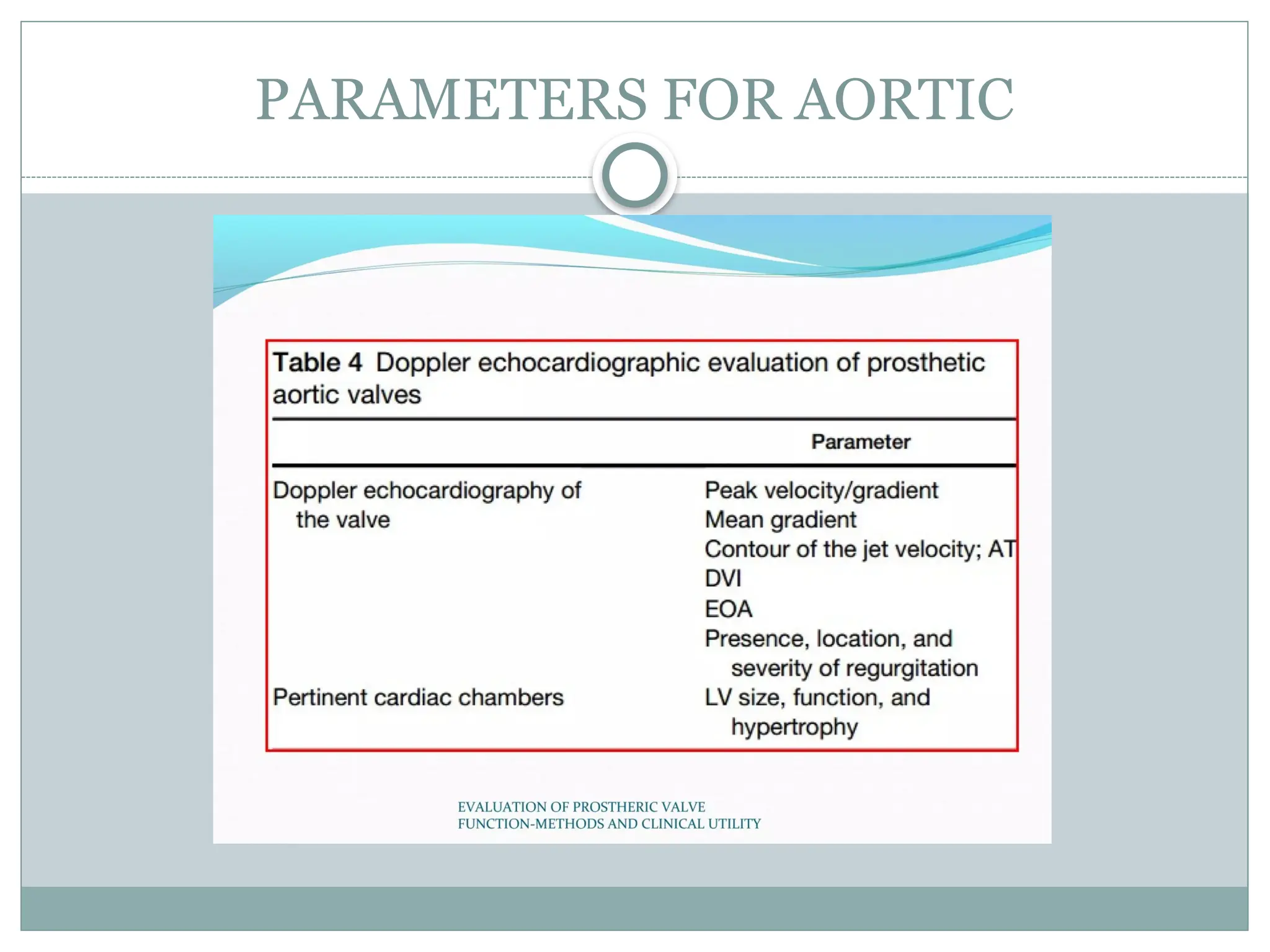
The document evaluates prosthetic valves using 2D echocardiography, Doppler techniques, and transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) to assess regurgitation, obstruction, and valve degeneration. It discusses the pressure half-time (PHT) as an important indicator of stenosis severity and provides insight into Doppler assessments, including flow velocities and pressure gradients. Clinical parameters for mitral and aortic valves are also outlined, highlighting the complexities and considerations in evaluating prosthetic valve function.