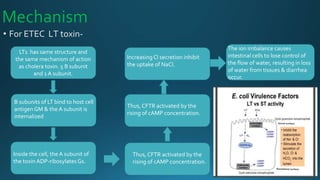
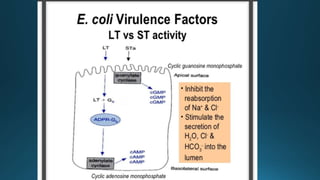
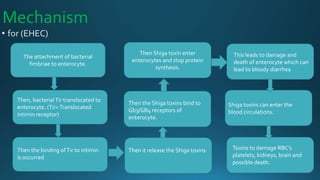
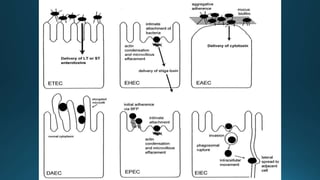
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a common bacterium that lives in the intestines of humans and animals. Certain strains of E. coli can cause illness. E. coli is characterized as a gram-negative, rod-shaped, facultative anaerobe that ferments glucose and lactose. Different pathogenic strains include enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) which produces heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins causing travelers' diarrhea; enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC) associated with acute and chronic diarrhea producing a heat-stable toxin; and enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) which causes bloody diarrhea and potentially hem