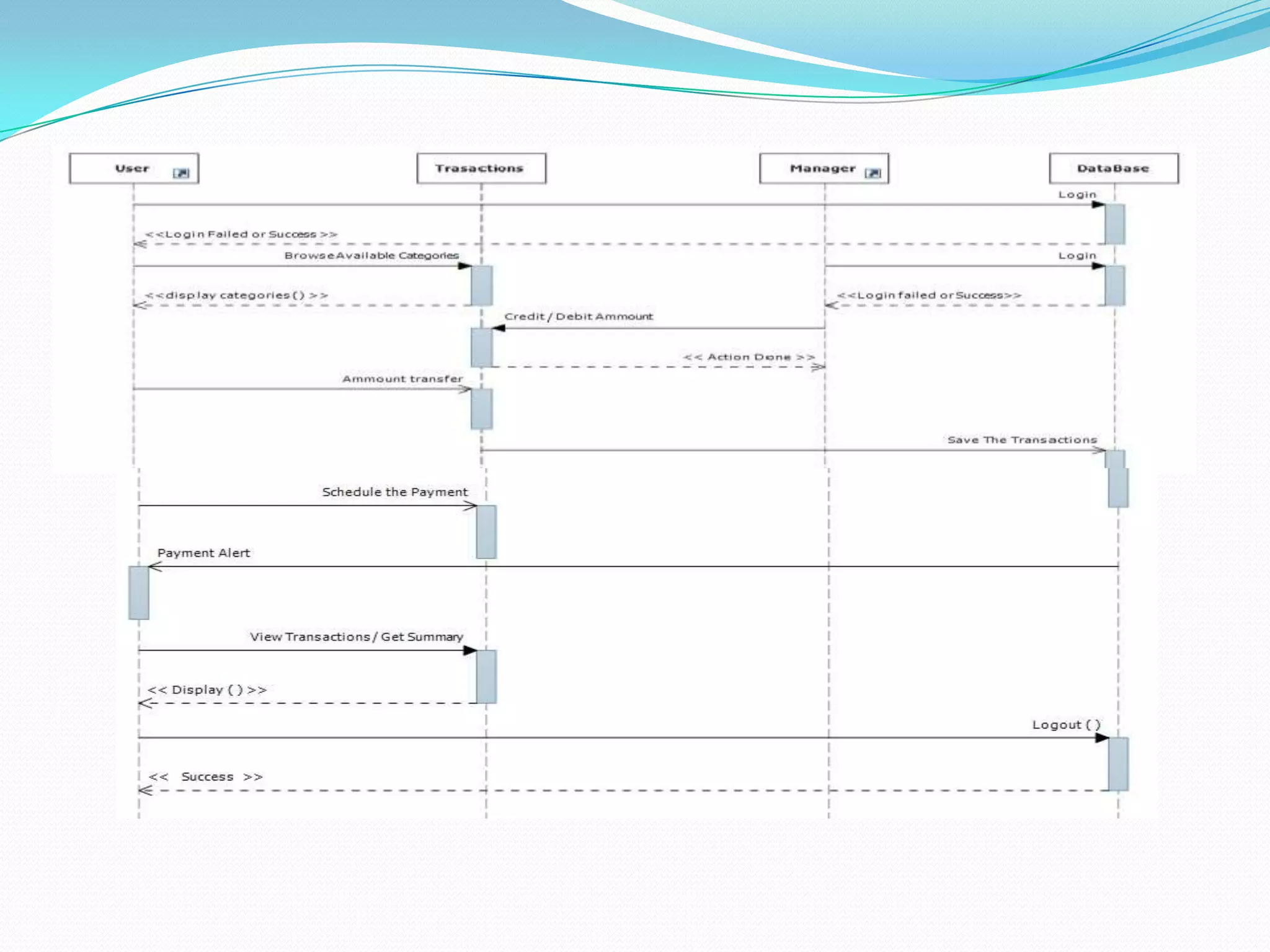
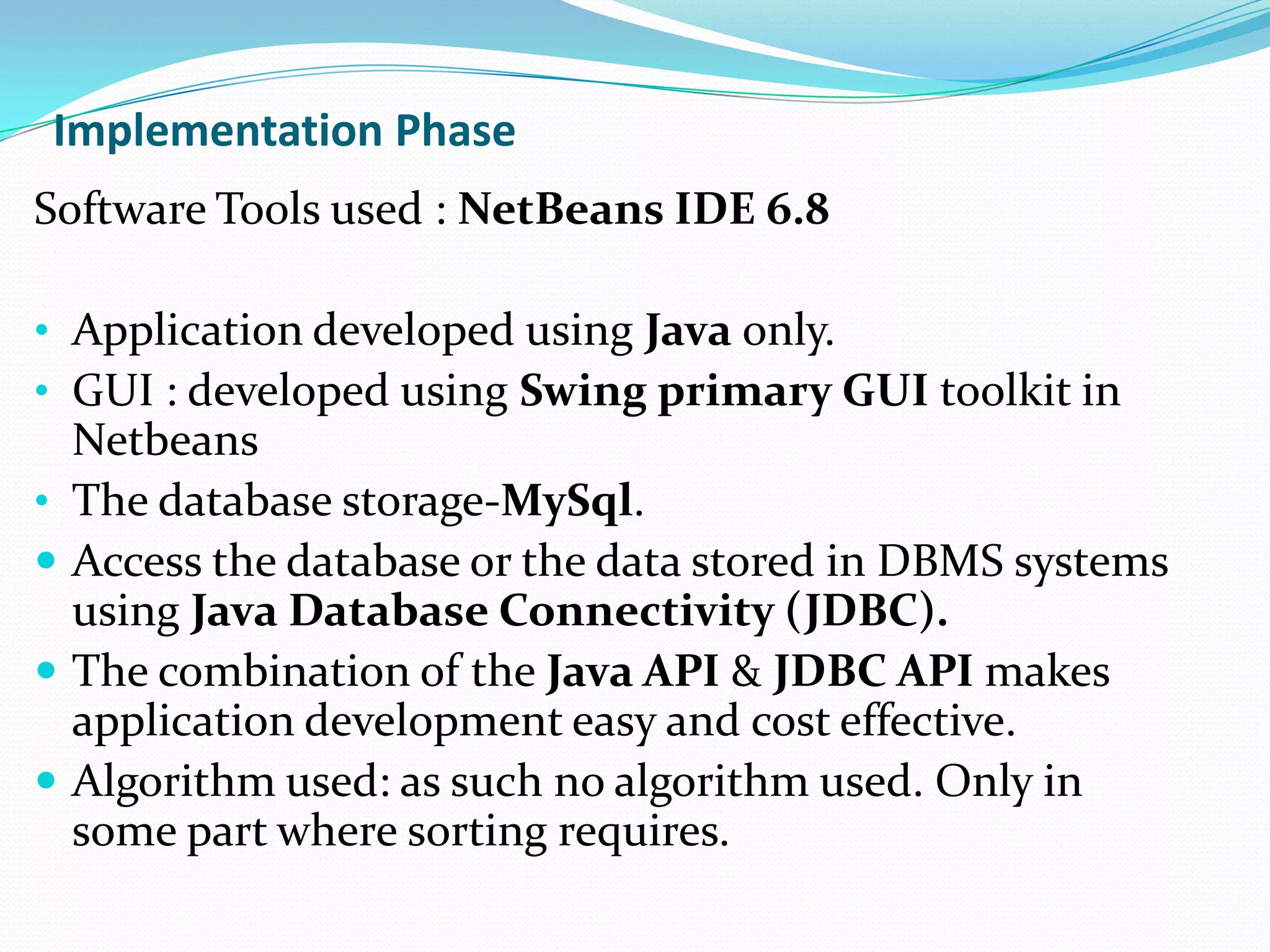
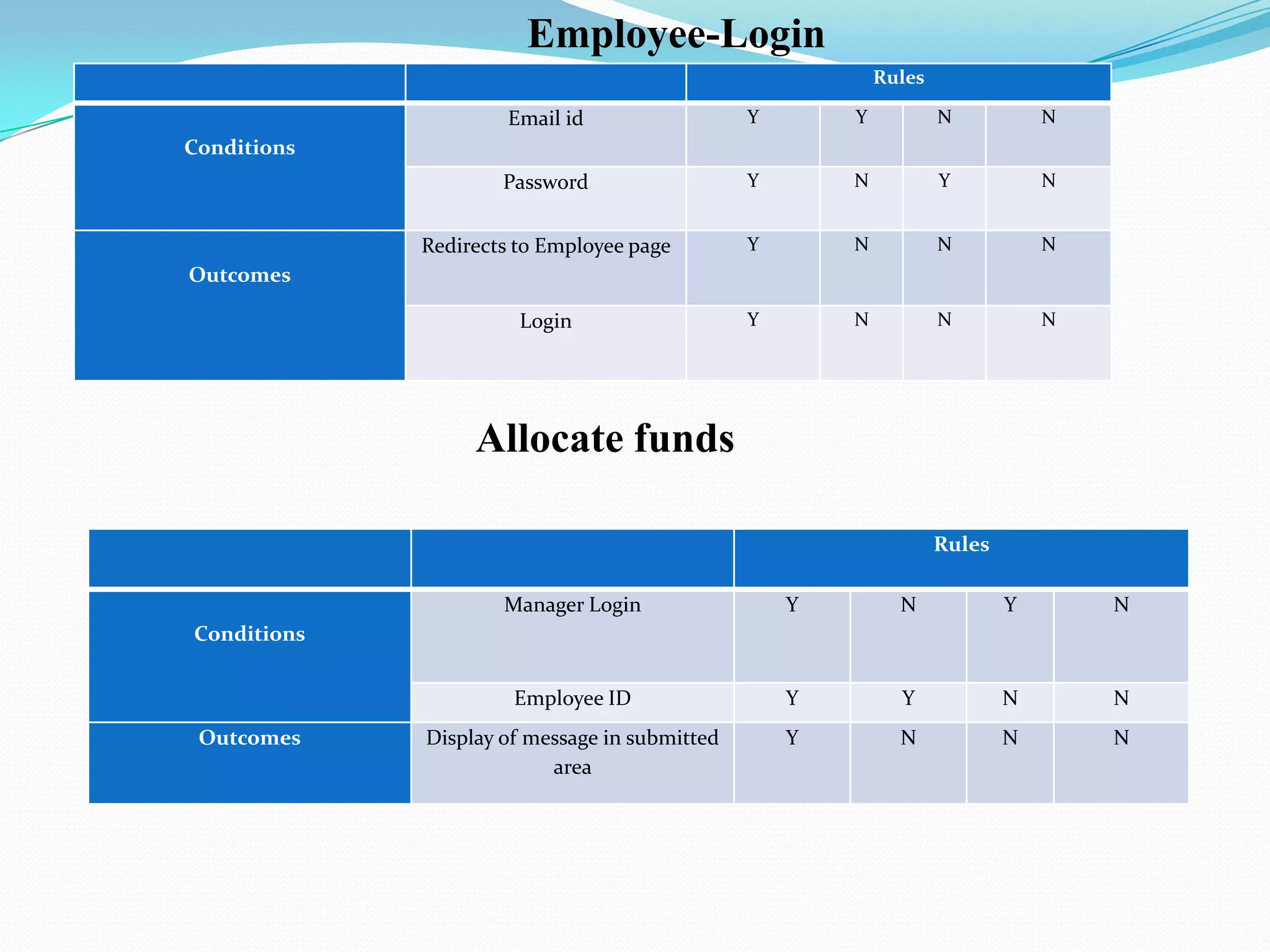
The document describes a GUI for an expense management system created by a group of students. The system allows users to track expenses, generate reports on spending by category and time period, and schedule payments. It was developed using Java, MySQL, and the NetBeans IDE following an evolutionary software process model. Testing of the system included black box and decision table techniques to ensure the interface and functionality worked as intended.
![Department of Computer Science and Engineering
GUI for Expense Finance Management
Group Members:
Sanket Ingale [ 09co36]
Laxmikant Patil [ 09co66 ]
Ambuj Lawania [09co08 ]
Adit Patel [ 09co05 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptfinal-121031015716-phpapp01/75/Expense-Manager-Application-in-JAVA-1-2048.jpg)