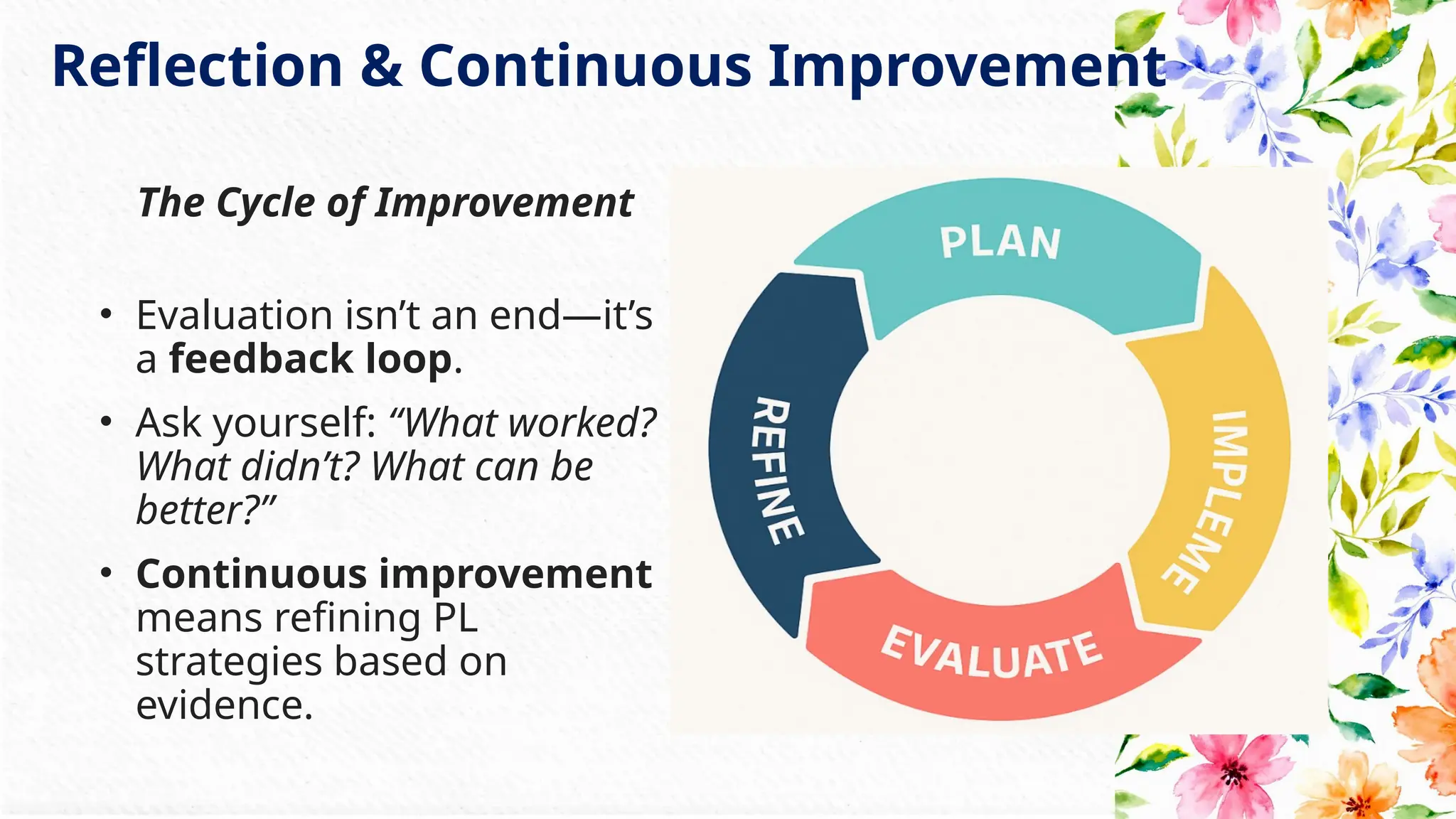
This presentation is part of Week 4 of the MOOC “Personalized Learning in Virtual Learning Environments: Leveraging Technology for Sustainable Student Engagement and SDG 4 Advancement.”
In this final module, the focus is on evaluation, reflection, and global alignment:
• Understanding why evaluation matters in personalized learning.
