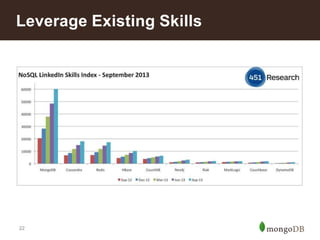
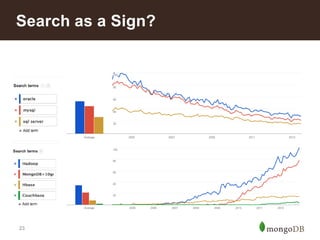
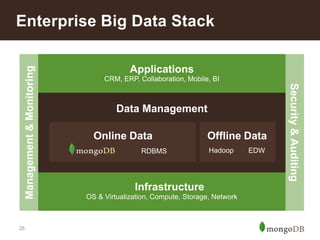
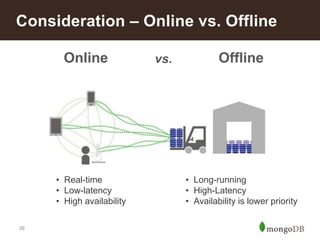
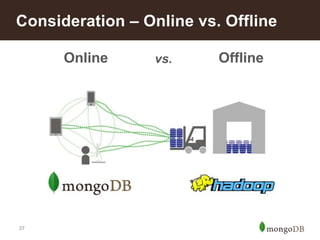
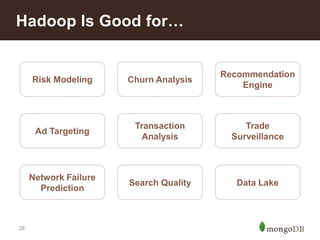
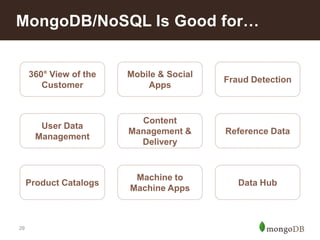
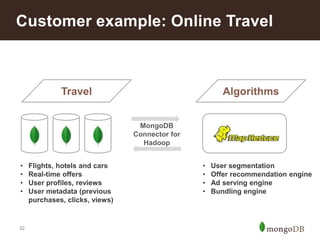
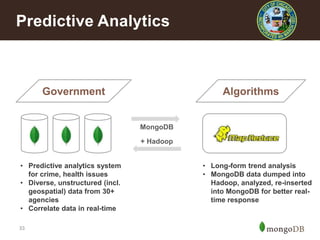
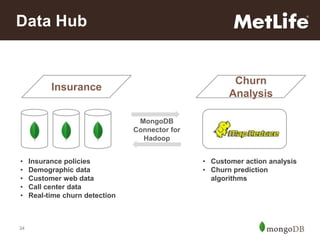
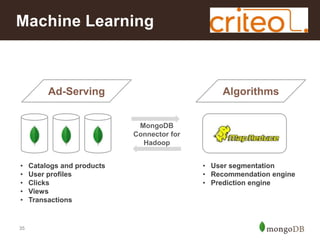
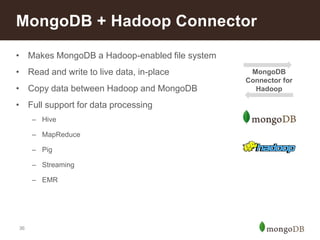
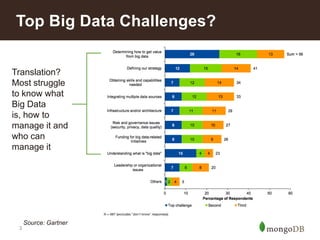
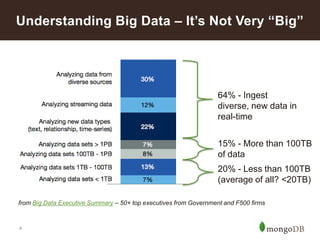
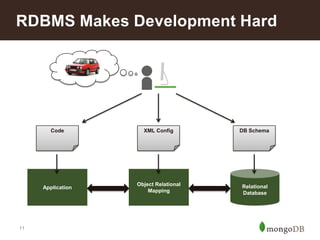
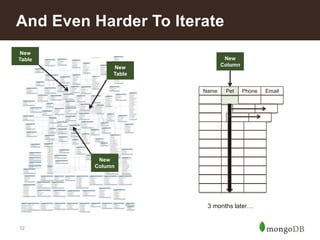
The document discusses key challenges in big data management, emphasizing the difficulties organizations face in understanding and handling it. It advocates for the use of NoSQL databases like MongoDB over traditional relational databases due to their scalability and flexibility. Additionally, it highlights the integration of tools like Hadoop with MongoDB for improved data processing and real-time analytics in various applications.








![From Complexity to Simplicity
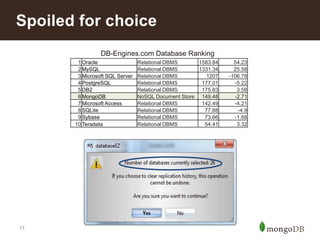
RDBMS
MongoDB
{
_id : ObjectId("4c4ba5e5e8aabf3"),
employee_name: "Dunham, Justin",
department : "Marketing",
title : "Product Manager, Web",
report_up: "Neray, Graham",
pay_band: “C",
benefits : [
{
type :
"Health",
plan : "PPO Plus" },
{
type :
"Dental",
plan : "Standard" }
]
}
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asay-yourbigdataarsenal-strata-october2013-131030150823-phpapp01/85/Essential-Tools-For-Your-Big-Data-Arsenal-13-320.jpg)



![Ask the Right Questions…
“Organizations already have people who know
their own data better than mystical data
scientists….Learning Hadoop [or MongoDB] is
easier than learning the company’s business.”
(Gartner, 2012)
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asay-yourbigdataarsenal-strata-october2013-131030150823-phpapp01/85/Essential-Tools-For-Your-Big-Data-Arsenal-21-320.jpg)