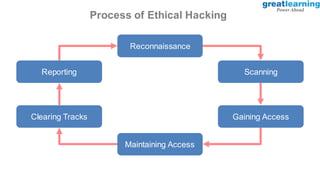
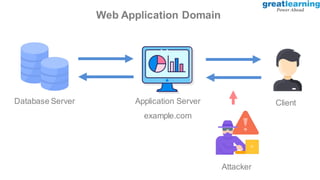
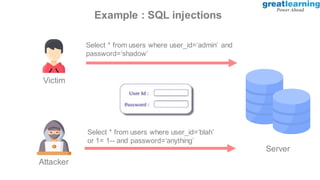
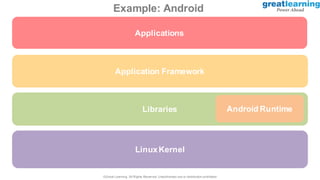
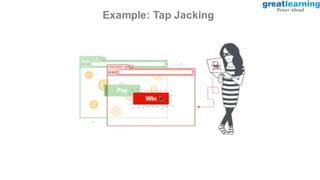
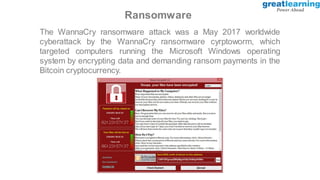
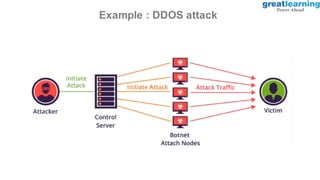
This document provides an introduction to ethical hacking. It defines ethical hacking as protecting interconnected systems from cyber attacks. It outlines different types of hackers and computer security threats. The goals of ethical hacking are to protect organizational privacy and report issues transparently. Skills, tools, and the process of ethical hacking involving reconnaissance, scanning, gaining access, maintaining access, and clearing tracks are described. Examples of hacking web applications, mobile devices, and networks are provided. Ethical hacking is applied across different domains including web applications, mobile apps, cloud computing, IoT, blockchain and edge computing.