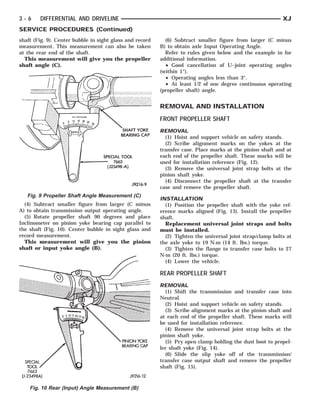
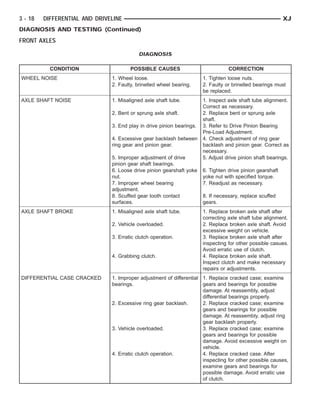
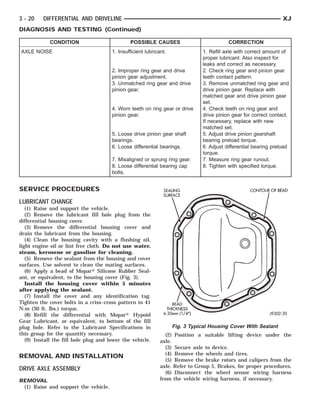
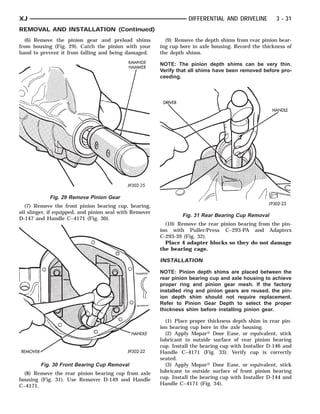
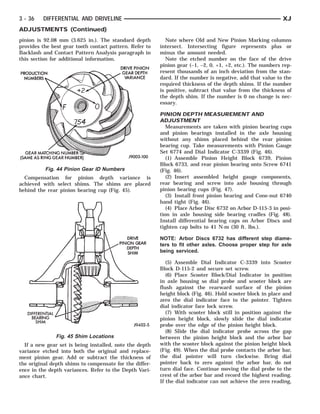
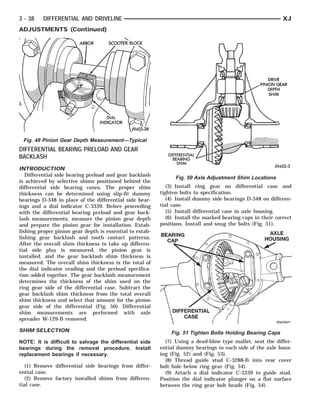
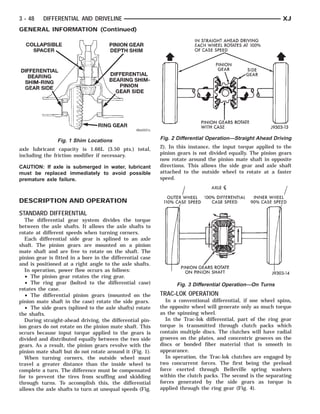
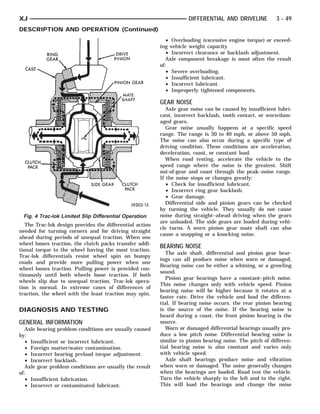
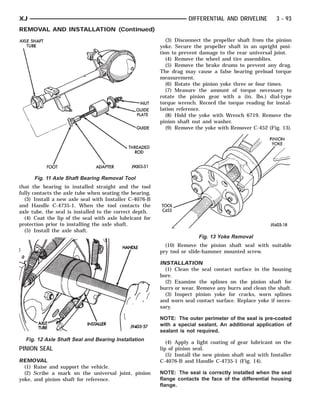
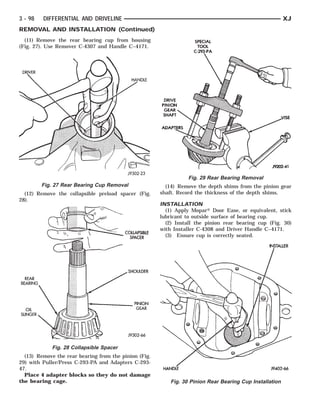
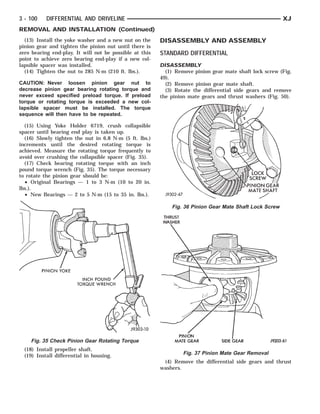
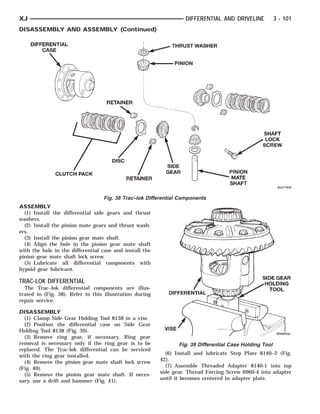
This document provides information about propeller shafts and drivelines. It discusses lubrication requirements, joint angles, types of universal joints, diagnosis of issues like runout and vibration, service procedures including measurement and adjustment, specifications, and removal/installation of front and rear propeller shafts. The document contains diagrams and explanations to aid technicians in maintenance and repair of these components.