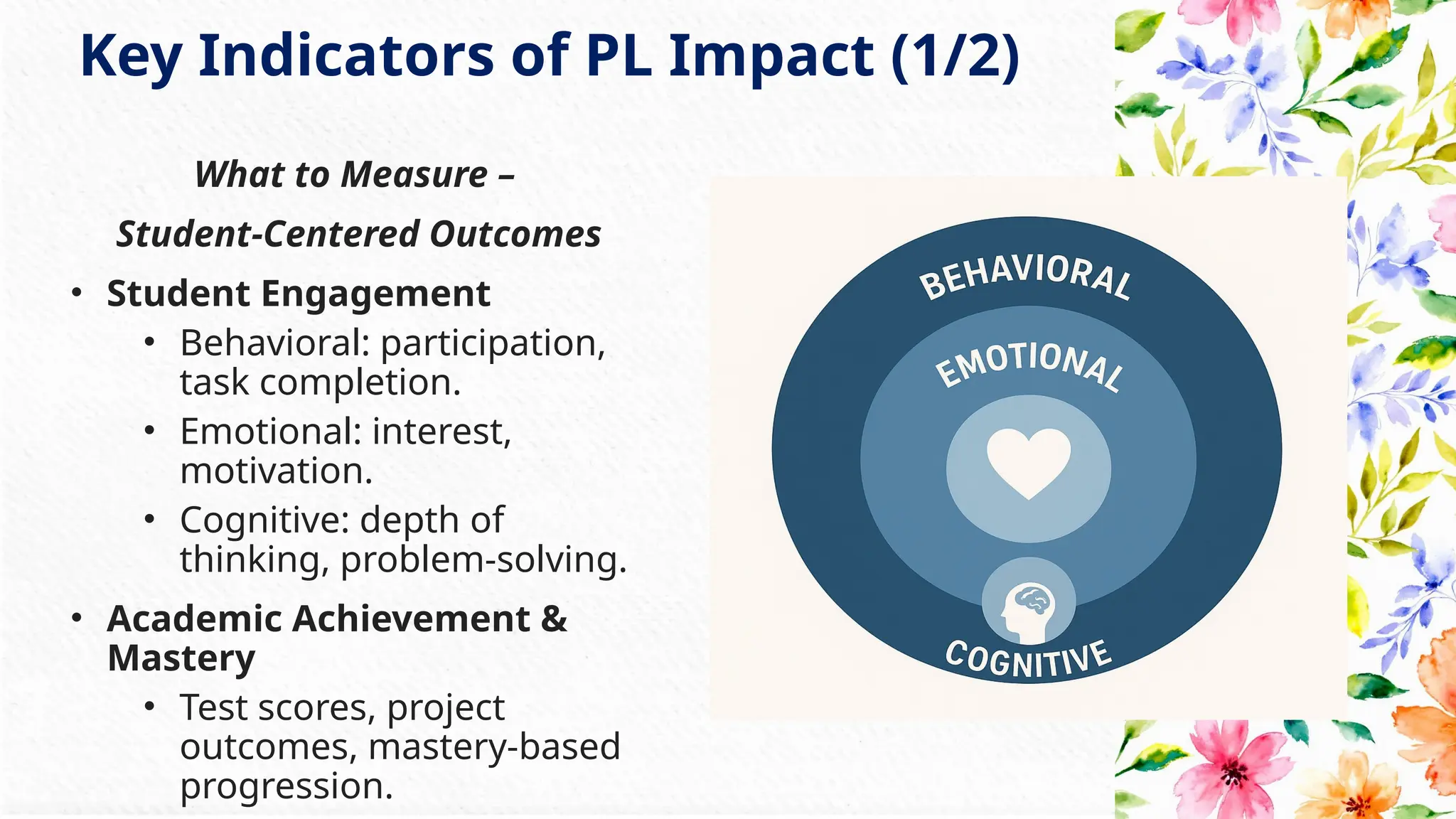
• Key indicators to measure learner engagement, autonomy, and equity.
• Tools and methods such as surveys, learning analytics, and reflective journals.
• Challenges in measuring impact and ways to address them.
• Linking personalized learning practices to SDG 4 (Quality Education) and its targets — ensuring inclusion, equity, lifelong learning, and sustainable educational development.
This PPT guides educators, researchers, and learners to reflect on their practices, adopt evidence-based improvements, and align teaching innovations with the global agenda for education.