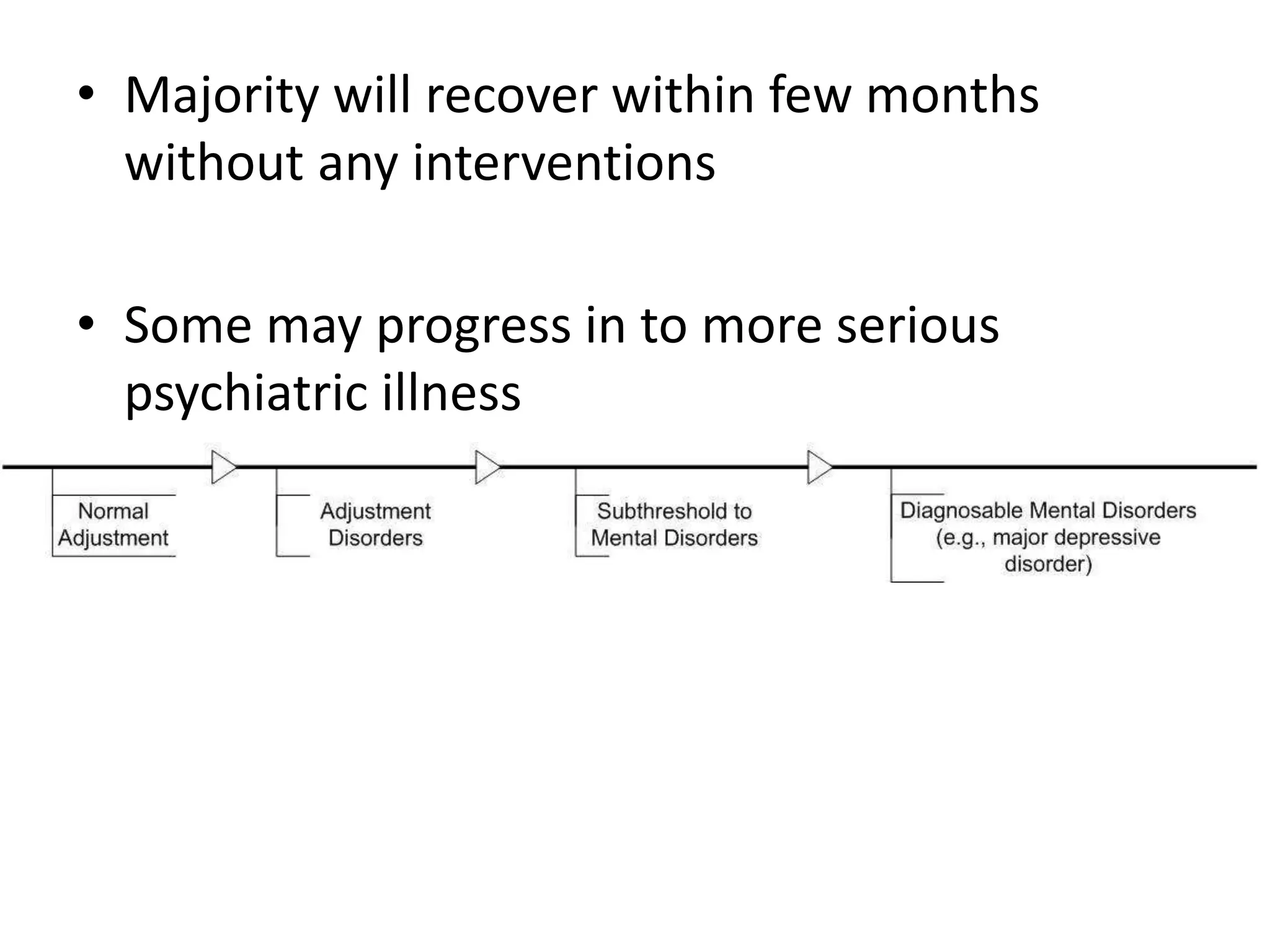
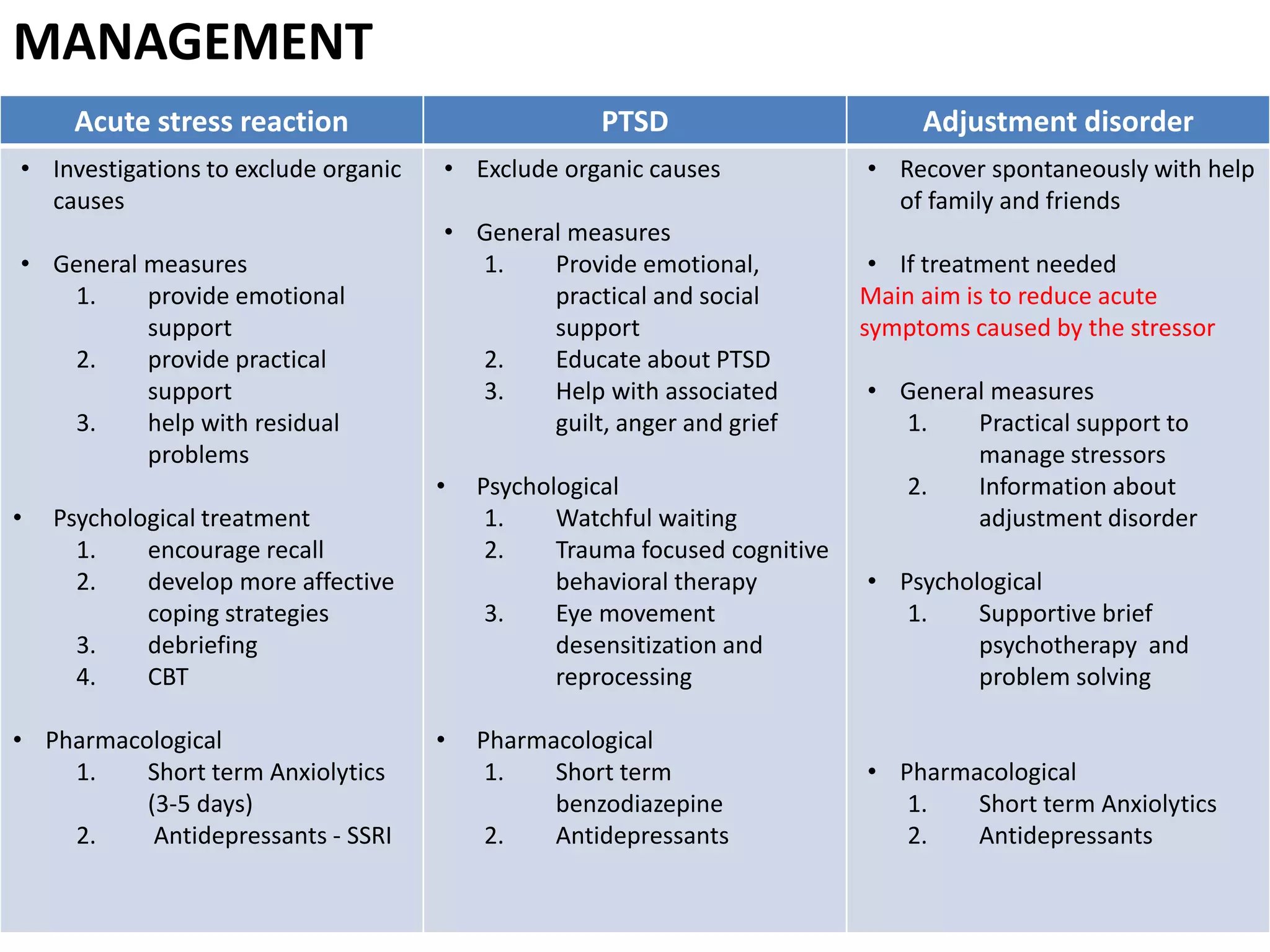
The document discusses reactions to stress, categorizing them into acute stress reaction, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and adjustment disorder, each with specific definitions and diagnostic criteria per ICD-10. Symptoms such as anxiety, emotional numbness, and coping strategies are highlighted, along with risk factors and differential diagnoses for each condition. Management strategies include emotional and practical support, psychological treatments, and pharmacological options.